Brass fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to zinc, making them ideal for marine and electrical applications. Zinc fasteners provide cost-effective strength and moderate corrosion resistance suitable for general-purpose use.
Table of Comparison
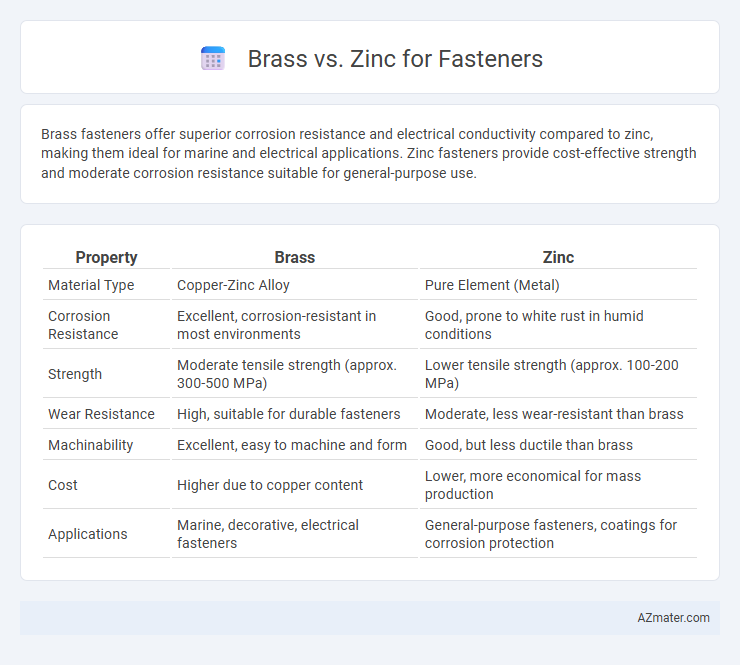
| Property | Brass | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Copper-Zinc Alloy | Pure Element (Metal) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, corrosion-resistant in most environments | Good, prone to white rust in humid conditions |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength (approx. 300-500 MPa) | Lower tensile strength (approx. 100-200 MPa) |
| Wear Resistance | High, suitable for durable fasteners | Moderate, less wear-resistant than brass |
| Machinability | Excellent, easy to machine and form | Good, but less ductile than brass |
| Cost | Higher due to copper content | Lower, more economical for mass production |
| Applications | Marine, decorative, electrical fasteners | General-purpose fasteners, coatings for corrosion protection |
Introduction: Brass vs Zinc Fasteners
Brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for marine and electrical applications. Zinc fasteners provide strong durability and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in construction and general hardware due to their resistance to rust and wear. The choice between brass and zinc fasteners depends on specific requirements such as environmental exposure, strength, and budget constraints.
Material Composition and Properties
Brass fasteners, composed primarily of copper and zinc with trace elements, exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for decorative and marine applications. Zinc fasteners, often made from pure zinc or zinc alloys, provide superior sacrificial corrosion protection and affordability but possess lower tensile strength and durability compared to brass. Material choice impacts fastener performance, with brass offering enhanced longevity in harsh environments and zinc favoring cost-effective, corrosion-resistant solutions.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Brass fasteners exhibit superior corrosion resistance in environments with high moisture and salt exposure, maintaining durability without rusting due to their copper-zinc alloy composition. Zinc fasteners provide good corrosion protection through galvanization but are prone to white rust and degradation when exposed to prolonged moisture or acidic conditions. For applications requiring long-term resistance in marine or humid atmospheres, brass fasteners offer enhanced longevity compared to zinc counterparts.
Strength and Durability Differences
Brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and moderate strength, making them ideal for decorative applications and environments with low mechanical stress. Zinc fasteners provide higher tensile strength and superior durability under heavy loads, commonly used in structural and industrial settings. Choosing between brass and zinc depends on whether the priority is corrosion resistance or mechanical performance.
Cost Analysis: Brass vs Zinc
Brass fasteners generally have a higher upfront cost compared to zinc fasteners due to the more expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes involved. Zinc fasteners offer a cost-effective alternative with lower material expenses and simpler production, making them ideal for large-scale applications where budget constraints are critical. Long-term durability and corrosion resistance of brass may reduce replacement frequency, potentially offsetting initial cost differences in some industrial environments.
Aesthetic and Finish Options
Brass fasteners offer a warm, golden hue that enhances aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for decorative applications requiring a classic or vintage look. Zinc fasteners typically have a silver-gray finish that can be further treated with plating or coating options to provide corrosion resistance and a sleek, modern appearance. Both materials support various finishes such as polished, brushed, or plated, but brass naturally maintains its luster longer without elaborate surface treatments.
Common Applications in Industry
Brass fasteners are widely used in marine, electrical, and decorative applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and aesthetic appeal. Zinc fasteners are common in construction, automotive, and general-purpose fastening where cost-effectiveness and good corrosion resistance in mild environments are required. Both materials offer unique advantages, with brass favored for durability and appearance in specialized applications, while zinc suits high-volume, budget-conscious projects.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Brass fasteners, composed mainly of copper and zinc, offer superior corrosion resistance and antimicrobial properties, reducing the need for harmful chemical treatments. Zinc fasteners, often galvanized, provide cost-effective corrosion protection but may release zinc particles during degradation that could impact aquatic ecosystems. Choosing brass over zinc can minimize environmental toxicity and exposure to harmful metals, especially in applications requiring frequent human contact or sensitive environments.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Brass fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and require less frequent maintenance, making them ideal for marine and outdoor installations where exposure to moisture is prevalent. Zinc fasteners provide higher strength and ease of installation due to their lightweight nature, but they may require protective coatings to prevent rusting in harsh environments. Choosing between brass and zinc depends on the specific application's exposure conditions and the desired balance between durability and installation efficiency.
Choosing the Right Fastener Material
Choosing the right fastener material depends on application requirements such as corrosion resistance, strength, and conductivity. Brass fasteners offer excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, making them ideal for marine and electrical applications. Zinc fasteners provide good corrosion protection through galvanization and are cost-effective for general-purpose use where high strength is not critical.
Infographic: Brass vs Zinc for Fastener
 azmater.com
azmater.com