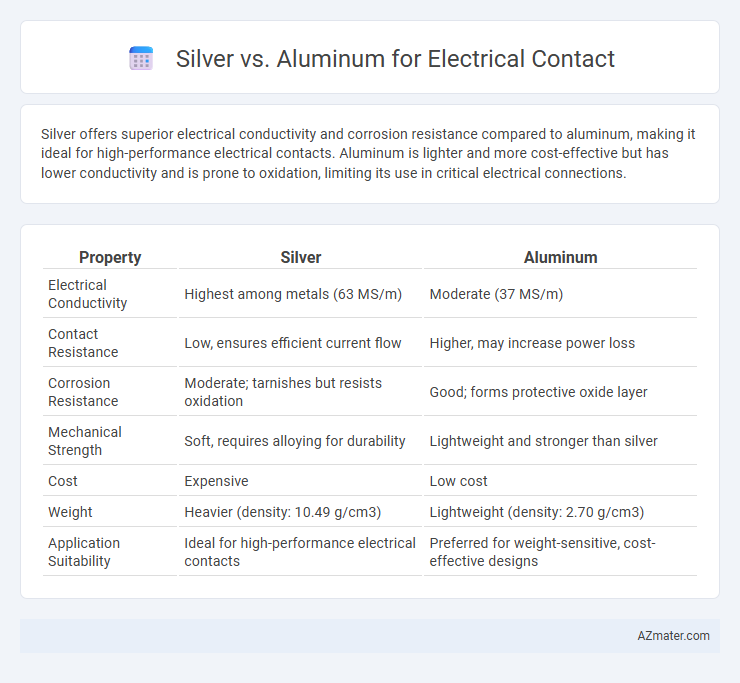
Silver offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts. Aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective but has lower conductivity and is prone to oxidation, limiting its use in critical electrical connections.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silver | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Highest among metals (63 MS/m) | Moderate (37 MS/m) |
| Contact Resistance | Low, ensures efficient current flow | Higher, may increase power loss |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; tarnishes but resists oxidation | Good; forms protective oxide layer |
| Mechanical Strength | Soft, requires alloying for durability | Lightweight and stronger than silver |
| Cost | Expensive | Low cost |
| Weight | Heavier (density: 10.49 g/cm3) | Lightweight (density: 2.70 g/cm3) |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-performance electrical contacts | Preferred for weight-sensitive, cost-effective designs |
Introduction: Silver vs Aluminum in Electrical Contacts
Silver offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it a preferred choice for high-performance electrical contacts. Aluminum, while more abundant and cost-effective, exhibits lower conductivity and forms an insulating oxide layer that can impair connectivity. Selecting between silver and aluminum depends on balancing conductivity requirements, durability, and budget constraints in electrical applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Silver showcases the highest electrical conductivity among all metals, with a conductivity value of approximately 63 x 10^6 S/m at 20degC, making it superior for electrical contact applications. Aluminum, while more cost-effective and lighter, has a significantly lower conductivity of about 37.7 x 10^6 S/m, which results in higher resistance and potential energy losses in electrical contacts. The choice between silver and aluminum depends heavily on the specific conductivity requirements and the balance between performance efficiency and material cost.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Silver exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, maintaining stable conductivity in harsh environments due to its noble metal properties. Aluminum tends to form an insulating oxide layer that can degrade electrical contact quality over time, reducing durability in electrical applications. The enhanced durability of silver contacts ensures longer service life and reliable performance, especially in high-demand or corrosive conditions.
Cost Analysis: Silver vs Aluminum
Silver offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum but comes at a significantly higher cost, often making it less economical for large-scale applications. Aluminum is more affordable and lightweight, making it a cost-effective choice for bulk electrical contacts despite its lower conductivity and susceptibility to oxidation. Choosing between silver and aluminum for electrical contacts involves balancing initial material costs against performance requirements and maintenance expenses.
Mechanical Strength and Reliability
Silver offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, enhancing the reliability of electrical contacts in demanding environments. Aluminum provides lower mechanical strength, which can lead to deformation and increased contact resistance under mechanical stress or vibration. The higher mechanical strength of silver ensures durability and consistent contact performance, making it the preferred choice for high-reliability electrical applications.
Thermal Conductivity Differences
Silver exhibits superior thermal conductivity at approximately 429 W/m*K, significantly outperforming aluminum's 237 W/m*K, which enhances heat dissipation in electrical contacts. This high thermal conductivity reduces the risk of overheating and improves contact reliability under high current conditions. Aluminum's lower thermal conductivity may lead to increased temperature rise and potential thermal stress, limiting its effectiveness in high-performance electrical contacts.
Applications in Industry
Silver's superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance make it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts in automotive and aerospace industries, where reliability under extreme conditions is critical. Aluminum, while less conductive, offers weight savings and cost efficiency, making it suitable for power distribution and overhead transmission lines in the energy sector. Both metals are chosen based on specific application needs, balancing conductivity, durability, and economic factors in industrial electrical contacts.
Maintenance and Longevity
Silver offers superior conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, resulting in lower maintenance requirements for electrical contacts. Its inherent durability and oxidation resistance enhance contact longevity, minimizing the risk of failure and the need for frequent replacements. Aluminum, while lightweight and cost-effective, is more prone to oxidation and wear, leading to increased maintenance and shorter contact lifespan in electrical applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Silver offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, resulting in longer-lasting electrical contacts with lower energy loss. Aluminum extraction and processing produce higher greenhouse gas emissions and consume more energy, making silver a more sustainable option despite its higher initial cost. The recyclability of silver further enhances its environmental profile, reducing the demand for virgin mining and supporting a circular economy in electrical components.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Silver offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts in critical applications. Aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective but has lower conductivity and oxidation concerns, requiring protective coatings for reliable contact. Selecting the right material depends on balancing conductivity requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Silver vs Aluminum for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com