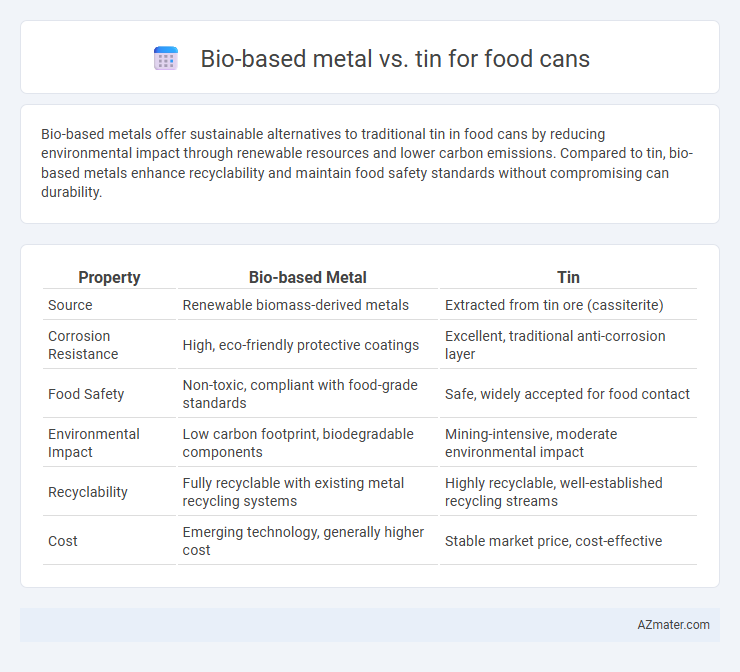
Bio-based metals offer sustainable alternatives to traditional tin in food cans by reducing environmental impact through renewable resources and lower carbon emissions. Compared to tin, bio-based metals enhance recyclability and maintain food safety standards without compromising can durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-based Metal | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable biomass-derived metals | Extracted from tin ore (cassiterite) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, eco-friendly protective coatings | Excellent, traditional anti-corrosion layer |
| Food Safety | Non-toxic, compliant with food-grade standards | Safe, widely accepted for food contact |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable components | Mining-intensive, moderate environmental impact |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable with existing metal recycling systems | Highly recyclable, well-established recycling streams |
| Cost | Emerging technology, generally higher cost | Stable market price, cost-effective |
Introduction to Food Can Materials
Food cans traditionally rely on tin coatings to prevent corrosion and preserve food quality, but bio-based metals are emerging as sustainable alternatives with reduced environmental impact. Bio-based metals incorporate organic, renewable materials in their protective layers, enhancing biodegradability and reducing reliance on scarce tin resources. Advances in bio-based coatings maintain food safety standards while promoting eco-friendly packaging solutions for the food industry.
Overview of Bio-Based Metals
Bio-based metals for food cans are derived from renewable resources, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional tin-coated steel. These metals typically incorporate organic compounds or biopolymers that enhance corrosion resistance and reduce environmental impact during production and disposal. Innovations in bio-based metal technology aim to improve sustainability while maintaining the durability and safety required for food packaging.
Tin: Properties and Food Safety
Tin offers excellent corrosion resistance and forms a protective oxide layer, making it ideal for food can linings. Its non-toxic nature and stability under various food acidity levels ensure food safety and prevent contamination. Certified food-grade tin coatings comply with stringent regulatory standards, safeguarding both product quality and consumer health.
Sustainability Comparison: Bio-Based Metal vs Tin
Bio-based metal alternatives for food cans offer a significant sustainability advantage over traditional tin due to their renewable sourcing and lower carbon footprint during production. Tin mining and refining involve high energy consumption and environmental degradation, whereas bio-based metals are derived from abundant, plant-based materials that reduce reliance on finite mineral resources. The recyclability of bio-based metals further enhances their environmental profile, promoting a circular economy and minimizing landfill waste compared to conventional tin cans.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Bio-based metal for food cans involves renewable materials such as biopolymers infused with metal particles, manufacturing through eco-friendly extrusion and lamination techniques that reduce carbon emissions. Tin cans rely on traditional tinplate production, requiring energy-intensive smelting and electroplating processes to coat steel sheets with tin for corrosion resistance. The bio-based method minimizes environmental impact by integrating sustainable resources and simpler processing steps, while tin manufacturing emphasizes durability and recyclability through established metallurgical practices.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Bio-based metals for food cans often present higher initial costs compared to traditional tin due to advanced extraction and processing techniques, but benefits in sustainability and biodegradability drive growing market interest. Tin remains cost-effective with well-established supply chains, yet fluctuating prices and regulatory pressures to adopt eco-friendly materials are shifting demand towards bio-based alternatives. Market trends indicate increasing investment in bio-based metal innovation, predicting gradual cost reductions and expanded adoption in the food packaging industry.
Food Preservation Performance
Bio-based metal coatings enhance food preservation by providing superior barrier properties against oxygen and moisture compared to traditional tin coatings, reducing the risk of oxidation and spoilage. These innovative materials exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, maintaining the can's integrity and preventing metal leaching into food. Research shows that bio-based coatings contribute to longer shelf life and better sensory quality of canned products, supporting safe and sustainable food packaging solutions.
Regulatory and Certification Requirements
Bio-based metals for food cans must comply with FDA and EFSA regulations ensuring material safety, non-toxicity, and food contact approval, similar to tin-based cans which have established compliance with these agencies. Certification requirements for bio-based metals increasingly demand sustainability verification through standardized labels like USDA BioPreferred or Cradle to Cradle, beyond traditional migration and corrosion tests required for tin coatings. Regulatory frameworks prioritize rigorous testing for chemical migration limits under EU Framework Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004, ensuring bio-based alternatives meet equivalent safety and quality standards as tin for food preservation.
Consumer Perception and Acceptance
Consumers increasingly favor bio-based metals for food cans due to their perceived environmental benefits and sustainability compared to traditional tin. Studies indicate that acceptance rises when bio-based materials are linked to reduced carbon footprints and recyclable properties, enhancing brand trust. However, clear labeling and education on safety and durability remain critical to boosting consumer confidence in bio-based alternatives over conventional tin packaging.
Future Prospects in Food Packaging Materials
Bio-based metals offer a sustainable alternative to traditional tin in food can manufacturing, reducing reliance on finite resources while maintaining corrosion resistance and safety standards. Innovations in bio-metal composites enhance biodegradability and lower carbon footprints, aligning with global sustainability targets in food packaging. The future of food packaging materials prioritizes eco-friendly bio-based metals to meet consumer demand for environmentally responsible products without compromising durability or food preservation quality.
Infographic: Bio-based metal vs Tin for Food Can
 azmater.com
azmater.com