Aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance, lightweight durability, and excellent barrier properties, making it ideal for long-term packaging applications. Tin provides effective protection against moisture and oxygen but lacks the strength and recyclability benefits of aluminum in modern packaging.
Table of Comparison
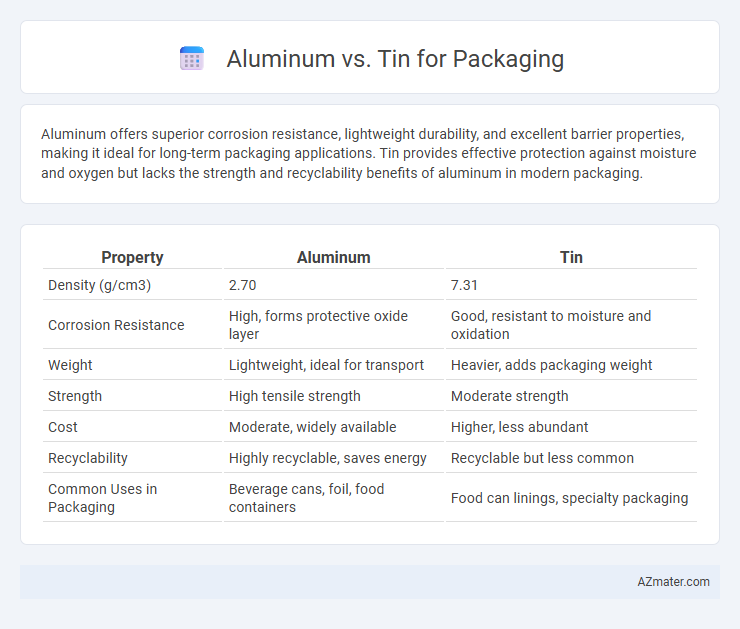
| Property | Aluminum | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.70 | 7.31 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, forms protective oxide layer | Good, resistant to moisture and oxidation |
| Weight | Lightweight, ideal for transport | Heavier, adds packaging weight |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate strength |
| Cost | Moderate, widely available | Higher, less abundant |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable, saves energy | Recyclable but less common |
| Common Uses in Packaging | Beverage cans, foil, food containers | Food can linings, specialty packaging |
Introduction: Aluminum vs Tin in Packaging
Aluminum and tin are widely used metals in packaging due to their unique properties that enhance product preservation and shelf life. Aluminum offers excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight durability, and superior barrier protection against moisture, air, and light, making it ideal for food and beverage cans. Tin, often used as a coating material on steel, provides corrosion resistance and prevents metal contamination, commonly applied in food cans to maintain product safety and flavor integrity.
Material Composition and Properties
Aluminum, composed primarily of aluminum metal with trace elements, offers excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight durability, and high malleability, making it ideal for packaging applications such as cans and foil. Tin, a soft, malleable metal often used as a coating for steel cans, provides corrosion resistance and non-toxic properties but lacks the strength and flexibility of aluminum. The choice between aluminum and tin in packaging depends on required durability, weight considerations, and resistance to environmental factors.
Weight and Durability Comparison
Aluminum packaging offers a significantly lighter weight compared to tin, reducing transportation costs and improving handling efficiency in supply chains. Durability-wise, aluminum provides excellent corrosion resistance and maintains structural integrity under various environmental conditions, outperforming tin in preventing contamination and extending shelf life. While tin is more prone to denting, aluminum's flexibility and strength make it a superior choice for lightweight, durable packaging solutions.
Barrier Protection: Moisture, Light, and Oxygen
Aluminum offers superior barrier protection against moisture, light, and oxygen, making it ideal for preserving product freshness and extending shelf life in packaging applications. Tin provides moderate protection but is more prone to corrosion and less effective at blocking light and oxygen compared to aluminum. Packaging materials utilizing aluminum foil significantly reduce oxygen permeability and light exposure, ensuring enhanced product stability in various conditions.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Aluminum packaging is highly favored for its exceptional recyclability, with a recycling rate exceeding 75%, which significantly reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to primary production. In contrast, tin packaging, often used as tinplate steel, is recyclable but involves more energy-intensive processes and lower recycling rates, contributing to a larger environmental footprint. Both materials benefit from closed-loop recycling systems, but aluminum's lightweight nature and infinite recyclability make it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Cost Efficiency in Production and Use
Aluminum packaging offers superior cost efficiency due to its lightweight nature, which reduces transportation expenses and material usage compared to heavier alternatives like tin. Tin, while providing excellent corrosion resistance, generally incurs higher production costs because of its raw material price and energy-intensive manufacturing process. The recyclability of aluminum further enhances cost savings by enabling lower energy consumption in production cycles, making it a more economically viable option for large-scale packaging applications.
Common Packaging Applications
Aluminum is widely used for beverage cans, food trays, and flexible packaging due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen. Tin-coated steel is commonly applied in food cans, especially for preserving acidic foods, offering durability and protection against rust. Both materials serve crucial roles in packaging, with aluminum favored for convenience and recyclability, while tin-coated steel provides structural strength and corrosion resistance for long-term storage.
Consumer Perception and Branding
Aluminum packaging is widely perceived as modern, durable, and environmentally sustainable, enhancing brand image through its lightweight and recyclable properties. Tin packaging, often associated with traditional and premium products, conveys a sense of quality and reliability but may be perceived as less eco-friendly compared to aluminum. Brands leveraging aluminum packaging benefit from positive consumer associations with innovation and sustainability, while tin packaging appeals to niche markets valuing classic aesthetics and robustness.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Aluminum offers superior food safety due to its non-toxic, corrosion-resistant properties and effective barrier against light, oxygen, and moisture, preventing food spoilage and contamination. Tin, often used as a protective coating for steel cans, provides excellent corrosion resistance but can pose risks if the coating deteriorates, potentially leading to metal leaching into food. Regulatory standards typically favor aluminum for direct food contact packaging due to its inertness and recyclability, ensuring higher food compatibility and consumer safety.
Future Trends in Metal Packaging
Aluminum and tin remain pivotal materials in metal packaging, with aluminum's lightweight, corrosion resistance, and recyclability driving its growing adoption in sustainable packaging solutions. Advances in nanotechnology and alloy development are enhancing aluminum's barrier properties, extending shelf life and reducing environmental impact. Tin-coated steel continues to be valuable for food safety, but emerging alternatives and coated aluminum substrates are shaping future trends focused on combining durability with eco-friendly attributes.
Infographic: Aluminum vs Tin for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com