Split leather offers durability and a natural texture ideal for high-quality upholstery, while faux leather provides a cost-effective, animal-friendly alternative with easier maintenance and consistent color. Choosing between split leather and faux leather depends on budget, aesthetic preference, and intended use of the upholstered furniture.
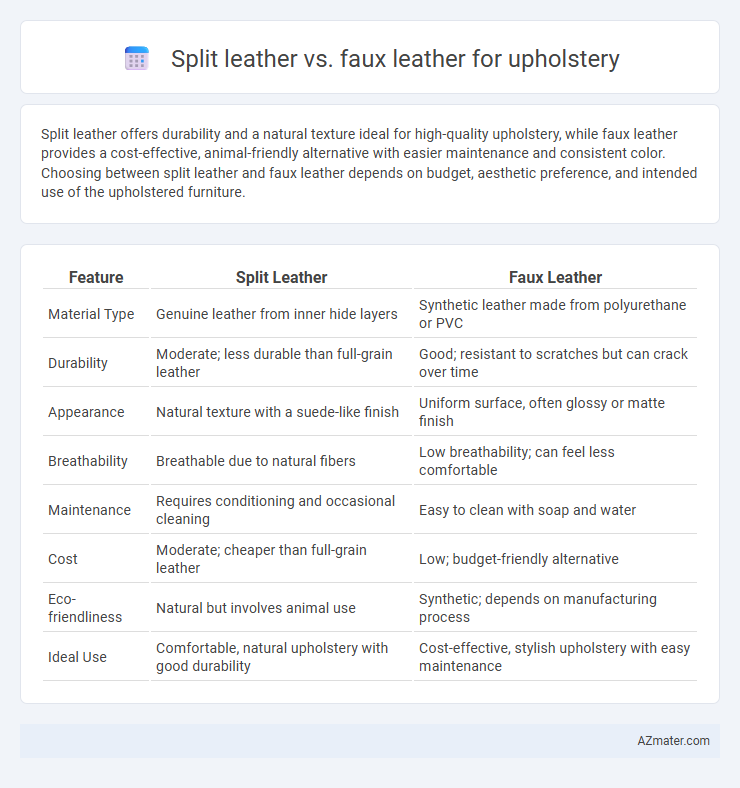
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Split Leather | Faux Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Genuine leather from inner hide layers | Synthetic leather made from polyurethane or PVC |
| Durability | Moderate; less durable than full-grain leather | Good; resistant to scratches but can crack over time |
| Appearance | Natural texture with a suede-like finish | Uniform surface, often glossy or matte finish |
| Breathability | Breathable due to natural fibers | Low breathability; can feel less comfortable |
| Maintenance | Requires conditioning and occasional cleaning | Easy to clean with soap and water |
| Cost | Moderate; cheaper than full-grain leather | Low; budget-friendly alternative |
| Eco-friendliness | Natural but involves animal use | Synthetic; depends on manufacturing process |
| Ideal Use | Comfortable, natural upholstery with good durability | Cost-effective, stylish upholstery with easy maintenance |
Understanding Split Leather: Composition and Properties
Split leather, derived from the fibrous lower layers of animal hides after separating the top grain, features a suede-like texture and porous surface that allows for enhanced breathability and absorption. Its composition comprises fibrous collagen bundles, which provide durability but less resistance to wear compared to top grain leather. Commonly used in upholstery where cost-effectiveness and texture variety are prioritized, split leather responds well to dyes, yet may require protective coatings to improve stain resistance and longevity.
Faux Leather Explained: Types and Manufacturing
Faux leather, also known as synthetic leather, is produced using polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) coatings on a fabric base such as polyester, offering a durable and cost-effective alternative to natural leather. PU leather is breathable and more flexible, while PVC leather tends to be more water-resistant but less breathable, making each type suitable for different upholstery applications. Manufacturing involves layering and embossing techniques that replicate the grain and texture of genuine leather, ensuring a consistent appearance and enhanced resistance to stains and wear.
Appearance and Texture: Split Leather vs Faux Leather
Split leather features a natural grain with a slightly rough texture, offering a more authentic and luxurious look compared to faux leather. Faux leather typically has a uniform appearance and smoother texture, created from synthetic materials designed to mimic genuine leather. The unique inconsistencies in split leather's surface provide a tactile depth and visual richness that faux leather often lacks.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Split leather offers superior durability and longevity for upholstery due to its robust fibrous structure derived from the lower layer of animal hide, providing enhanced resistance to wear and tear. Faux leather, typically made from polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride, tends to degrade faster with prolonged use and exposure to sunlight, making it less durable over time. High-quality split leather can last decades with proper care, whereas faux leather often requires replacement within a few years under heavy usage conditions.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Split leather requires regular conditioning to prevent drying and cracking, and it should be cleaned with a damp cloth or specialized leather cleaner to maintain its natural texture. Faux leather is more resistant to stains and easier to clean, often only needing a wipe with soapy water and no conditioning. Both materials benefit from prompt spill cleanup, but faux leather generally offers lower maintenance and greater durability against moisture and everyday wear.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Split leather, derived from the fibrous lower layer of animal hide, involves significant resource-intensive processes and chemical treatments, leading to a higher environmental footprint compared to synthetic alternatives. Faux leather, often made from polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride, offers greater sustainability through its lower water usage and elimination of animal farming, but its production relies on fossil fuels and generates non-biodegradable waste. Choosing eco-friendly upholstery requires balancing the durability and biodegradability of split leather against the recyclable potential and chemical concerns associated with faux leather manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Which is More Budget-Friendly?
Split leather, derived from the lower layers of animal hide, generally costs less than full-grain leather but remains pricier than faux leather due to its durability and natural texture. Faux leather, made from synthetic materials like polyurethane, offers a highly budget-friendly option with lower initial costs and minimal maintenance expenses. For upholstery, faux leather provides a more economical choice without sacrificing aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for cost-conscious projects.
Comfort and Breathability in Upholstery Use
Split leather offers superior comfort and breathability in upholstery due to its natural fiber structure, allowing better air circulation and moisture absorption compared to faux leather. Faux leather, made from synthetic materials like polyurethane, tends to trap heat and moisture, reducing comfort during prolonged use. Choosing split leather enhances seating comfort and durability in environments where breathability is essential.
Best Applications: Where Each Material Excels
Split leather excels in upholstery for furniture and car interiors due to its natural durability, breathability, and authentic texture, making it ideal for high-use environments where longevity is crucial. Faux leather is best suited for decorative upholstery, office chairs, and areas requiring easy maintenance and resistance to stains or moisture, offering a cost-effective alternative with a wide range of finishes. Commercial spaces and budget-conscious projects often benefit from faux leather's versatility, while premium residential or automotive applications favor split leather for its luxurious feel and aging quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Upholstery Project
Split leather offers superior durability, breathability, and a natural patina that enhances with age, making it ideal for high-traffic upholstery projects requiring long-lasting quality. Faux leather is more affordable, water-resistant, and available in a wider range of colors and textures, suited for budget-conscious designs or pet-friendly furniture. Evaluating factors such as maintenance, budget, environmental impact, and aesthetic preferences will help ensure the right choice for your specific upholstery project needs.
Infographic: Split leather vs Faux leather for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com