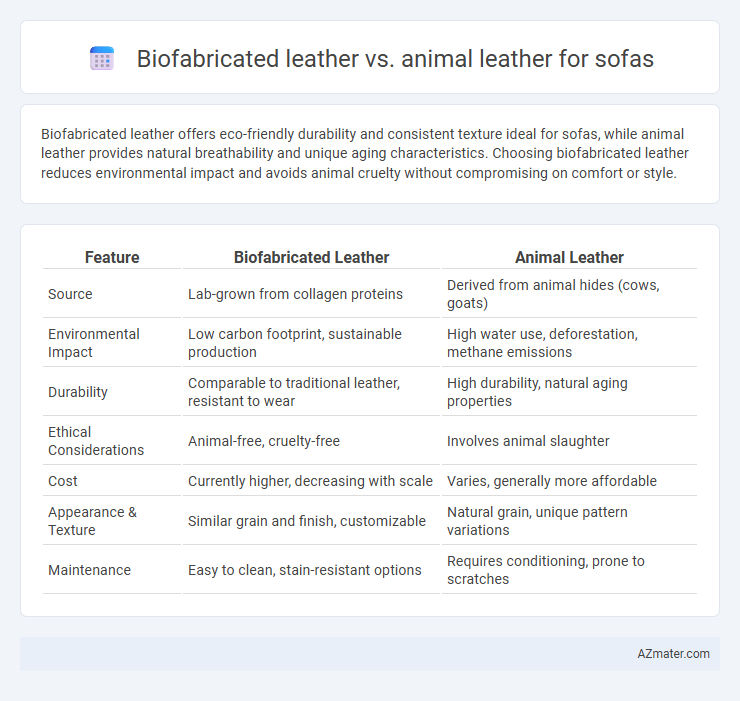
Biofabricated leather offers eco-friendly durability and consistent texture ideal for sofas, while animal leather provides natural breathability and unique aging characteristics. Choosing biofabricated leather reduces environmental impact and avoids animal cruelty without compromising on comfort or style.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Animal Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown from collagen proteins | Derived from animal hides (cows, goats) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable production | High water use, deforestation, methane emissions |
| Durability | Comparable to traditional leather, resistant to wear | High durability, natural aging properties |
| Ethical Considerations | Animal-free, cruelty-free | Involves animal slaughter |
| Cost | Currently higher, decreasing with scale | Varies, generally more affordable |
| Appearance & Texture | Similar grain and finish, customizable | Natural grain, unique pattern variations |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, stain-resistant options | Requires conditioning, prone to scratches |
Introduction to Biofabricated Leather and Animal Leather
Biofabricated leather, produced through microbial fermentation and cellular agriculture, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional animal leather by reducing environmental impact and ethical concerns. Animal leather, derived from the hides of cattle, is prized for its natural durability and classic aesthetic but involves significant resource use and animal welfare issues. Comparing these materials for sofas highlights biofabricated leather's innovation in sustainability against the long-established quality and texture of animal leather.
Production Processes: Biofabrication vs Traditional Tanning
Biofabricated leather for sofas is produced using cellular agriculture techniques, where animal cells are cultured in a lab environment to create a material that mimics traditional leather without animal slaughter or environmental damage. Traditional tanning of animal leather involves treating rawhide with chemicals such as chromium salts to preserve and strengthen the hide, a process that generates significant water pollution and waste. Biofabrication offers a controlled, scalable, and more sustainable production method that reduces reliance on livestock, minimizes harmful chemical use, and cuts down on the carbon footprint associated with conventional leather tanning.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biofabricated leather significantly reduces environmental impact compared to traditional animal leather by minimizing deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water usage associated with cattle farming. The production process of biofabricated leather consumes up to 90% less water and produces 80% fewer carbon emissions than conventional leather tanning. This sustainable alternative offers a cruelty-free solution that addresses ethical concerns while supporting eco-friendly furniture manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity: Which Leather Lasts Longer?
Biofabricated leather demonstrates significantly enhanced durability compared to traditional animal leather, resisting cracking and wear under prolonged use in sofa upholstery. Its engineered microscopic structure provides superior longevity by maintaining flexibility and strength over time, making it less prone to fading and deterioration. Animal leather, while naturally strong, requires regular maintenance to prevent drying and cracking, often resulting in a shorter lifespan for sofa applications.
Aesthetic Qualities: Look and Feel Differences
Biofabricated leather offers a uniform, customizable texture with consistent color options, enhancing modern sofa aesthetics through innovative design flexibility. Animal leather provides a natural, rich patina that develops unique character and depth over time, appealing to those who value traditional craftsmanship and authenticity. The tactile experience of biofabricated leather is often smoother and cooler, while animal leather delivers a warm, supple feel that improves with age.
Cost Analysis: Price Points and Affordability
Biofabricated leather for sofas currently commands higher price points than traditional animal leather due to advanced manufacturing technologies and limited production scale. While animal leather prices vary from $50 to $150 per square foot depending on quality, biofabricated leather ranges between $100 to $250 per square foot, reflecting its sustainable and cruelty-free benefits. Mass production advancements and technological innovation are expected to reduce biofabricated leather costs, gradually improving affordability in the luxury furniture market.
Ethical Considerations: Animal Welfare and Sustainability
Biofabricated leather offers a significant ethical advantage over animal leather by eliminating the need for animal farming and slaughter, thereby reducing animal suffering and promoting cruelty-free production. It also supports sustainability through lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced water consumption, and minimal land use compared to traditional leather derived from cattle farming. These factors contribute to a more environmentally friendly and socially responsible choice for sofa upholstery, aligning with growing consumer demand for ethical and sustainable home furnishings.
Maintenance and Care: Cleaning and Preservation
Biofabricated leather offers easier maintenance with resistance to stains, requiring only mild soap and water for cleaning compared to animal leather's need for specialized leather cleaners and conditioners. Animal leather demands regular conditioning to prevent cracking, while biofabricated options maintain flexibility without extensive preservation efforts. The durability against moisture and wear in biofabricated leather reduces long-term care costs, making it a practical choice for sofa upholstery.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Biofabricated leather is gaining traction among environmentally conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional animal leather for sofas. Market trends indicate a rising demand for cruelty-free, biodegradable materials that offer similar durability and aesthetic appeal to animal leather. Despite higher initial costs, biofabricated leather's reduced environmental impact and ethical benefits are driving preference shifts in premium and eco-friendly furniture segments.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Sofa Materials
Biofabricated leather presents a sustainable alternative to traditional animal leather, offering comparable durability and aesthetic appeal without the ethical concerns associated with animal farming. Advances in biotechnology enable the production of customizable textures and colors, promising a future where sofa materials can be tailored for enhanced comfort and environmental impact. As consumer demand shifts towards eco-friendly products, biofabricated leather is poised to revolutionize the sofa industry by reducing carbon footprints and resource consumption.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Animal leather for Sofa
 azmater.com
azmater.com