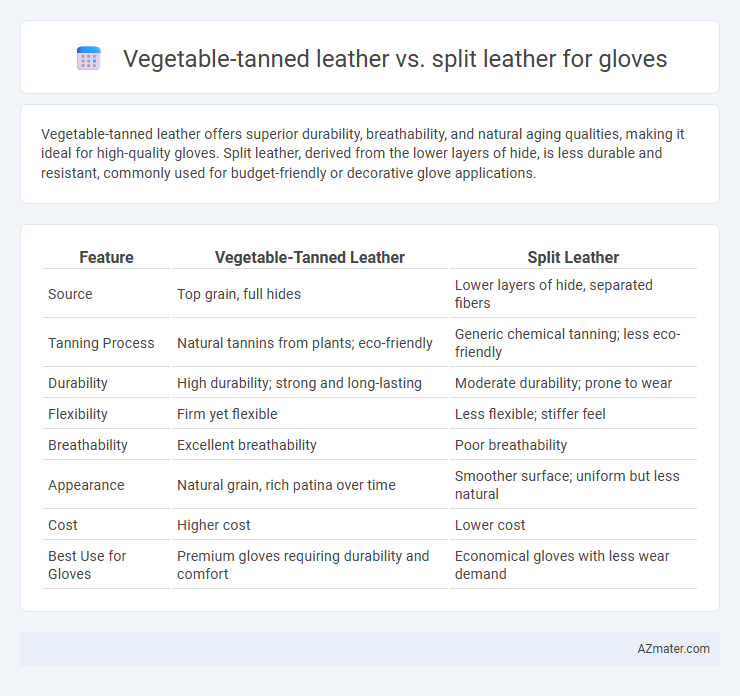
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability, breathability, and natural aging qualities, making it ideal for high-quality gloves. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of hide, is less durable and resistant, commonly used for budget-friendly or decorative glove applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Top grain, full hides | Lower layers of hide, separated fibers |
| Tanning Process | Natural tannins from plants; eco-friendly | Generic chemical tanning; less eco-friendly |
| Durability | High durability; strong and long-lasting | Moderate durability; prone to wear |
| Flexibility | Firm yet flexible | Less flexible; stiffer feel |
| Breathability | Excellent breathability | Poor breathability |
| Appearance | Natural grain, rich patina over time | Smoother surface; uniform but less natural |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Best Use for Gloves | Premium gloves requiring durability and comfort | Economical gloves with less wear demand |
Introduction: Understanding Glove Leather Types
Vegetable-tanned leather, known for its natural tanning process using plant-based tannins, offers durability, rich patina development, and superior breathability ideal for gloves requiring flexibility and comfort. Split leather, created by splitting the hide's fibrous lower layers, is often less durable and less breathable but more affordable, making it suitable for budget-conscious glove designs with moderate wear. Understanding these leather types helps in selecting gloves that balance quality, longevity, and cost based on specific use and performance needs.
What is Vegetable-Tanned Leather?
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, resulting in a durable and environmentally friendly leather ideal for gloves that require breathability and stiffness. This tanning process preserves the leather's natural hide structure, enhancing its strength and ability to mold comfortably over time compared to split leather, which is made from the fibrous lower layer of the hide and tends to be less durable and more prone to wear. Vegetable-tanned gloves offer superior longevity, better resistance to moisture and heat, and develop a unique patina, making them a premium choice for quality leather gloves.
What is Split Leather?
Split leather is the lower layer of a hide separated from the top grain during the leather splitting process, often used in glove making for its affordability and flexibility. Unlike vegetable-tanned leather, which features the full grain preserved and tanned with natural tannins for durability and breathability, split leather is typically less durable and more prone to wear. Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior protection and aging, while split leather is favored for cost-effective, lightweight glove applications.
Key Differences: Vegetable-Tanned vs Split Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins from plant sources, resulting in a durable, flexible, and breathable material ideal for high-quality gloves with excellent aging properties. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of a hide and often coated or bonded, tends to be less durable and less breathable, making it a more affordable but lower-quality option for gloves. Key differences include the tanning process, durability, breathability, and overall glove performance, with vegetable-tanned leather offering superior comfort and longevity compared to split leather.
Durability Comparison for Gloves
Vegetable-tanned leather exhibits superior durability for gloves due to its natural tanning process that enhances toughness and resistance to wear and tear over time. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, tends to be less durable as it lacks the dense grain structure of the top layer, making it more prone to stretching and damage. For gloves subjected to heavy use, vegetable-tanned leather ensures longer-lasting protection and maintains structural integrity better than split leather.
Comfort and Flexibility in Use
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior comfort and flexibility for gloves due to its natural tanning process, which preserves the leather's softness and breathability, allowing it to mold comfortably to the hand over time. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, tends to be stiffer and less flexible, often requiring additional treatments to enhance comfort but typically lacking the same durability and moldability as vegetable-tanned. Gloves made from vegetable-tanned leather provide enhanced dexterity and reduced break-in time, making them ideal for prolonged and detailed use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Vegetable-tanned leather for gloves is more environmentally sustainable due to its use of natural tannins from plant sources, reducing reliance on harmful chemicals and minimizing toxic waste compared to chrome-tanned split leather. Split leather, often derived from lower-quality layers of the hide, undergoes extensive chemical treatments that contribute to higher pollution and energy consumption during processing. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather supports eco-friendly practices by promoting biodegradability and reducing the carbon footprint associated with glove manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Which Leather is More Affordable?
Vegetable-tanned leather generally costs more than split leather due to its natural tanning process, higher quality, and durability, making it a pricier option for glove manufacturing. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of a hide, is more affordable but tends to sacrifice strength and longevity compared to vegetable-tanned leather. Cost efficiency in glove production often leans toward split leather when budget constraints are critical, despite the trade-off in performance and aesthetic appeal.
Best Applications for Each Leather Type in Gloves
Vegetable-tanned leather excels in glove applications requiring durability, rigidity, and natural breathability, making it ideal for heavy-duty work gloves and outdoor gloves used in gardening, farming, or construction. Split leather, derived from the fibrous part of the hide, offers greater flexibility and softness, making it a preferred choice for gloves demanding dexterity and comfort, such as driving gloves and casual wear gloves. The best use of vegetable-tanned leather focuses on protection and longevity, while split leather prioritizes ease of movement and lightweight wearability.
Choosing the Right Leather for Your Glove Needs
Vegetable-tanned leather offers durability and natural breathability, making it ideal for high-quality gloves requiring long-lasting comfort and environmental sustainability. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, is more affordable but less durable and less resistant to moisture, suitable for budget-friendly gloves or casual use. Selecting the right leather depends on balancing durability, flexibility, and cost relative to the glove's intended use, such as heavy-duty work or light protective wear.
Infographic: Vegetable-tanned leather vs Split leather for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com