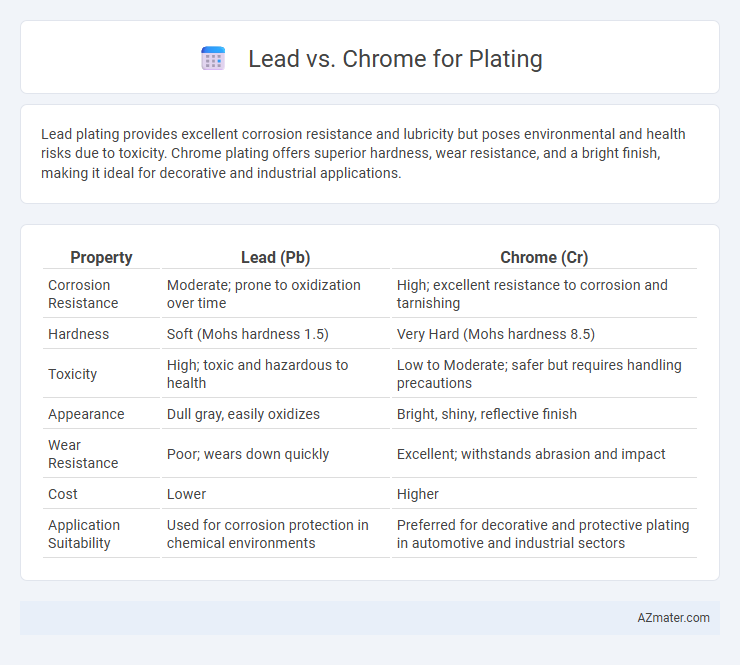
Lead plating provides excellent corrosion resistance and lubricity but poses environmental and health risks due to toxicity. Chrome plating offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and a bright finish, making it ideal for decorative and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead (Pb) | Chrome (Cr) |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to oxidization over time | High; excellent resistance to corrosion and tarnishing |
| Hardness | Soft (Mohs hardness 1.5) | Very Hard (Mohs hardness 8.5) |
| Toxicity | High; toxic and hazardous to health | Low to Moderate; safer but requires handling precautions |
| Appearance | Dull gray, easily oxidizes | Bright, shiny, reflective finish |
| Wear Resistance | Poor; wears down quickly | Excellent; withstands abrasion and impact |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application Suitability | Used for corrosion protection in chemical environments | Preferred for decorative and protective plating in automotive and industrial sectors |
Introduction to Metal Plating: Lead vs Chrome
Metal plating involves depositing a thin layer of metal on a substrate to enhance corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Lead plating offers excellent corrosion resistance and malleability, making it suitable for chemical and battery applications, whereas chrome plating provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and a reflective finish ideal for automotive and decorative uses. Choosing between lead and chrome plating depends on specific performance requirements such as environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and desired surface characteristics.
Chemical Properties of Lead and Chrome Plating
Lead plating offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its low reactivity and high density, forming a stable oxide layer that protects underlying metals. Chrome plating, primarily using hexavalent chromium, provides superior hardness and wear resistance alongside a bright, reflective finish. Both plating types enhance durability, but chrome plating is favored for its hardness and aesthetic appeal, while lead plating excels in chemical stability and corrosion protection.
Historical Applications of Lead and Chrome Plating
Lead plating was widely used historically for its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to protect metal surfaces in harsh environments, particularly in chemical processing and battery manufacturing. Chrome plating emerged later, favored for its superior hardness, aesthetic appeal with a bright, reflective finish, and enhanced wear resistance, making it prevalent in automotive and decorative applications. Both materials played crucial roles in industrial advancements, with lead's toxicity eventually prompting a shift toward safer alternatives like chrome in many applications.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Hardness
Lead plating offers exceptional corrosion resistance but has lower hardness and durability compared to chrome plating, which is renowned for its superior wear resistance and hardness. Chrome plating typically achieves a microhardness of 800-1,200 Vickers, significantly outperforming lead's softer surface characteristics. This makes chrome plating the preferred choice for applications requiring high durability and scratch resistance, while lead is more suitable for environments prioritizing chemical stability.
Environmental Impact and Safety Concerns
Lead plating poses significant environmental hazards due to its high toxicity and potential to contaminate soil and water, leading to strict regulatory restrictions. Chrome plating, while also involving hazardous chemicals like hexavalent chromium, offers improved safety through better containment methods and advances in trivalent chromium alternatives, which are less harmful. Proper waste management and adherence to environmental regulations are critical for minimizing health risks associated with both plating materials.
Cost Analysis: Lead Plating vs Chrome Plating
Lead plating typically incurs lower material costs compared to chrome plating due to the relative abundance and lower market price of lead. Chrome plating, while more expensive, offers superior durability and corrosion resistance, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that initial savings from lead plating may be offset by higher replacement or repair costs over time compared to chrome plating.
Aesthetic Differences: Appearance and Finish
Lead plating offers a dull gray finish with a softer, matte appearance, making it suitable for applications requiring corrosion resistance without shine. Chrome plating provides a bright, reflective, and mirror-like finish, enhancing the aesthetic appeal with its high gloss and smooth surface. The contrast between lead's muted tone and chrome's lustrous shine influences the choice in decorative and functional plating needs.
Industry Uses: Automotive, Marine, and Industrial Sectors
Lead plating offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent machinability, making it ideal for automotive fuel systems and marine applications exposed to harsh saltwater environments. Chrome plating provides exceptional hardness and wear resistance, commonly used in automotive parts like pistons and industrial machinery components requiring durability and aesthetic appeal. Both materials are essential in industrial sectors, with lead preferred for chemical resistance and chrome favored for mechanical performance and surface protection.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance Issues
Lead plating faces increasing regulatory restrictions due to its toxicity and environmental hazards, with agencies like RoHS and REACH imposing strict limits or bans on lead use in electronics and consumer products. Chrome plating, particularly hexavalent chromium, is also heavily regulated under OSHA and EPA standards because of its carcinogenic properties, necessitating rigorous safety controls and emissions management. Compliance challenges for both metals drive industries to adopt safer alternatives or advanced treatment technologies to meet environmental and workplace safety mandates.
Future Trends in Metal Plating Technologies
Future trends in metal plating technologies emphasize the gradual shift from traditional lead plating to environmentally friendly chromium alternatives due to stricter regulations and health concerns associated with lead toxicity. Advances in trivalent chromium plating and nano-coating techniques offer enhanced corrosion resistance and superior hardness while reducing hazardous waste. Emerging innovations also focus on sustainable processes, such as closed-loop recycling systems and non-toxic electrolytes, driving the industry toward greener and more efficient metal finishing solutions.
Infographic: Lead vs Chrome for Plating
 azmater.com
azmater.com