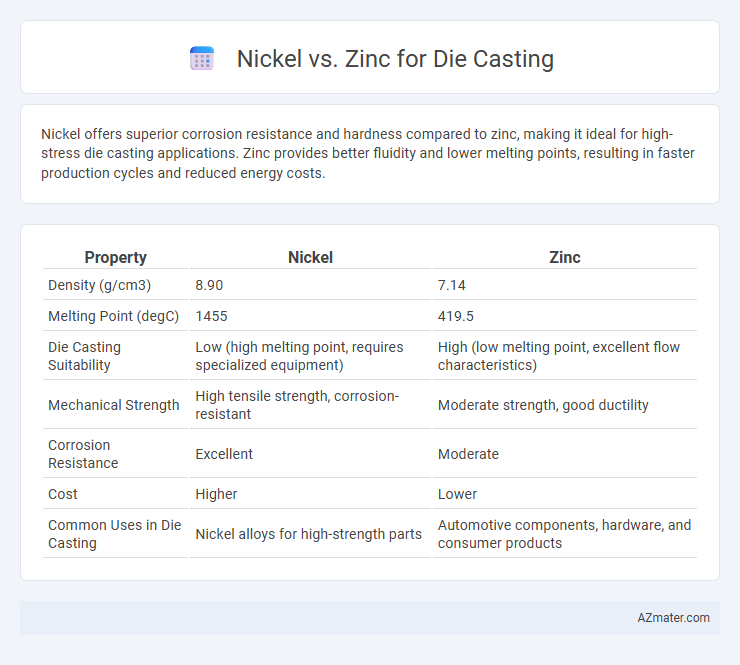
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and hardness compared to zinc, making it ideal for high-stress die casting applications. Zinc provides better fluidity and lower melting points, resulting in faster production cycles and reduced energy costs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 8.90 | 7.14 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 1455 | 419.5 |
| Die Casting Suitability | Low (high melting point, requires specialized equipment) | High (low melting point, excellent flow characteristics) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, corrosion-resistant | Moderate strength, good ductility |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Uses in Die Casting | Nickel alloys for high-strength parts | Automotive components, hardware, and consumer products |
Introduction to Die Casting: Nickel vs Zinc
Die casting utilizes metals with ideal fluidity and mechanical properties, where nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and tensile strength compared to zinc. Zinc, favored for its low melting point and excellent castability, provides affordable and precise components with good wear resistance. Choosing between nickel and zinc depends on the application's durability requirements, cost constraints, and surface finish quality.
Material Properties of Nickel and Zinc
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance, higher melting point (1455degC), and excellent mechanical strength compared to zinc, which melts at a lower temperature (419.5degC) and provides good ductility but lower tensile strength. Zinc's lower melting point enables faster production cycles and better detail reproduction, whereas nickel's robustness ensures durability in high-stress applications. The choice between nickel and zinc in die casting primarily depends on the required material performance, with nickel favored for high-strength, wear-resistant parts and zinc preferred for economical, complex shapes.
Advantages of Nickel in Die Casting
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength in die casting compared to zinc, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace components. Its excellent hardness and wear resistance extend the lifespan of die-cast parts under mechanical stress. Nickel alloys also provide better dimensional stability and improved surface finish, enhancing the overall quality and performance of die-cast products.
Advantages of Zinc in Die Casting
Zinc offers superior fluidity compared to nickel, enabling easier filling of intricate die casting molds and finer detail reproduction. Its lower melting point reduces energy consumption and minimizes tool wear during the casting process. Zinc alloys provide excellent corrosion resistance and dimensional stability, making them ideal for high-precision applications in automotive and electronics industries.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nickel die casting alloys generally exhibit higher mechanical strength compared to zinc counterparts, with tensile strengths often exceeding 70 ksi, making them suitable for high-stress applications. Zinc alloys typically have lower tensile strength, ranging from 40 to 60 ksi, but offer superior ductility and impact resistance. The choice between nickel and zinc depends on the specific requirements for strength, wear resistance, and weight in die-cast components.
Corrosion Resistance: Nickel vs Zinc
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc due to its dense, stable oxide layer that protects against oxidation and harsh environments. Zinc, while cost-effective and providing moderate corrosion protection through sacrificial anodic action, is more susceptible to degradation in acidic or saline conditions. Applications demanding enhanced durability and resistance to rust typically favor nickel die cast components over zinc.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Nickel die casting offers superior corrosion resistance and strength but comes at a higher material and processing cost compared to zinc. Zinc is more cost-efficient due to its lower raw material price and faster solidification rates, which reduce cycle times and energy consumption. Availability of zinc is generally more widespread and stable, making it a preferred choice for high-volume, budget-sensitive die casting applications.
Applications of Nickel and Zinc Die Cast Parts
Nickel die cast parts excel in high-performance automotive components, aerospace hardware, and electronic connectors due to their superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Zinc die cast parts are widely used in consumer electronics housings, hardware fittings, and decorative components because of their excellent dimensional accuracy and cost-effectiveness. Both materials offer unique benefits, with nickel favored for durability in harsh environments and zinc chosen for precision and economical mass production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nickel die casting involves higher energy consumption and generates more greenhouse gases compared to zinc, which has a lower melting point and requires less energy during the casting process. Zinc offers better recyclability, with a recycling rate exceeding 85%, contributing to a reduced environmental footprint and resource conservation. The sustainability of zinc die casting is further enhanced by its minimal waste production and lower emissions, making it a more eco-friendly choice in industrial applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Die Casting Needs
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance, enhanced hardness, and excellent wear properties, making it ideal for high-performance die casting applications requiring durability and precision. Zinc is favored for its low melting point, excellent fluidity, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for complex shapes and high-volume production runs. Selecting the best material depends on application demands such as mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and manufacturing efficiency.
Infographic: Nickel vs Zinc for Die casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com