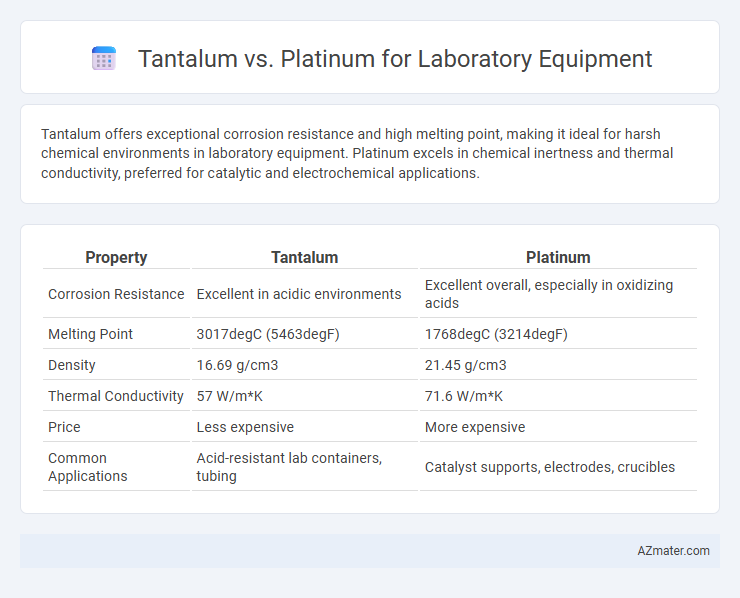
Tantalum offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments in laboratory equipment. Platinum excels in chemical inertness and thermal conductivity, preferred for catalytic and electrochemical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Platinum |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in acidic environments | Excellent overall, especially in oxidizing acids |
| Melting Point | 3017degC (5463degF) | 1768degC (3214degF) |
| Density | 16.69 g/cm3 | 21.45 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 57 W/m*K | 71.6 W/m*K |
| Price | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Common Applications | Acid-resistant lab containers, tubing | Catalyst supports, electrodes, crucibles |
Introduction to Tantalum and Platinum in Laboratory Equipment
Tantalum and platinum are highly valued for their exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal materials for laboratory equipment exposed to aggressive chemicals. Tantalum excels in environments with strong acids such as hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, offering superior performance and longevity compared to many metals. Platinum, known for its excellent thermal stability and inertness, is commonly used in high-precision laboratory instruments and catalytic applications where purity and resistance to oxidation are critical.
Material Properties: Tantalum vs Platinum
Tantalum exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point at 3017degC, making it ideal for highly acidic environments in laboratory equipment, while platinum offers superior chemical inertness and excellent thermal conductivity with a melting point of 1768degC. Tantalum's ductility and strength under extreme conditions surpass platinum, which is prized for its stability and resistance to oxidation. The choice between tantalum and platinum hinges on the specific laboratory application, where tantalum excels in durability under corrosive conditions and platinum provides unmatched chemical purity and conductivity.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to platinum, especially in aggressive chemical environments such as hydrofluoric acid and sulfuric acid, making it ideal for laboratory equipment exposed to highly corrosive substances. Platinum offers excellent resistance to oxidation and chemical attack at high temperatures but can be susceptible to attack by hot aqua regia, limiting its use in specific corrosive conditions. The exceptional inertness and durability of tantalum in strong acids provide a more reliable material choice for long-term laboratory applications requiring maximum corrosion resistance.
Chemical Compatibility and Reactivity
Tantalum exhibits exceptional chemical resistance to strong acids such as hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, making it highly suitable for handling aggressive chemical reactions in laboratory equipment. Platinum offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains stability in oxidizing environments, including exposure to aqua regia and hot gases. Both metals provide outstanding reactivity profiles, with tantalum excelling in alkali resistance and platinum in catalytic performance, influencing their selection based on specific experimental conditions.
Thermal Conductivity and Stability
Tantalum exhibits superior thermal stability compared to platinum, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 3000degC, which is crucial for high-temperature laboratory equipment. Platinum offers higher thermal conductivity, approximately 71.6 W/m*K, allowing for efficient heat transfer in precision instruments. The choice between tantalum and platinum depends on whether thermal resistance or conductivity is prioritized in specific laboratory applications.
Cost Analysis: Tantalum vs Platinum
Tantalum offers a significantly lower cost per gram compared to platinum, making it a more budget-friendly choice for laboratory equipment. While platinum's high resistance to corrosion and superior conductivity justify its premium price, tantalum provides adequate performance at a fraction of the expense. Laboratories aiming to optimize cost without compromising durability often prefer tantalum over platinum for specialized applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance and excellent mechanical strength, making it highly durable under aggressive chemical environments commonly encountered in laboratory settings. Platinum offers exceptional mechanical stability and resistance to deformation at high temperatures, ensuring longevity in precision applications involving thermal cycling. For laboratory equipment requiring robustness against mechanical stress and chemical degradation, tantalum provides optimal durability, while platinum excels in thermal resilience and maintaining structural integrity.
Applications in Laboratory Settings
Tantalum's exceptional corrosion resistance and high melting point make it ideal for crucibles and electrodes in aggressive chemical environments, while platinum's superior catalytic properties and biocompatibility position it as the preferred choice for electrochemical sensors and medical laboratory instruments. Tantalum is favored in high-temperature applications such as chemical reactors and spectrometry components, where durability under extreme conditions is essential. Platinum excels in precise analytical tools including mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, and fuel cells due to its stable electrical conductivity and resistance to chemical degradation.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tantalum offers exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for long-term use in harsh laboratory environments with minimal maintenance requirements. Platinum, though highly corrosion-resistant and chemically inert, generally demands more frequent cleaning and careful handling to maintain its surface integrity over time. Both metals exhibit excellent longevity, but tantalum's robustness under extreme chemical conditions often results in lower upkeep costs and extended equipment lifespan.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Laboratory Needs
Tantalum excels in laboratory equipment where superior corrosion resistance and high melting points are required, making it ideal for handling aggressive chemicals and high-temperature processes. Platinum offers exceptional catalytic properties and excellent resistance to oxidation, often preferred for applications involving chemical reactions and high-precision instruments. Choosing the right material depends on specific laboratory needs such as chemical compatibility, temperature ranges, and budget considerations to ensure durability and performance.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Platinum for Laboratory Equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com