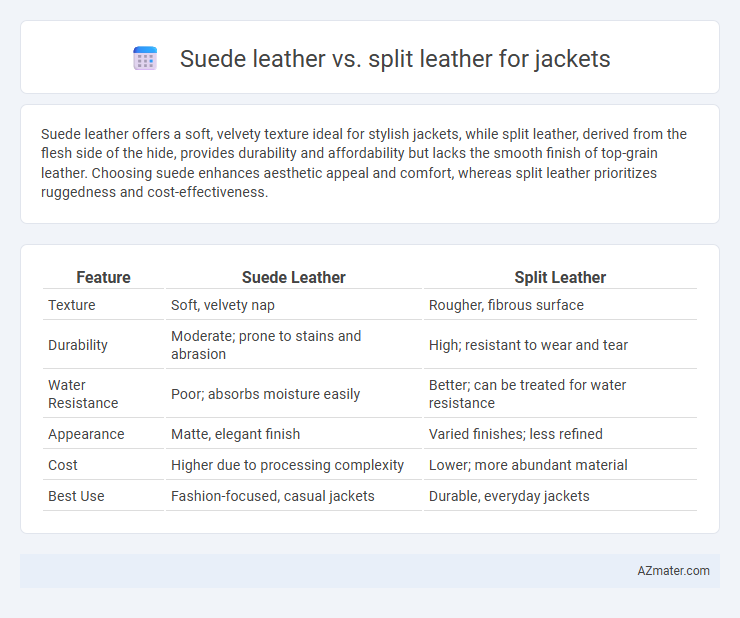
Suede leather offers a soft, velvety texture ideal for stylish jackets, while split leather, derived from the flesh side of the hide, provides durability and affordability but lacks the smooth finish of top-grain leather. Choosing suede enhances aesthetic appeal and comfort, whereas split leather prioritizes ruggedness and cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Suede Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Soft, velvety nap | Rougher, fibrous surface |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to stains and abrasion | High; resistant to wear and tear |
| Water Resistance | Poor; absorbs moisture easily | Better; can be treated for water resistance |
| Appearance | Matte, elegant finish | Varied finishes; less refined |
| Cost | Higher due to processing complexity | Lower; more abundant material |
| Best Use | Fashion-focused, casual jackets | Durable, everyday jackets |
Understanding Suede Leather: Key Characteristics
Suede leather, crafted from the underside of animal hides, offers a soft, napped finish with a velvety texture that distinguishes it from the rougher surface of split leather. This type of leather provides enhanced breathability and flexibility, making it ideal for jackets that prioritize comfort and style. While suede requires more care to prevent stains and water damage, its luxurious appearance and supple feel make it a preferred choice for premium outerwear.
What is Split Leather? Composition and Features
Split leather is produced by dividing a hide into layers, typically from the fibrous part beneath the top grain, resulting in a suede-like finish used for jackets. It consists of the inner layers of the hide, offering a softer texture but lower durability and breathability compared to top grain or full grain leathers. Split leather jackets provide an affordable option with a distinctive velvety appearance but may require additional treatment for water resistance and longevity.
Suede Leather vs Split Leather: Texture Comparison
Suede leather features a soft, velvety texture achieved by buffing the underside of full-grain leather, offering a luxurious and smooth finish ideal for jackets. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, has a rougher and more fibrous surface, often treated or embossed to mimic grain leather but lacking the natural softness of suede. The tactile difference highlights suede leather's premium feel against the more rugged and less refined texture of split leather jackets.
Durability: Which Leather Lasts Longer?
Suede leather, made from the inner layer of animal hide, is softer but more prone to wear and damage compared to split leather, which is derived from the fibrous part beneath the top grain and treated for enhanced toughness. Split leather jackets benefit from thicker, denser fibers, making them more resistant to scratches, moisture, and abrasion over time. When prioritizing durability, split leather typically outlasts suede due to its robust composition and better protection against environmental factors.
Comfort and Wearability: A Side-by-Side Review
Suede leather offers superior softness and breathability compared to split leather, enhancing overall comfort when worn as a jacket. Split leather, derived from the lower layer of the hide, is generally stiffer and less flexible, which can impact long-term wearability and ease of movement. Suede jackets often provide a more luxurious feel and better moisture absorption, making them ideal for moderate climates and stylish, comfortable wear.
Stain Resistance and Maintenance Needs
Suede leather, with its soft, napped finish, is more prone to stains and requires frequent cleaning and protective treatments to maintain its appearance. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, typically features a rougher texture and tends to resist stains better due to its denser surface, making it easier to clean and maintain. Regular conditioning and water repellents are essential for both types to enhance durability and preserve their look over time.
Breathability and Climate Suitability
Suede leather, made from the underside of the animal hide, offers superior breathability compared to split leather due to its softer, more porous texture, making it ideal for moderate climates where ventilation is key. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, is typically denser and less breathable, providing enhanced durability and water resistance suited for cooler, damp weather conditions. Breathability in suede enhances comfort in warmer environments, while split leather's robustness favors protection in harsher climates.
Style and Aesthetic Differences
Suede leather features a soft, napped finish that creates a luxurious, matte texture ideal for casual and sophisticated jackets, enhancing a stylish, vintage-inspired look. Split leather, derived from the fibrous part of the hide separated from the top-grain layer, has a rougher texture and less durability, often finished with a synthetic coating that gives a uniform but less refined appearance. The distinct tactile qualities and surface finishes of suede and split leather significantly influence the jacket's overall aesthetic, with suede offering a premium, elegant appeal compared to the rugged, budget-friendly style of split leather.
Pricing: Value for Money
Suede leather jackets generally command higher prices due to their soft texture and luxurious appearance, offering better durability and a premium feel compared to split leather. Split leather jackets are more affordable but tend to lack the resilience and refined finish, making them less cost-effective over time. Choosing suede leather provides greater value for money for those seeking longevity and style in their jacket investment.
Which Jacket Should You Choose?
Suede leather jackets offer a soft, velvety texture and elegant appearance, making them ideal for stylish, casual wear, while split leather jackets provide durability and a more rugged look suitable for everyday use and rougher conditions. Suede requires more care and is less resistant to water and stains compared to split leather, which is made from the fibrous underside of the hide and often treated for enhanced toughness. Choose a suede jacket for fashion-forward outfits and mild weather, or a split leather jacket for long-lasting wear and versatility in various environments.
Infographic: Suede leather vs Split leather for Jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com