Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, offers superior durability and a deeper, richer color, making it ideal for medals intended to symbolize strength and tradition. Brass, composed of copper and zinc, provides a brighter, gold-like appearance but is softer and less wear-resistant than bronze.
Table of Comparison
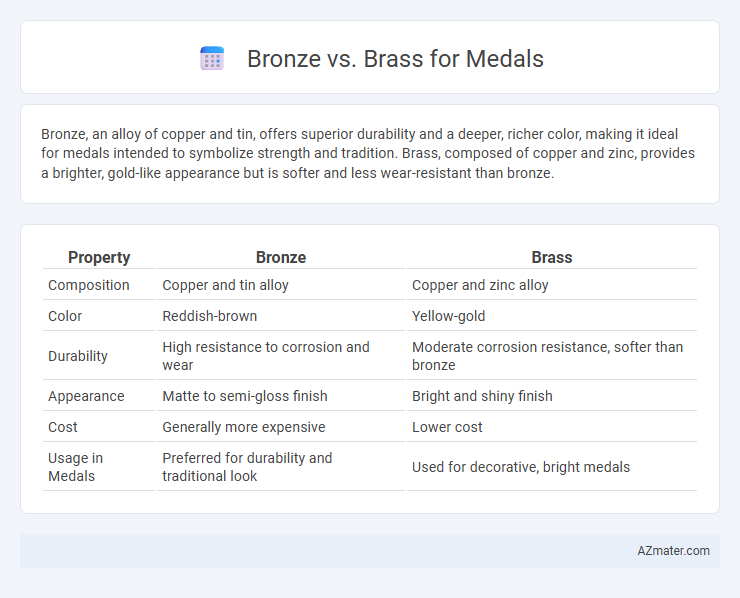
| Property | Bronze | Brass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and tin alloy | Copper and zinc alloy |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Yellow-gold |
| Durability | High resistance to corrosion and wear | Moderate corrosion resistance, softer than bronze |
| Appearance | Matte to semi-gloss finish | Bright and shiny finish |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Lower cost |
| Usage in Medals | Preferred for durability and traditional look | Used for decorative, bright medals |
Introduction to Bronze and Brass Medals
Bronze medals, primarily composed of copper and tin, are known for their durability, corrosion resistance, and rich, warm brown color, making them a traditional choice for third-place awards in competitions. Brass medals, an alloy of copper and zinc, offer a bright, gold-like appearance with excellent malleability and cost-effectiveness, often used for decorative and recognition purposes. Both bronze and brass medals provide distinct aesthetic qualities and physical properties, influencing their selection based on the desired look, feel, and budget for awards.
Composition Differences: Bronze vs Brass
Bronze for medals primarily consists of copper combined with tin, typically around 88% copper and 12% tin, which provides enhanced durability and a reddish-brown hue. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, with zinc content ranging from 5% to 40%, resulting in a brighter yellowish appearance and greater malleability. The distinct compositions influence medal properties: bronze offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance, while brass allows for easier detailed engraving and a shinier finish.
Historical Significance of Bronze and Brass Medals
Bronze medals have a rich historical significance dating back to ancient civilizations where bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, symbolized durability and achievement in warfare and athletic contests. Brass, composed of copper and zinc, gained prominence in medal crafting during the Renaissance, valued for its bright, gold-like appearance and corrosion resistance. Both materials reflect distinct cultural and technological advancements, with bronze emphasizing tradition and strength, while brass highlights aesthetic appeal and innovation in medal design.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetics
Bronze medals feature a rich, warm reddish-brown color that develops a natural patina over time, enhancing their vintage appeal and adding depth to their texture. Brass medals, composed of copper and zinc, exhibit a bright, golden-yellow sheen that maintains a shiny, polished look, giving a more vibrant and eye-catching appearance. The choice between bronze and brass medals hinges on the desired aesthetic impact, with bronze offering a classic, timeless feel and brass providing a more striking, radiant finish.
Durability and Longevity
Bronze offers superior durability and longevity for medals due to its high resistance to corrosion and wear, making it ideal for long-lasting awards. Brass, while aesthetically similar with a bright gold-like appearance, tends to tarnish and degrade faster over time when exposed to moisture and air. Choosing bronze ensures the medal maintains its structural integrity and appearance through years of handling and environmental exposure.
Cost Comparison: Bronze vs Brass
Bronze medals typically cost more than brass due to their higher copper content and superior durability, making them a preferred choice for long-lasting awards. Brass, composed mainly of copper and zinc, is usually less expensive and offers a similar aesthetic but tends to tarnish more quickly. Budget-conscious organizations often choose brass medals to balance cost efficiency with visual appeal in award production.
Customization and Engraving Options
Bronze medals offer a classic, warm tone that enhances detailed engravings with a rich patina developing over time, making them ideal for deep, clear customization. Brass medals provide a brighter, gold-like appearance that retains engraving precision while allowing for various finishes such as polishing or antiquing to enhance visual contrast. Both metals support laser and rotary engraving techniques, but brass often accommodates vibrant color fills that highlight text and logos for a standout, customizable medal design.
Weight and Feel of the Medals
Bronze medals typically feel heavier than brass medals due to their higher density, often around 8.9 g/cm3 compared to brass's 8.4 g/cm3. The weight difference influences the medal's perceived quality and durability, with bronze offering a solid, substantial feel. Bronze medals also tend to have a slightly rougher texture, while brass medals present a smoother, shinier finish.
Popular Uses in Award Ceremonies
Bronze medals are traditionally awarded for third place in sports and academic competitions, symbolizing durability and historical significance, while brass medals, often chosen for their bright gold-like appearance, are popular in corporate awards and commemorative events. Bronze's rich, reddish-brown tone conveys prestige and timeless value, making it a preferred choice for Olympic bronze medals and military honors. Brass offers a cost-effective alternative with excellent corrosion resistance, frequently used in customized medals and trophies for local sports leagues and educational achievements.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Medal
Choosing between bronze and brass for your medal depends on the desired appearance and durability; bronze offers a rich, darker tone with excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting awards. Brass, characterized by a bright yellow-gold finish, provides a more economical option with good strength but may tarnish over time, requiring regular polishing. Consider the medal's intended use and aesthetic preferences to select the material that best aligns with the award's significance and longevity.
Infographic: Bronze vs Brass for Medal
 azmater.com
azmater.com