Bronze, composed primarily of copper and tin, offers superior durability and a classic antique appearance, making it ideal for long-lasting coins. Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective, but less durable, often used for low-value or commemorative coins.
Table of Comparison
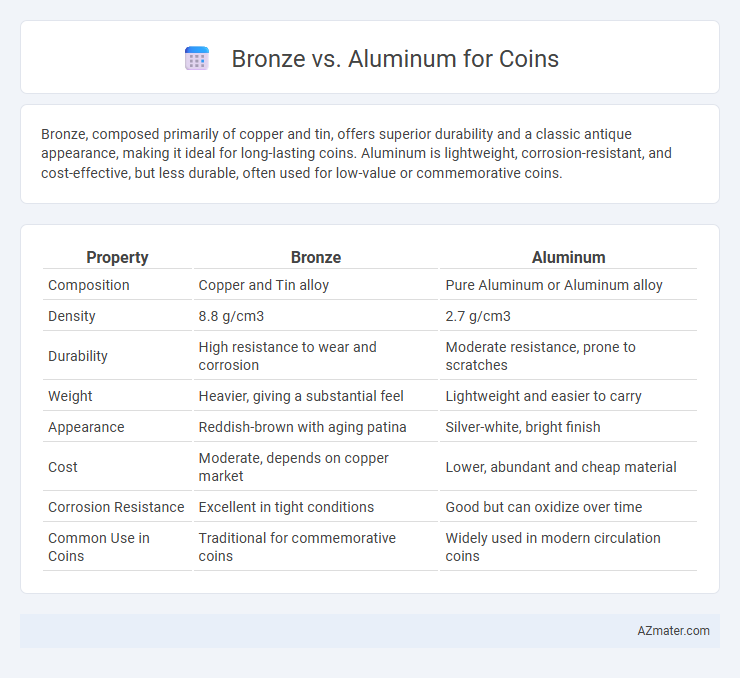
| Property | Bronze | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Tin alloy | Pure Aluminum or Aluminum alloy |
| Density | 8.8 g/cm3 | 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and corrosion | Moderate resistance, prone to scratches |
| Weight | Heavier, giving a substantial feel | Lightweight and easier to carry |
| Appearance | Reddish-brown with aging patina | Silver-white, bright finish |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on copper market | Lower, abundant and cheap material |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in tight conditions | Good but can oxidize over time |
| Common Use in Coins | Traditional for commemorative coins | Widely used in modern circulation coins |
Introduction to Coinage Materials
Bronze and aluminum have distinct properties influencing their use in coinage, with bronze known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for long-lasting coins. Aluminum offers a lightweight and cost-effective alternative, often used in modern currencies requiring high production volume. Material selection impacts coin appearance, weight, and lifespan, essential factors in currency design and minting.
Historical Use of Bronze and Aluminum in Coins
Bronze has been historically preferred for coins due to its durability, resistance to corrosion, and relatively low cost, with notable examples dating back to ancient Rome and Greece. Aluminum coins emerged in the early 20th century as a lightweight, corrosion-resistant alternative, especially during wartime when other metals were scarce. The transition from bronze to aluminum in numismatics reflects evolving metallurgical technology and economic considerations in minting practices worldwide.
Physical Properties: Bronze vs Aluminum
Bronze coins exhibit higher density and greater hardness compared to aluminum, resulting in increased durability and resistance to wear. Aluminum coins are lightweight with excellent corrosion resistance but possess lower tensile strength, making them more prone to deformation. The thermal conductivity of aluminum surpasses bronze, affecting coin temperature regulation in various environments.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Bronze coins exhibit superior durability and wear resistance due to their copper-tin alloy composition, which offers excellent corrosion resistance and hardness ideal for long-term circulation. Aluminum coins, while lightweight and corrosion-resistant, generally possess lower wear resistance and are more prone to surface damage over time. The choice between bronze and aluminum for coins depends largely on the balance between durability requirements and production cost efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Bronze offers superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for coins exposed to outdoor or humid environments where durability is critical. The copper content in bronze forms a protective patina that prevents further oxidation, enhancing longevity significantly. Aluminum, while lightweight and resistant to mild corrosion, tends to oxidize quickly and deteriorate faster under harsh conditions, reducing its effectiveness for long-term coin durability.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Bronze coins typically cost more due to the higher price of copper and tin compared to aluminum, which is abundant and inexpensive. Economic considerations favor aluminum for large-scale minting because its lightweight nature reduces transportation and handling expenses. The durability of bronze can justify its higher initial cost in long-term circulation, impacting overall economic efficiency depending on coin lifespan requirements.
Aesthetic Qualities and Appearance
Bronze coins exhibit a warm, rich brownish hue with a subtle patina that enhances their vintage and classic appeal, often preferred for commemorative and historical themes. Aluminum coins possess a bright, silvery-white finish, offering a sleek, modern look with excellent resistance to tarnishing and corrosion, which ensures long-lasting clarity and shine. The choice between bronze and aluminum impacts not only color and surface texture but also the visual weight and tactile impression of the coin.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bronze coins are primarily composed of copper and tin, metals that require intensive mining processes leading to significant ecological disruption and higher carbon emissions compared to aluminum. Aluminum is more sustainable due to its abundant availability, lightweight nature, and high recyclability, enabling energy-efficient production and reduced environmental footprint throughout its lifecycle. The use of aluminum in coinage supports circular economy principles by facilitating easier recycling with lower energy input, making it a more environmentally responsible choice over bronze.
Counterfeiting and Security Features
Bronze coins typically offer higher resistance to counterfeiting due to their unique alloy composition and distinct patina that is difficult to replicate, enhancing security features. Aluminum coins, while lightweight and corrosion-resistant, are more susceptible to forgery because their surface can be easily altered or mimicked with lower-cost materials. Advanced security features such as micro-engraving and RFID integration are more effectively implemented in bronze coins owing to their sturdier and denser metal properties.
Verdict: Choosing Between Bronze and Aluminum for Coins
Bronze offers superior durability and a classic appeal due to its traditional alloy composition of copper and tin, making it ideal for collectible coins and long-term circulation. Aluminum provides lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion, reducing production costs and increasing ease of handling in mass minting. The choice between bronze and aluminum coins depends on the desired balance of durability, aesthetic value, and cost efficiency for specific coinage purposes.
Infographic: Bronze vs Aluminum for Coin
 azmater.com
azmater.com