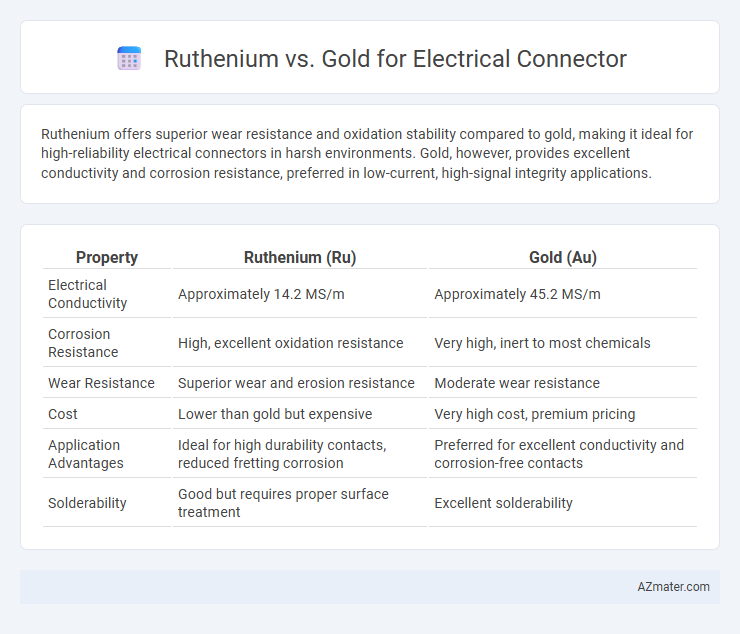
Ruthenium offers superior wear resistance and oxidation stability compared to gold, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical connectors in harsh environments. Gold, however, provides excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, preferred in low-current, high-signal integrity applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Gold (Au) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Approximately 14.2 MS/m | Approximately 45.2 MS/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, excellent oxidation resistance | Very high, inert to most chemicals |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear and erosion resistance | Moderate wear resistance |
| Cost | Lower than gold but expensive | Very high cost, premium pricing |
| Application Advantages | Ideal for high durability contacts, reduced fretting corrosion | Preferred for excellent conductivity and corrosion-free contacts |
| Solderability | Good but requires proper surface treatment | Excellent solderability |
Introduction: Ruthenium vs Gold in Electrical Connectors
Ruthenium and gold are prominent materials used in electrical connectors, each offering distinct advantages in conductivity and durability. Ruthenium provides superior wear resistance and corrosion protection, making it ideal for connectors in harsh environments. Gold, renowned for excellent electrical conductivity and resistance to oxidation, remains the standard choice for high-reliability and low-resistance connections.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Ruthenium offers excellent electrical conductivity, often comparable to gold, with a resistivity around 7.1 uO*cm, making it a strong candidate for electrical connectors. Gold, a traditional choice, has a slightly lower resistivity of about 2.44 uO*cm, providing superior conductivity and corrosion resistance. In high-reliability applications, ruthenium-plated connectors enhance durability and wear resistance while maintaining efficient electrical performance.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance compared to gold, making it highly effective in harsh or chemically aggressive environments. Its exceptional hardness and durability reduce wear and prolong the lifecycle of electrical connectors under frequent mating cycles. Gold, while excellent for conductivity, is softer and more prone to wear, limiting its long-term durability in demanding applications.
Cost Analysis: Ruthenium vs Gold
Ruthenium offers a cost-effective alternative to gold in electrical connectors, with prices typically ranging at a fraction of gold's market value, making it highly attractive for large-scale applications. Although gold provides superior corrosion resistance and conductivity, ruthenium's hardness and wear resistance contribute to longer connector lifespan, reducing maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership, connectors with ruthenium plating can deliver substantial savings without compromising performance in demanding electronic environments.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Ruthenium-plated electrical connectors offer superior wear resistance compared to gold due to ruthenium's hardness and resistance to erosion and corrosion, making them ideal for high-cycle applications. Gold connectors provide excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance but are softer, leading to faster wear under frequent mating and demating cycles. Ruthenium coatings extend connector longevity by maintaining consistent electrical performance in harsh environments, while gold's performance may degrade more rapidly with mechanical abrasion.
Contact Resistance Performance
Ruthenium offers significantly lower contact resistance compared to gold, enhancing signal integrity and minimizing power loss in electrical connectors. Its superior resistance to wear and corrosion maintains consistent low resistance over extended cycles, crucial for high-reliability applications. Gold provides excellent initial conductivity but can suffer from increased contact resistance due to surface degradation under mechanical stress and tarnishing.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Ruthenium offers exceptional wear resistance and corrosion protection in electrical connectors, making it ideal for high-reliability applications in aerospace, telecommunications, and automotive industries where durability is critical. Gold connectors provide superior conductivity and oxidation resistance, widely used in consumer electronics and high-frequency signal transmission to ensure stable performance under varying environmental conditions. Both metals enhance connector lifespan and signal integrity, but ruthenium's hardness suits harsh, high-vibration environments while gold remains preferred for low-voltage, precision electronics.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Ruthenium offers superior environmental benefits over gold in electrical connectors due to its greater abundance and lower ecological impact during extraction and processing. Its higher durability and corrosion resistance extend connector lifespan, reducing waste and resource consumption associated with frequent replacements. Gold, while highly conductive and resistant to oxidation, involves more intensive mining processes with significant environmental degradation and finite reserves, making ruthenium a more sustainable choice in eco-conscious electronic manufacturing.
Manufacturing and Plating Considerations
Ruthenium offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance compared to gold, making it ideal for manufacturing durable electrical connectors that withstand high wear cycles. The plating process for ruthenium requires precise control of deposition parameters to achieve a uniform, defect-free coating, often involving electrochemical plating methods with specialized electrolytes. Gold plating, while softer and more malleable, provides excellent conductivity and oxidation resistance, facilitating easier deposition through standard electroplating techniques but requiring thicker layers to maintain long-term performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Connectors
Ruthenium offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance compared to gold, making it ideal for high-wear electrical connectors in harsh environments. Gold excels in conductivity and oxidation resistance, providing reliable performance in low-current, delicate electronic applications. Selecting the right material depends on the specific requirements of durability, conductivity, and cost-effectiveness in the intended connector use case.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Gold for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com