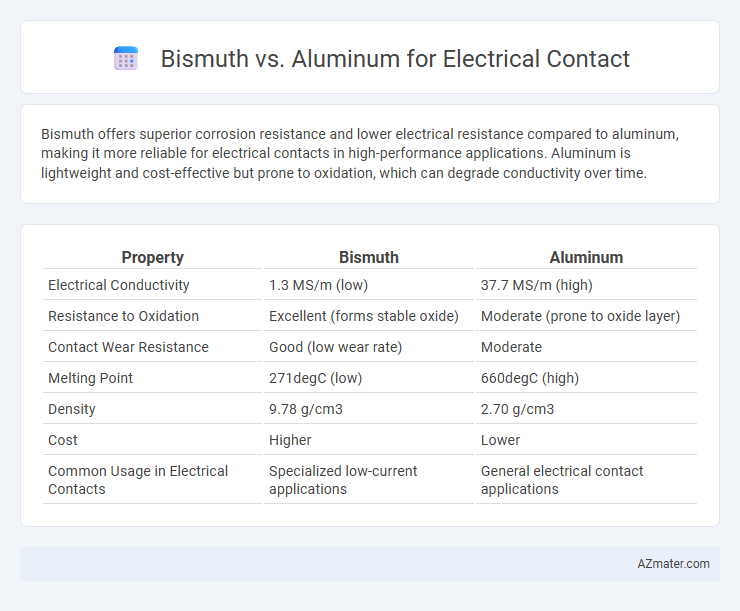
Bismuth offers superior corrosion resistance and lower electrical resistance compared to aluminum, making it more reliable for electrical contacts in high-performance applications. Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective but prone to oxidation, which can degrade conductivity over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bismuth | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 1.3 MS/m (low) | 37.7 MS/m (high) |
| Resistance to Oxidation | Excellent (forms stable oxide) | Moderate (prone to oxide layer) |
| Contact Wear Resistance | Good (low wear rate) | Moderate |
| Melting Point | 271degC (low) | 660degC (high) |
| Density | 9.78 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Usage in Electrical Contacts | Specialized low-current applications | General electrical contact applications |
Introduction to Bismuth and Aluminum in Electrical Contacts
Bismuth is a heavy metal known for its low electrical conductivity and high resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for specialized electrical contact applications requiring minimal oxidation and improved durability. Aluminum is a lightweight metal with excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in power transmission and general electrical fittings but prone to surface oxidation that can affect contact performance. Both metals offer distinct advantages in electrical contacts, with bismuth favored for precision and stability in low-current scenarios, while aluminum suits high-current and cost-sensitive applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Bismuth exhibits significantly lower electrical conductivity (~7.7% IACS) compared to aluminum, which has high conductivity (~61% IACS), making aluminum more efficient for electrical contacts. Aluminum's superior conductivity ensures lower resistance and energy loss in circuits, whereas bismuth's poor conductivity limits its use primarily to specialized applications like thermal fuses or low-current contacts. Selecting aluminum over bismuth enhances performance in high-current electrical contacts due to its favorable conductivity and cost-effectiveness.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Management
Bismuth exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity than aluminum, approximately 8 W/m*K compared to aluminum's 205 W/m*K, making aluminum superior for efficient heat dissipation in electrical contacts. Aluminum's high thermal conductivity enables rapid heat transfer, reducing the risk of overheating and enhancing the reliability of electrical connections. In contrast, bismuth's poor heat management capability limits its use in high-current or high-temperature applications where thermal performance is critical.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Stability
Bismuth offers superior corrosion resistance in electrical contacts compared to aluminum, resisting oxidation and maintaining stable conductivity in harsh environments. Aluminum, while lightweight and cost-effective, forms an oxide layer that can degrade contact quality over time and reduce environmental stability. Utilizing bismuth in electrical contacts enhances durability and performance in corrosive or high-moisture conditions where aluminum's oxide formation limits reliability.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Bismuth offers lower thermal conductivity and higher brittleness compared to aluminum, making it less ideal for electrical contacts requiring flexibility and impact resistance. Aluminum provides superior mechanical strength and excellent corrosion resistance, enhancing durability in electrical contact applications. Its lightweight nature combined with good conductivity ensures longer lifespan and consistent performance under mechanical stress.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Bismuth is more expensive and less abundant than aluminum, impacting its cost-effectiveness for electrical contacts. Aluminum offers high availability and low cost, making it a preferred choice for large-scale or budget-sensitive applications. Cost considerations favor aluminum, while bismuth is typically reserved for specialized contacts requiring its unique properties despite higher expense.
Ease of Manufacturing and Fabrication
Bismuth offers easier machining and casting due to its low melting point of 271degC, enabling precision in small electrical contact components without extensive tooling wear. Aluminum, with a higher melting point of 660degC, requires more robust fabrication techniques such as extrusion and CNC machining, which can increase production time and costs. However, aluminum's lightweight and excellent conductivity make it favorable for large-scale manufacturing despite the relative difficulty in fabrication compared to bismuth.
Compatibility with Other Materials
Bismuth exhibits superior compatibility with noble metals such as gold, silver, and copper due to its low reactivity and minimal intermetallic formation, reducing contact corrosion and wear in electrical applications. Aluminum tends to form oxide layers rapidly, which can increase contact resistance and impair performance when mating with metals like copper or silver without proper surface treatment. Selecting bismuth for electrical contacts ensures better long-term stability and reduced galvanic corrosion when paired with diverse conductive materials.
Typical Applications in Electrical Engineering
Bismuth alloys are commonly used in electrical contacts for circuit breakers and relays due to their excellent thermal conductivity and low electrical resistance, which help prevent contact welding and improve arc quenching. Aluminum contacts are favored in high-current applications and overhead power lines because of their lightweight and good electrical conductivity, although they require coatings to resist oxidation and wear. Both materials serve distinct roles in electrical engineering, with bismuth alloys preferred for precision switching devices and aluminum for cost-effective, large-scale power distribution components.
Summary: Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Contacts
Bismuth offers superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts where durability is crucial. Aluminum provides excellent conductivity and lightweight properties, suitable for applications requiring efficient current flow and cost-effectiveness. Selecting between bismuth and aluminum depends on balancing electrical conductivity needs with environmental factors and mechanical strength requirements.
Infographic: Bismuth vs Aluminum for Electrical contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com