Bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with adhesive, offers a cost-effective, durable jacket option with a uniform texture but less breathability compared to suede leather. Suede leather, produced from the underside of animal hide, provides a soft, supple feel and stylish matte finish ideal for lightweight jackets but requires more care to prevent stains and damage.
Table of Comparison
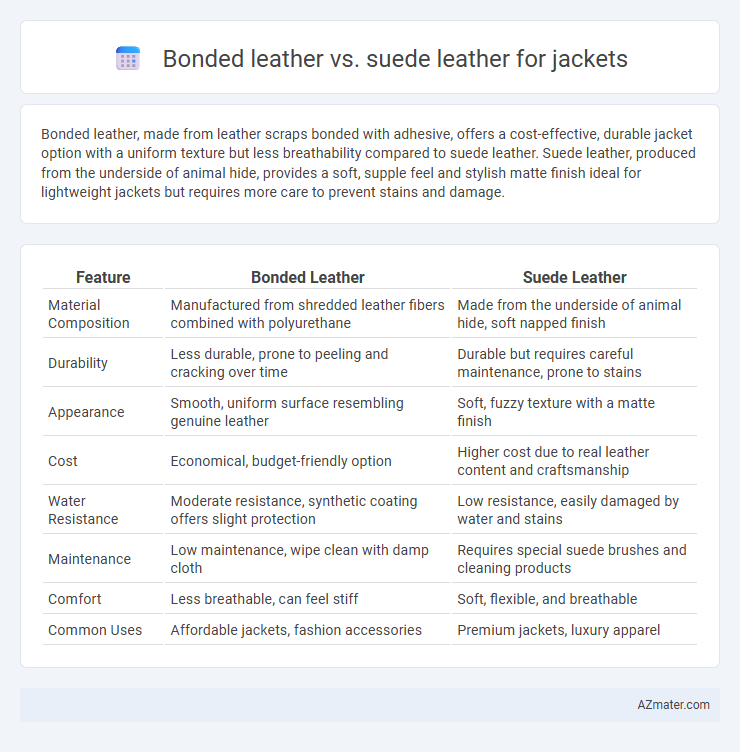
| Feature | Bonded Leather | Suede Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Manufactured from shredded leather fibers combined with polyurethane | Made from the underside of animal hide, soft napped finish |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to peeling and cracking over time | Durable but requires careful maintenance, prone to stains |
| Appearance | Smooth, uniform surface resembling genuine leather | Soft, fuzzy texture with a matte finish |
| Cost | Economical, budget-friendly option | Higher cost due to real leather content and craftsmanship |
| Water Resistance | Moderate resistance, synthetic coating offers slight protection | Low resistance, easily damaged by water and stains |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, wipe clean with damp cloth | Requires special suede brushes and cleaning products |
| Comfort | Less breathable, can feel stiff | Soft, flexible, and breathable |
| Common Uses | Affordable jackets, fashion accessories | Premium jackets, luxury apparel |
Introduction to Bonded and Suede Leather Jackets
Bonded leather jackets are crafted from shredded leather fibers combined with polyurethane, offering an affordable and eco-friendly alternative to genuine leather with a consistent texture and durability suitable for fashion wear. Suede leather jackets, made from the underside of animal hides, provide a soft, velvety texture with a luxurious feel, though they require careful maintenance due to their delicate surface prone to stains and water damage. Both materials present distinct aesthetic and functional qualities, making choice dependent on budget, style preference, and intended use.
What is Bonded Leather?
Bonded leather is a material made from shredded leather fibers combined with a polyurethane or latex backing, offering a cost-effective alternative to genuine leather for jackets. It provides a similar appearance and texture but lacks the durability and breathability of real leather or suede. Bonded leather jackets are typically more affordable and require careful maintenance to avoid cracking or peeling over time.
What is Suede Leather?
Suede leather is a type of leather with a napped finish, made from the underside of animal hides, primarily lamb, goat, or calfskin, offering a soft, velvety texture ideal for jackets. Unlike bonded leather, which is made by combining leather scraps with polyurethane and other adhesives, suede provides natural breathability and flexibility, enhancing comfort and durability. Suede's unique texture and appearance are prized for stylish, luxurious outerwear but require more careful maintenance to protect against moisture and stains.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Bonded leather jackets exhibit a smooth and uniform texture with a glossy finish, mimicking genuine leather but often lacking the natural grain and depth found in suede. Suede leather jackets are characterized by their soft, napped surface, offering a matte appearance and a plush, velvety feel that enhances tactile comfort and visual warmth. The appearance of bonded leather appears more polished and consistent, while suede provides a rugged yet refined texture, influencing overall jacket aesthetics significantly.
Durability and Longevity
Bonded leather jackets offer moderate durability due to their composite construction but tend to wear out and peel faster than genuine leather, making them less suitable for long-term use. Suede leather jackets, made from the underside of animal hide, provide a softer texture and higher breathability but require careful maintenance to prevent damage from moisture and abrasion. For longevity, high-quality suede leather outperforms bonded leather when properly cared for, as bonded leather's synthetic layers degrade more quickly over time.
Comfort and Wearability
Bonded leather jackets offer a smooth, consistent surface that provides moderate breathability but can feel less flexible compared to suede leather, which is known for its exceptional softness and pliability, enhancing comfort and ease of movement. Suede's natural texture allows for better air circulation, making it more comfortable for extended wear in varying temperatures, whereas bonded leather may cause discomfort during prolonged use due to limited breathability. When prioritizing wearability, suede leather jackets typically adapt better to body contours and maintain comfort through long-term wear, while bonded leather jackets might show stiffness and reduced comfort over time.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Bonded leather jackets require minimal maintenance but are less durable than suede, often needing gentle cleaning with a damp cloth and occasional conditioning to prevent cracking. Suede leather demands more careful upkeep, including regular brushing with a suede brush and the use of specialized suede cleaners to maintain its texture and prevent stains. Both materials benefit from water-resistant sprays, but suede is more susceptible to water damage and staining, necessitating more diligent care to preserve its appearance.
Price Differences
Bonded leather jackets typically cost less than suede leather jackets due to their manufacturing process, which involves blending leather scraps with polyurethane, making them more affordable but less durable. Suede leather jackets, made from the underside of animal hides, offer a softer texture and higher quality, reflected in their higher price point. Consumers willing to invest in longevity and premium feel often choose suede despite its increased cost, while bonded leather suits budget-conscious buyers seeking style with less financial commitment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bonded leather jackets are made from leather scraps mixed with synthetic materials, resulting in a lower environmental impact due to utilizing waste but involving polymers that reduce biodegradability. Suede leather, derived from animal hides with minimal chemical treatment, offers a more natural decomposition process but contributes higher resource consumption and animal farming emissions. Choosing between bonded leather and suede leather for jackets involves balancing waste reduction against biodegradability and resource intensity in sustainability considerations.
Which Leather is Best for Your Jacket?
Suede leather offers superior breathability, softness, and durability, making it ideal for high-quality jackets with a luxurious texture and long-lasting wear. Bonded leather, made by fusing leather scraps with polyurethane, is more affordable but less durable and prone to cracking over time, suitable for budget-friendly jackets with a leather-like appearance. Choosing the best leather depends on your preference for authentic texture and longevity (suede) versus cost-effectiveness and easy maintenance (bonded leather).
Infographic: Bonded leather vs Suede leather for Jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com