Ruthenium enhances stainless steel's corrosion resistance and hardness, outperforming chromium in high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments. Chromium primarily provides oxidation resistance and basic corrosion protection, making ruthenium a superior alloying element for advanced stainless steel applications.
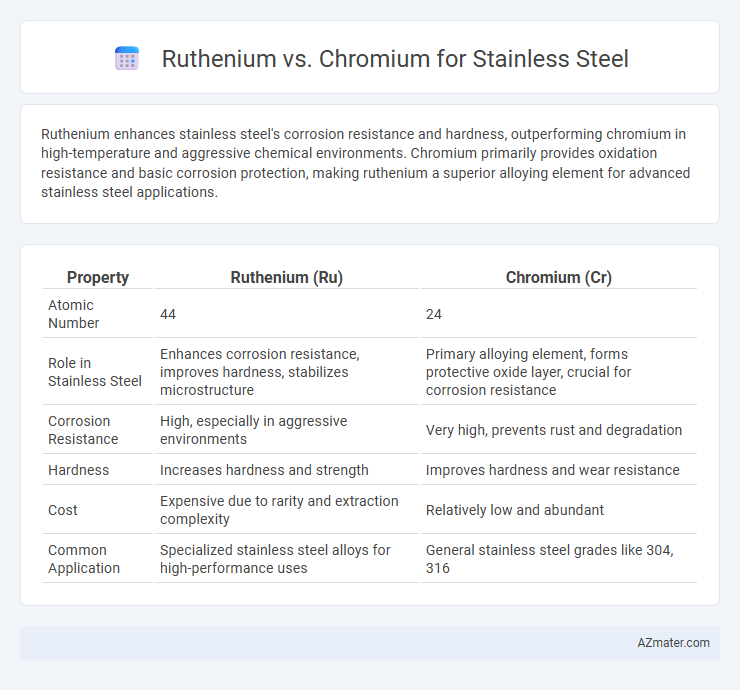
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Chromium (Cr) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 44 | 24 |
| Role in Stainless Steel | Enhances corrosion resistance, improves hardness, stabilizes microstructure | Primary alloying element, forms protective oxide layer, crucial for corrosion resistance |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, especially in aggressive environments | Very high, prevents rust and degradation |
| Hardness | Increases hardness and strength | Improves hardness and wear resistance |
| Cost | Expensive due to rarity and extraction complexity | Relatively low and abundant |
| Common Application | Specialized stainless steel alloys for high-performance uses | General stainless steel grades like 304, 316 |
Introduction to Ruthenium and Chromium in Stainless Steel
Ruthenium enhances stainless steel by improving corrosion resistance and wear properties, especially in harsh chemical environments, due to its noble metal characteristics. Chromium is a fundamental alloying element that forms a passive oxide layer, providing stainless steel with essential corrosion resistance and hardness. Combining ruthenium and chromium in stainless steel optimizes performance, balancing enhanced durability and chemical stability for industrial applications.
Chemical Properties and Composition
Ruthenium enhances stainless steel by improving corrosion resistance and hardness due to its noble metal characteristics and higher electronegativity compared to chromium. Chromium is a crucial alloying element in stainless steel, forming a passive oxide layer that prevents rust and increases durability. The inclusion of ruthenium in stainless steel alloys modifies the chemical composition by increasing the metal's resistance to oxidation and acid attack beyond what standard chromium content achieves.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Ruthenium enhances stainless steel corrosion resistance by improving pitting and crevice corrosion resistance, especially in chloride environments, outperforming chromium in aggressive conditions. While chromium forms a passive oxide layer that provides general corrosion protection, ruthenium's ability to stabilize this layer increases durability in highly corrosive media. Incorporating ruthenium into stainless steel alloys results in superior resistance to localized corrosion compared to chromium-only alloys.
Impact on Mechanical Strength
Ruthenium enhances stainless steel's mechanical strength by improving hardness and tensile strength through solid-solution strengthening and grain refinement, making it especially beneficial in high-temperature and corrosive environments. Chromium contributes primarily to corrosion resistance and forms a stable oxide layer, but its impact on mechanical strength is less pronounced compared to ruthenium. Combining ruthenium with chromium in stainless steel formulations results in an optimized balance of enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Influence on Stainless Steel’s Durability
Ruthenium enhances stainless steel's durability by improving corrosion resistance and increasing resistance to pitting in harsh environments, making it ideal for marine and chemical applications. Chromium is essential for forming the protective oxide layer that prevents rust and general corrosion, significantly contributing to stainless steel's baseline durability. The combination of chromium with small additions of ruthenium results in stainless steel grades with superior strength, prolonged lifespan, and enhanced performance in aggressive conditions.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Ruthenium significantly increases the cost of stainless steel due to its rarity and high market price compared to chromium, a more abundant and economical element widely used in steel alloys. Chromium enhances corrosion resistance and durability at a lower cost, making it the preferred choice for large-scale industrial applications where cost efficiency is critical. The economic considerations favor chromium for stainless steel production unless specific properties provided by ruthenium justify the additional expense in high-performance or specialized uses.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Ruthenium enhances corrosion resistance and hardness in stainless steel, making it ideal for chemical processing and aerospace industries where durability under extreme conditions is critical. Chromium, a fundamental alloying element, provides essential oxidation resistance and strength, widely used in construction, automotive, and food processing sectors. The choice between ruthenium and chromium depends on specific application requirements, with ruthenium offering superior performance in high-stress environments but at a higher cost compared to chromium's cost-effective protection.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Ruthenium enhances stainless steel corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing waste, which contributes to environmental sustainability. Chromium, essential for stainless steel's protective oxide layer, is abundant and more cost-effective but involves energy-intensive mining processes with significant ecological impact. Balancing Ruthenium's superior durability against Chromium's accessibility highlights the trade-offs in sustainability efforts within stainless steel production.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Ruthenium-enhanced stainless steel exhibits superior corrosion resistance and maintains structural integrity at high temperatures, outperforming chromium in extreme oxidative environments. Chromium contributes to the formation of a protective oxide layer, but ruthenium's catalytic properties improve passivation and reduce pitting corrosion under aggressive chemical exposure. These performance characteristics make ruthenium alloyed stainless steel ideal for aerospace, chemical processing, and marine applications where durability and longevity under extreme conditions are critical.
Future Trends in Stainless Steel Alloying
Ruthenium is emerging as a promising alloying element in stainless steel due to its ability to enhance corrosion resistance and improve high-temperature performance without significantly increasing cost. Chromium remains the backbone of stainless steel composition, providing essential oxidation resistance and strength, but future trends indicate a gradual shift towards optimizing compositions with minor additions of ruthenium for specialized applications. Advances in powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing further enable the precise incorporation of ruthenium, driving innovations in ultra-high-performance stainless steel alloys.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Chromium for Stainless Steel
 azmater.com
azmater.com