Bismuth cookware offers excellent non-toxic, low thermal conductivity benefits, promoting even heat distribution and energy efficiency. Stainless steel cookware provides superior durability, corrosion resistance, and high heat tolerance, making it ideal for long-term, heavy-duty cooking.
Table of Comparison
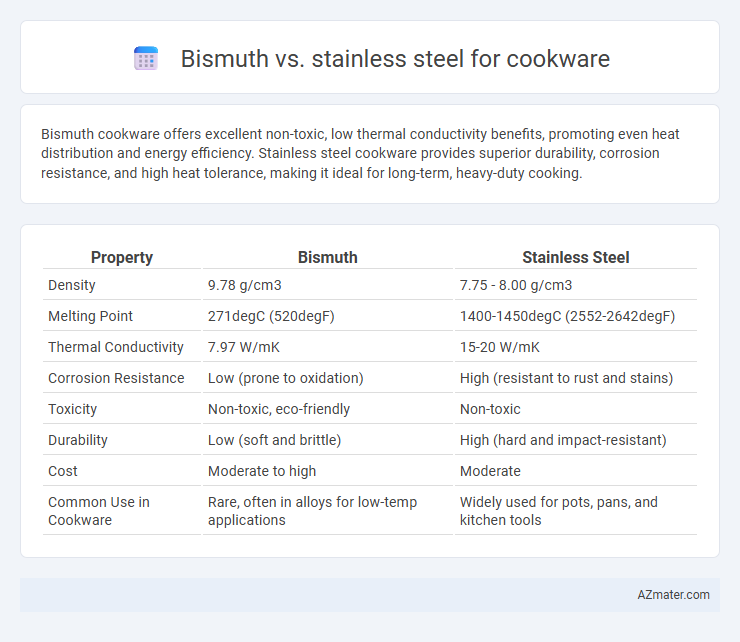
| Property | Bismuth | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 9.78 g/cm3 | 7.75 - 8.00 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 271degC (520degF) | 1400-1450degC (2552-2642degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 7.97 W/mK | 15-20 W/mK |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low (prone to oxidation) | High (resistant to rust and stains) |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Non-toxic |
| Durability | Low (soft and brittle) | High (hard and impact-resistant) |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Common Use in Cookware | Rare, often in alloys for low-temp applications | Widely used for pots, pans, and kitchen tools |
Introduction to Bismuth and Stainless Steel Cookware
Bismuth cookware offers a non-toxic, eco-friendly alternative with excellent heat distribution and natural antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for health-conscious cooking. Stainless steel cookware is renowned for its durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures, often featuring alloys like chromium and nickel for enhanced performance. Both materials provide distinct benefits, with bismuth standing out for its safety and thermal efficiency, while stainless steel excels in longevity and versatility for diverse cooking techniques.
Composition and Material Properties
Bismuth cookware is composed primarily of bismuth, a non-toxic, heavy metal with low thermal conductivity, which offers gentle, even heat distribution but slower temperature responsiveness compared to stainless steel. Stainless steel cookware consists mostly of iron alloys containing chromium and nickel, providing high durability, corrosion resistance, and excellent heat conduction suited for rapid cooking. Bismuth's non-reactive nature prevents food contamination, while stainless steel's robust structure withstands high temperatures and mechanical wear, making the choice dependent on cooking style and performance needs.
Heat Conductivity and Distribution
Bismuth offers moderate heat conductivity but lags behind stainless steel, which provides superior thermal conduction and even heat distribution critical for precise cooking. Stainless steel's dense structure ensures consistent temperature control, reducing hotspots and improving overall cook performance. Bismuth's lower conductivity may lead to uneven cooking, making stainless steel a preferred choice for efficient and reliable cookware.
Durability and Longevity
Stainless steel cookware is renowned for its exceptional durability and resistance to rust, corrosion, and staining, ensuring long-term use even under high heat and frequent cleaning. Bismuth cookware, while offering good thermal conductivity and non-toxicity, lacks the same level of robustness and may be more prone to wear and deformation over time. For longevity, stainless steel remains the superior choice due to its sturdy alloy composition and resilience against physical and chemical wear.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Bismuth cookware is valued for its non-toxic properties, as it does not leach harmful metals into food, making it a safer alternative to traditional heavy metals. Stainless steel, while generally safe, can sometimes release trace amounts of nickel and chromium, which may pose risks for individuals with allergies or sensitivities. Both materials resist corrosion and maintain structural integrity, but bismuth's hypoallergenic nature offers an advantage in minimizing toxicity concerns in cookware.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Bismuth cookware requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to maintain its unique appearance and prevent damage to its delicate surface. Stainless steel is highly durable and can withstand rigorous scrubbing, dishwasher use, and high-temperature cleaning with minimal risk of corrosion or discoloration. Regular polishing can help preserve bismuth's luster, while stainless steel demands less frequent polishing, making it a more low-maintenance option for everyday cooking.
Cooking Performance and Food Reactivity
Bismuth cookware offers excellent heat conductivity, allowing for even cooking and precise temperature control, while stainless steel tends to heat less uniformly but provides durability and resistance to corrosion. Bismuth is generally non-reactive, making it safe for acidic and alkaline foods without altering flavor or causing discoloration. Stainless steel may react with highly acidic foods, potentially imparting a metallic taste, but its inert nature overall makes it widely suitable for diverse cooking applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bismuth cookware offers a lower environmental impact during production compared to stainless steel due to its non-toxic, naturally abundant properties and energy-efficient extraction methods. Stainless steel, while highly durable and recyclable, requires intensive mining and refining processes that contribute significantly to carbon emissions and resource depletion. Choosing bismuth cookware supports sustainability by reducing ecological footprints and promoting safer disposal without heavy metal contamination.
Cost Comparison and Value for Money
Bismuth cookware typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its rarity and specialized manufacturing processes compared to stainless steel, which is widely produced and more affordable. Stainless steel offers excellent value for money with its durability, corrosion resistance, and low maintenance, making it a cost-effective choice for everyday cooking. While bismuth cookware may provide unique benefits like non-toxicity and thermal conductivity, stainless steel remains the preferred option for budget-conscious consumers seeking long-term performance.
Which Cookware Material Should You Choose?
Bismuth cookware offers excellent heat conductivity and is non-toxic, making it ideal for precise cooking and health-conscious users, while stainless steel is prized for its durability, resistance to corrosion, and versatility in various cooking conditions. Choosing between bismuth and stainless steel depends on your cooking style: bismuth is suitable for low to medium heat and delicate tasks, whereas stainless steel excels under high heat and heavy use. Stainless steel cookware often includes an aluminum or copper core for improved heat distribution, providing a balance of performance and longevity.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Stainless steel for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com