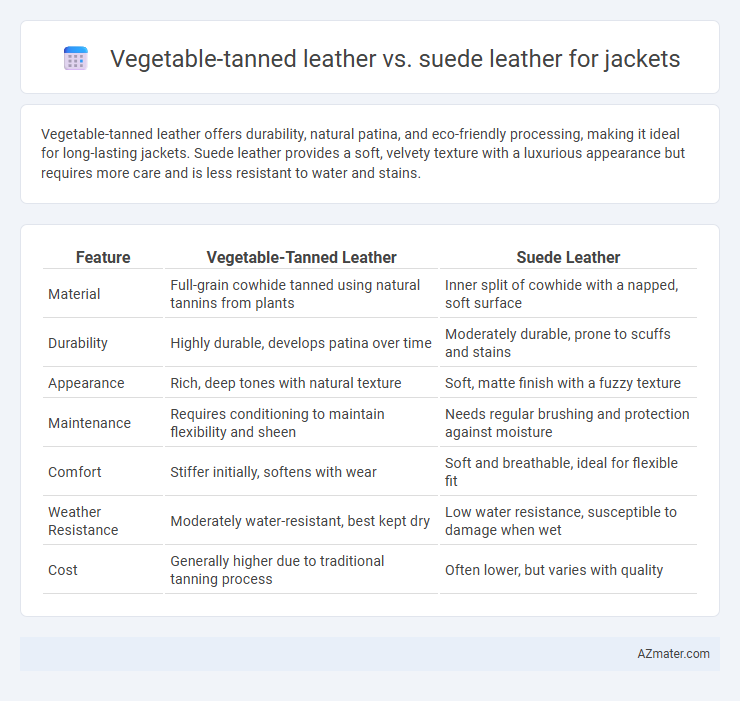
Vegetable-tanned leather offers durability, natural patina, and eco-friendly processing, making it ideal for long-lasting jackets. Suede leather provides a soft, velvety texture with a luxurious appearance but requires more care and is less resistant to water and stains.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Suede Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Full-grain cowhide tanned using natural tannins from plants | Inner split of cowhide with a napped, soft surface |
| Durability | Highly durable, develops patina over time | Moderately durable, prone to scuffs and stains |
| Appearance | Rich, deep tones with natural texture | Soft, matte finish with a fuzzy texture |
| Maintenance | Requires conditioning to maintain flexibility and sheen | Needs regular brushing and protection against moisture |
| Comfort | Stiffer initially, softens with wear | Soft and breathable, ideal for flexible fit |
| Weather Resistance | Moderately water-resistant, best kept dry | Low water resistance, susceptible to damage when wet |
| Cost | Generally higher due to traditional tanning process | Often lower, but varies with quality |
Introduction: Understanding Leather Types for Jackets
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins from tree bark and plants, offering durability, a rich patina, and eco-friendly qualities ideal for jackets. Suede leather, made from the underside of animal hides, provides a soft, velvety texture with a more delicate and matte finish, favored for its unique aesthetic in jacket designs. Both leather types differ significantly in maintenance, appearance, and wear resistance, influencing their suitability for various jacket styles and uses.
What is Vegetable-Tanned Leather?
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, resulting in a durable and eco-friendly material known for developing a rich patina over time. Unlike suede leather, which is created by sanding the inner surface of the hide to produce a soft, fuzzy texture, vegetable-tanned leather maintains a firm and smooth finish ideal for structured jackets. This tanning process enhances the leather's breathability and longevity, making vegetable-tanned leather jackets a premium choice for both style and sustainability.
What is Suede Leather?
Suede leather is a type of leather made from the underside of animal hides, primarily lamb, goat, or calf, known for its soft, napped finish and porous texture. Unlike vegetable-tanned leather, which undergoes a natural tanning process using tannins from plant materials, suede is typically chrome-tanned, resulting in a more flexible and lightweight material ideal for jackets. Suede leather requires careful maintenance to prevent staining and water damage, making it a stylish yet delicate choice for outerwear.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Vegetable-tanned leather for jackets offers a smooth, firm surface with a natural patina that deepens over time, highlighting its rich, earthy tones and classic look. Suede leather features a soft, napped texture with a matte finish that provides a casual, tactile appeal, often resulting in a lighter, more velvety appearance. The contrast between vegetable-tanned leather's polished, durable feel and suede's plush, delicate surface makes each material uniquely suited to different style preferences and jacket designs.
Durability: Vegetable-Tanned vs Suede
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability compared to suede leather for jackets due to its thicker, firmer texture and natural tanning process that enhances resistance to wear and tear. Suede, made from the underside of animal hides, is softer and more prone to scuffing, staining, and water damage, making it less durable in rugged conditions. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather ensures a longer-lasting jacket that maintains structural integrity over time.
Breathability and Comfort Factors
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior breathability due to its natural tanning process, allowing better moisture absorption and air circulation, which enhances comfort during prolonged wear. Suede leather, with its napped surface, provides a softer texture but tends to trap heat and moisture, potentially reducing breathability compared to vegetable-tanned leather. For jackets prioritizing long-term comfort and ventilation, vegetable-tanned leather is generally more advantageous.
Aging and Patina Development
Vegetable-tanned leather develops a rich, deep patina over time, showcasing natural color variations and enhanced texture that highlight its organic tanning process. Suede leather, while softer and more pliable, tends to age more subtly with a muted, matte finish, developing a slight nap wear rather than a distinct patina. For jackets, vegetable-tanned leather offers a dynamic and evolving aesthetic, whereas suede provides a consistently smooth appearance that ages with gentle softness.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Vegetable-tanned leather jackets require regular conditioning with natural oils to maintain flexibility and prevent drying or cracking. Suede leather jackets demand careful brushing with a suede brush and immediate treatment with a suede protector spray to avoid stains and water damage. Both materials benefit from storage in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to preserve their texture and color.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vegetable-tanned leather uses natural tannins derived from tree bark and plants, resulting in a biodegradable and less chemically-intensive process compared to chrome-tanned leather, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Suede, typically made from the underside of animal hides and often chrome-tanned, involves more chemical treatments that can lead to higher water pollution and longer degradation periods. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather jackets supports reduced toxic waste and a more eco-friendly production cycle, whereas suede jackets may have a larger environmental footprint due to intensive chemical use.
Which Leather is Better for Jackets?
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability and develops a rich patina over time, making it ideal for long-lasting jackets that improve with age. Suede leather, characterized by its soft, napped finish, provides a lightweight and stylish option but requires more careful maintenance due to its susceptibility to water and stains. For jackets that combine resilience and timeless appeal, vegetable-tanned leather generally outperforms suede in terms of longevity and weather resistance.
Infographic: Vegetable-tanned leather vs Suede leather for Jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com