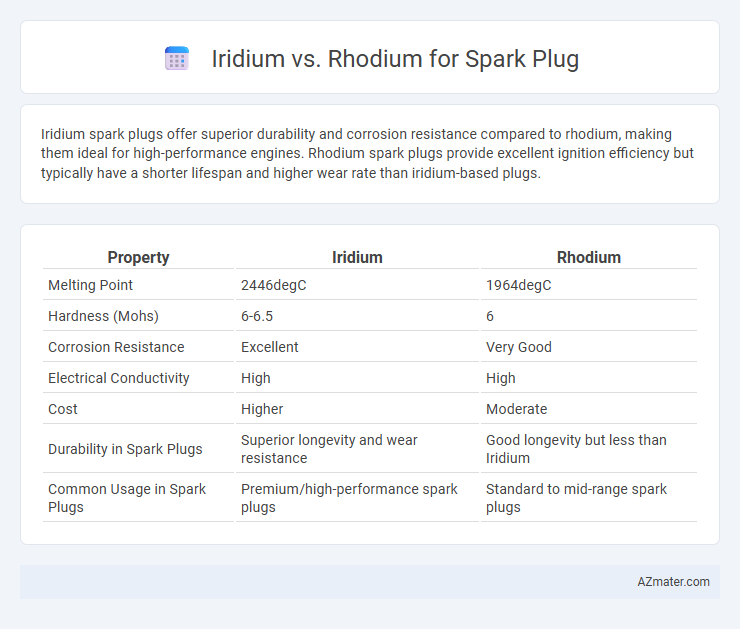
Iridium spark plugs offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to rhodium, making them ideal for high-performance engines. Rhodium spark plugs provide excellent ignition efficiency but typically have a shorter lifespan and higher wear rate than iridium-based plugs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Iridium | Rhodium |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 2446degC | 1964degC |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6-6.5 | 6 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Electrical Conductivity | High | High |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
| Durability in Spark Plugs | Superior longevity and wear resistance | Good longevity but less than Iridium |
| Common Usage in Spark Plugs | Premium/high-performance spark plugs | Standard to mid-range spark plugs |
Introduction to Spark Plug Materials
Iridium and rhodium are premium materials commonly used in spark plugs due to their exceptional durability and high melting points, which enhance ignition performance. Iridium offers excellent wear resistance and conductivity, making it ideal for fine-wire spark plugs that improve fuel efficiency and combustion stability. Rhodium, although less common, provides superior hardness and corrosion resistance, contributing to longer-lasting spark plugs that maintain optimal engine performance.
Overview of Iridium Spark Plugs
Iridium spark plugs feature a fine wire center electrode made from iridium, a metal known for its exceptional hardness and high melting point, which enhances durability and performance under extreme engine conditions. These plugs offer superior ignition efficiency and longer lifespan compared to traditional copper or platinum plugs, making them ideal for high-performance and modern engines. The iridium tip allows for a more precise spark and better fuel combustion, improving overall engine stability and fuel economy.
Overview of Rhodium Spark Plugs
Rhodium spark plugs offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to traditional spark plugs, making them an excellent choice for high-performance engines. Their fine wire electrodes reduce voltage requirements and improve ignitability, resulting in more efficient combustion and enhanced fuel economy. Known for longevity, rhodium spark plugs maintain optimal engine performance and reduce maintenance frequency over time.
Conductivity and Performance Comparison
Iridium spark plugs offer superior conductivity due to iridium's high melting point and excellent electrical properties, enabling consistent spark generation and improved engine performance. Rhodium spark plugs provide enhanced durability and corrosion resistance but have slightly lower electrical conductivity compared to iridium, potentially affecting ignition efficiency under extreme conditions. Overall, iridium plugs excel in delivering higher conductivity and stable performance, while rhodium plugs prioritize longevity and corrosion resistance in demanding environments.
Durability and Longevity
Iridium spark plugs boast superior durability due to their high melting point of 2446degC, which allows them to withstand extreme temperatures and wear longer than rhodium counterparts. Rhodium, while also corrosion-resistant and hard, has a lower melting point of 1966degC, resulting in slightly reduced lifespan under high-performance conditions. Iridium's ultra-fine wire design and excellent erosion resistance contribute to enhanced longevity, often lasting up to 60,000 to 120,000 miles compared to rhodium's typical range of 30,000 to 60,000 miles.
Resistance to Corrosion and Wear
Iridium spark plugs exhibit superior resistance to corrosion and wear due to iridium's high melting point of 2,447degC and excellent oxidation resistance, ensuring longer service life under extreme combustion temperatures. Rhodium spark plugs also offer good corrosion resistance, but iridium's enhanced durability and hardness make it more effective in preventing electrode erosion and maintaining optimal spark performance. This superior wear resistance results in consistent ignition efficiency and reduced maintenance needs for iridium-plug-equipped engines.
Cost and Availability
Iridium spark plugs are generally more affordable and readily available compared to rhodium spark plugs, which tend to be rarer and significantly more expensive due to rhodium's scarcity in the market. While both metals offer excellent durability and performance, iridium's widespread availability results in lower production costs and greater accessibility for consumers. The higher cost and limited supply of rhodium make it a premium option often reserved for high-performance or luxury automotive applications.
Impact on Engine Efficiency
Iridium spark plugs offer superior engine efficiency due to their fine electrode tips, which provide consistently strong and precise sparks, enhancing fuel combustion. Rhodium spark plugs, while also durable, feature a higher melting point and resistance to wear, contributing to longer service life but slightly less efficient ignition performance. The improved ignition stability of iridium plugs typically results in better fuel economy and lower emissions compared to rhodium alternatives.
Maintenance and Replacement Intervals
Iridium spark plugs typically offer longer maintenance and replacement intervals than rhodium spark plugs due to their superior durability and high melting point of 2446degC, which ensures consistent performance in high-temperature engine environments. Rhodium plugs, although corrosion-resistant with a melting point of 1964degC, generally require more frequent replacement because they wear faster under similar conditions. Choosing iridium-plated spark plugs can reduce maintenance frequency, leading to lower long-term costs and improved engine efficiency.
Choosing the Right Spark Plug Material
Iridium spark plugs offer superior durability and better ignition performance due to their fine wire center electrode, which ensures efficient fuel combustion and longer lifespan compared to traditional materials. Rhodium spark plugs provide excellent wear resistance and stable sparking with a slightly higher price point and are ideal for high-performance engines requiring optimal conductivity and thermal stability. Choosing between iridium and rhodium depends on the engine's requirements for durability, ignition precision, and cost-effectiveness, with iridium favored for longevity and rhodium preferred for precision and extreme conditions.
Infographic: Iridium vs Rhodium for Spark Plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com