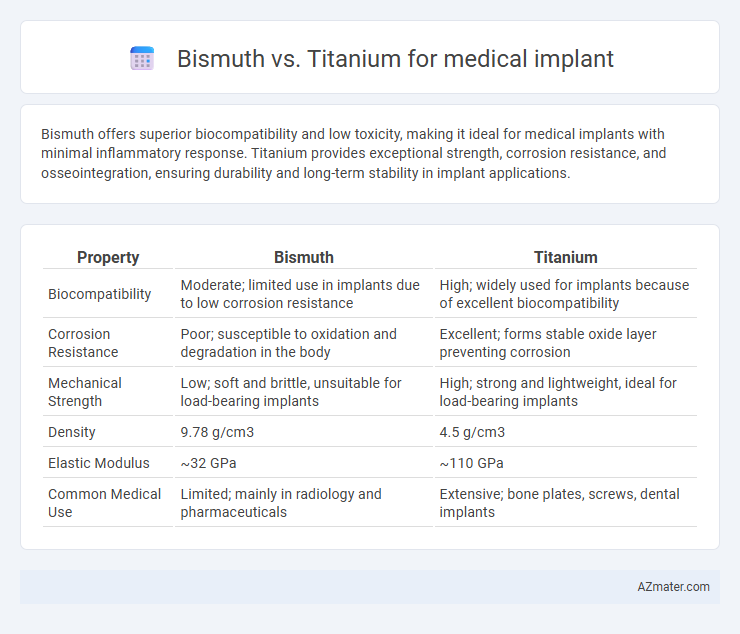
Bismuth offers superior biocompatibility and low toxicity, making it ideal for medical implants with minimal inflammatory response. Titanium provides exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and osseointegration, ensuring durability and long-term stability in implant applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | Moderate; limited use in implants due to low corrosion resistance | High; widely used for implants because of excellent biocompatibility |
| Corrosion Resistance | Poor; susceptible to oxidation and degradation in the body | Excellent; forms stable oxide layer preventing corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength | Low; soft and brittle, unsuitable for load-bearing implants | High; strong and lightweight, ideal for load-bearing implants |
| Density | 9.78 g/cm3 | 4.5 g/cm3 |
| Elastic Modulus | ~32 GPa | ~110 GPa |
| Common Medical Use | Limited; mainly in radiology and pharmaceuticals | Extensive; bone plates, screws, dental implants |
Introduction to Bismuth and Titanium in Medical Implants
Bismuth and titanium are both materials used in medical implants with distinct properties influencing their applications. Titanium is renowned for its high strength, corrosion resistance, and excellent biocompatibility, making it a standard choice for orthopedic, dental, and cardiovascular implants. Bismuth, although less common, offers unique features such as radiopacity and antimicrobial properties, which can enhance implant performance in specific medical scenarios.
Material Properties Comparison: Bismuth vs Titanium
Titanium exhibits superior strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making it the preferred choice for medical implants over bismuth. Bismuth, while non-toxic and having low thermal conductivity, lacks the mechanical durability and corrosion resistance essential for long-term implant stability. Titanium's ability to osseointegrate with bone tissue further enhances its effectiveness in orthopedic and dental applications compared to bismuth.
Biocompatibility and Safety Profiles
Bismuth exhibits excellent biocompatibility with low toxicity, making it suitable for certain medical applications but it lacks the mechanical strength required for load-bearing implants. Titanium is widely preferred in medical implants due to its superior biocompatibility, high corrosion resistance, and strong safety profile, minimizing adverse tissue reactions and promoting osseointegration. Clinical studies consistently demonstrate titanium's reliable performance in orthopedic and dental implants, highlighting its role as a safer and more durable choice compared to bismuth.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity in Implants
Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance in medical implants due to its stable oxide layer, which prevents degradation in bodily fluids and extends implant longevity. Bismuth, while biocompatible, lacks the robust corrosion resistance of titanium, making it less ideal for long-term implantation. The enhanced durability of titanium implants results in reduced risk of implant failure and fewer revision surgeries over time.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Bismuth exhibits lower mechanical strength and flexibility compared to titanium, making it less suitable for load-bearing medical implants. Titanium's high tensile strength, excellent fatigue resistance, and biocompatibility allow it to withstand significant mechanical stress while maintaining flexibility crucial for dynamic body environments. These properties make titanium the preferred choice in orthopedic and dental implants, ensuring durability and patient safety.
Imaging Compatibility: MRI and CT Scan Considerations
Bismuth exhibits lower magnetic susceptibility than titanium, resulting in minimal artifacts during MRI scans and improved imaging clarity, crucial for accurate diagnostics. Titanium's paramagnetic properties lead to moderate image distortion in MRI, posing challenges for clear visualization near implants. In CT scans, both metals provide good radiopacity, but bismuth's higher atomic number enhances contrast resolution, facilitating better differentiation of surrounding tissues.
Allergic Reactions and Toxicity Risks
Bismuth exhibits low toxicity and is rarely associated with allergic reactions, making it a favorable choice in certain medical implants; however, its mechanical properties limit widespread usage. Titanium is highly biocompatible with minimal allergic responses, widely preferred in medical implants for its strong corrosion resistance and negligible toxicity. Both metals demonstrate low allergenicity, but titanium's extensive clinical history and favorable osseointegration profile reduce long-term adverse effects compared to bismuth.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Bismuth offers limited use in medical implants due to low mechanical strength and scarcity, resulting in higher production costs and lower availability compared to titanium. Titanium remains the preferred material with excellent biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and widespread availability, ensuring cost-effective manufacturing for large-scale implant production. The global titanium supply chain supports consistent pricing, making it the more economically viable choice for durable medical implant applications.
Current Applications and Clinical Outcomes
Bismuth and titanium are both used in medical implants, with titanium being the gold standard due to its exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength, widely applied in orthopedic, dental, and cardiovascular implants. Bismuth, primarily utilized in specialized coatings and radiopaque agents, shows potential for antimicrobial properties but is less common as a bulk implant material. Clinical outcomes favor titanium implants for long-term durability and osseointegration, while bismuth's role remains adjunctive, enhancing implant imaging and infection control.
Future Trends in Implant Materials: Bismuth vs Titanium
Bismuth is emerging as a promising material for medical implants due to its excellent biocompatibility and antimicrobial properties, which reduce infection risks and enhance patient outcomes. Titanium remains the gold standard for implants because of its superior strength, corrosion resistance, and osseointegration capabilities, ensuring long-term durability and stability. Future trends indicate a growing interest in composite materials combining bismuth's bioactivity with titanium's mechanical robustness to optimize implant performance and promote faster healing.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Titanium for Medical implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com