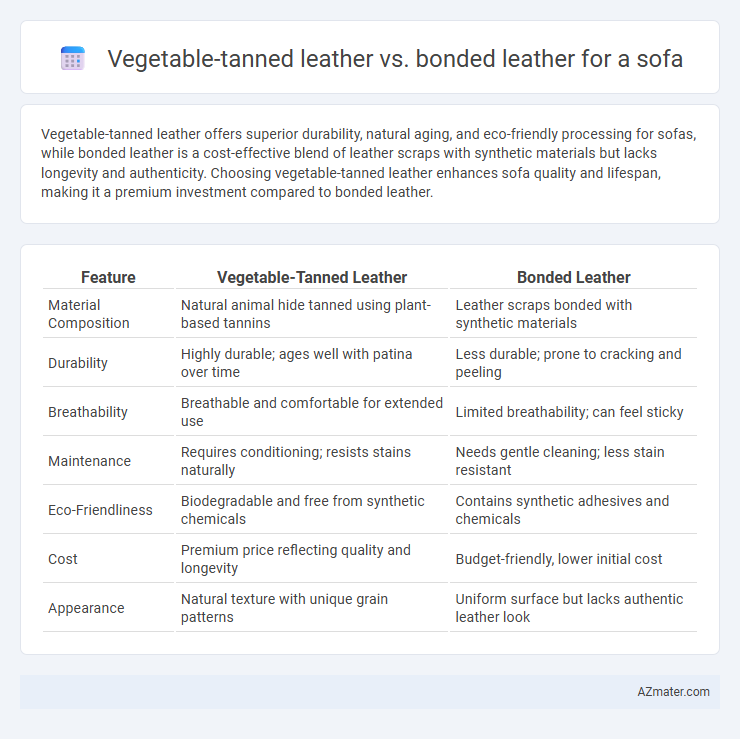
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability, natural aging, and eco-friendly processing for sofas, while bonded leather is a cost-effective blend of leather scraps with synthetic materials but lacks longevity and authenticity. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather enhances sofa quality and lifespan, making it a premium investment compared to bonded leather.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Bonded Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural animal hide tanned using plant-based tannins | Leather scraps bonded with synthetic materials |
| Durability | Highly durable; ages well with patina over time | Less durable; prone to cracking and peeling |
| Breathability | Breathable and comfortable for extended use | Limited breathability; can feel sticky |
| Maintenance | Requires conditioning; resists stains naturally | Needs gentle cleaning; less stain resistant |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable and free from synthetic chemicals | Contains synthetic adhesives and chemicals |
| Cost | Premium price reflecting quality and longevity | Budget-friendly, lower initial cost |
| Appearance | Natural texture with unique grain patterns | Uniform surface but lacks authentic leather look |
Introduction to Sofa Leather Types
Vegetable-tanned leather offers durability and a natural patina, making it ideal for high-quality sofas that age gracefully over time. Bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, provides an affordable alternative but is less durable and prone to peeling. Understanding these difference helps consumers choose the best sofa leather based on budget, longevity, and aesthetic preferences.
What is Vegetable-Tanned Leather?
Vegetable-tanned leather is derived from animal hides treated using natural tannins found in tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, resulting in a durable, breathable, and environmentally friendly material. Unlike bonded leather, which is made from leather scraps bonded together with adhesives and synthetic materials, vegetable-tanned leather offers superior strength, longevity, and develops a rich patina over time. This type of leather is prized in sofa manufacturing for its natural texture, aesthetic appeal, and sustainability, making it a premium choice for high-quality furniture.
What is Bonded Leather?
Bonded leather is a material made by shredding scrap leather fibers and bonding them together with a polyurethane or latex backing, creating a synthetic surface that mimics genuine leather. It offers a more affordable alternative to vegetable-tanned leather but lacks the durability, natural aging, and breathability of full-grain or top-grain leather. This engineered product is commonly used in sofas to provide a leather-like appearance at a lower cost, though it may peel and wear faster over time.
Durability: Vegetable-Tanned vs Bonded Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather provides superior durability for sofas due to its natural tanning process that preserves the hide's strength and flexibility, ensuring long-lasting wear and resistance to cracking. Bonded leather, composed of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, tends to wear out quickly, peels over time, and lacks the structural integrity of full hides. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather enhances sofa longevity and maintains aesthetic appeal through years of regular use.
Comfort and Feel Comparison
Vegetable-tanned leather offers a natural, breathable surface that softens and develops a rich patina over time, enhancing comfort and providing a luxurious feel for sofas. In contrast, bonded leather, made from shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane and other materials, tends to have a synthetic texture that feels less supple and can wear unevenly, impacting long-term comfort. The durability and aging properties of vegetable-tanned leather ensure a more comfortable and tactile experience compared to the often stiffer, less breathable bonded leather upholstery.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vegetable-tanned leather, made using natural tannins from plant materials, offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly option compared to bonded leather, which combines leather scraps with synthetic adhesives and chemicals that hinder decomposition. The production of vegetable-tanned leather typically results in lower toxic waste and reduced environmental pollution, promoting sustainability in leather manufacturing. In contrast, bonded leather's synthetic components contribute to microplastic pollution and limit recyclability, making it a less sustainable choice for sofa upholstery.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Vegetable-tanned leather requires regular conditioning with natural oils to maintain its durability and develop a rich patina over time, while avoiding excessive moisture and direct sunlight to prevent cracking. Bonded leather demands less intensive care but should be cleaned gently with a damp cloth and mild soap, avoiding harsh chemicals that can cause peeling or discoloration. Proper maintenance of vegetable-tanned leather extends its lifespan significantly compared to bonded leather, which typically has a shorter durability due to its composite material nature.
Cost Differences and Value for Money
Vegetable-tanned leather sofas typically cost significantly more than bonded leather due to the natural tanning process and durability, often ranging from $1,000 to $3,000 for quality pieces. Bonded leather sofas, made from scraps bonded with polyurethane, are usually priced between $300 and $800, offering a budget-friendly option but lower longevity and aging quality. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather provides better value for money over time due to its durability, natural patina development, and ease of maintenance compared to the less durable, synthetic surface of bonded leather.
Aesthetic Appeal and Aging Over Time
Vegetable-tanned leather showcases a rich, natural patina that deepens in color and texture, enhancing a sofa's aesthetic appeal with unique character over time. Bonded leather, made from shredded leather fibers bonded with polyurethane and latex, tends to wear evenly but lacks the authentic aging process, often peeling or cracking after prolonged use. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather ensures a luxurious, evolving finish, while bonded leather offers a more affordable, uniform look but with limited durability in aging.
Which Leather is Best for Your Sofa?
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability, natural aging, and eco-friendly processing, making it ideal for long-lasting, high-quality sofas. Bonded leather, composed of leftover leather fibers mixed with polyurethane, is more affordable but less durable and prone to peeling over time. For a sofa investment prioritizing longevity and authentic leather feel, vegetable-tanned leather is the best choice.
Infographic: Vegetable-tanned leather vs Bonded leather for Sofa
 azmater.com
azmater.com