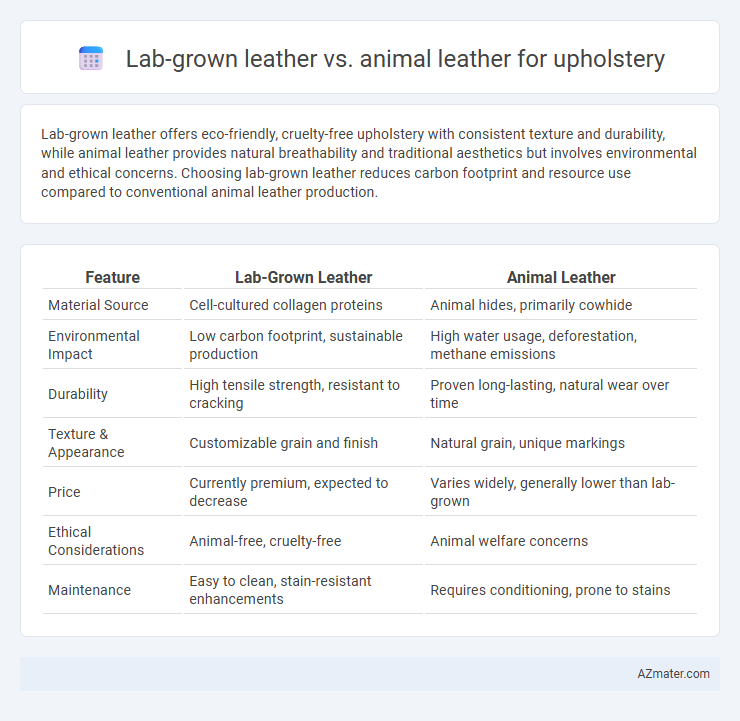
Lab-grown leather offers eco-friendly, cruelty-free upholstery with consistent texture and durability, while animal leather provides natural breathability and traditional aesthetics but involves environmental and ethical concerns. Choosing lab-grown leather reduces carbon footprint and resource use compared to conventional animal leather production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lab-Grown Leather | Animal Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Cell-cultured collagen proteins | Animal hides, primarily cowhide |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable production | High water usage, deforestation, methane emissions |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to cracking | Proven long-lasting, natural wear over time |
| Texture & Appearance | Customizable grain and finish | Natural grain, unique markings |
| Price | Currently premium, expected to decrease | Varies widely, generally lower than lab-grown |
| Ethical Considerations | Animal-free, cruelty-free | Animal welfare concerns |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, stain-resistant enhancements | Requires conditioning, prone to stains |
Introduction to Lab-Grown Leather and Animal Leather
Lab-grown leather, produced through biofabrication using collagen proteins, offers a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional animal leather sourced from cattle hides. This innovative material replicates the texture, durability, and flexibility of animal leather while significantly reducing environmental impacts such as deforestation, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions. Upholstery applications benefit from lab-grown leather's consistent quality and potential for customization, contrasting with the variable characteristics and ethical concerns associated with animal-derived leather.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Lab-grown leather for upholstery involves cultivating animal cells in controlled bioreactors, significantly reducing resource consumption and waste compared to traditional tanning processes used for animal leather. Animal leather manufacturing requires raising livestock, followed by extensive chemical treatments and drying stages to transform hides into durable upholstery material. The lab-grown method offers a more sustainable and consistent production cycle with less environmental impact, while animal leather production remains resource-intensive and reliant on large-scale agricultural inputs.
Material Performance and Durability
Lab-grown leather for upholstery offers consistent material performance with enhanced resistance to wear, moisture, and fading compared to traditional animal leather. Its engineered fibers provide superior durability and uniform thickness, reducing cracking and peeling over time. Animal leather, while naturally strong and breathable, tends to vary in quality and requires regular maintenance to preserve its longevity and aesthetic appeal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lab-grown leather drastically reduces the environmental footprint compared to traditional animal leather by minimizing land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, making it a more sustainable choice for upholstery. Unlike animal leather, which involves livestock farming that contributes to deforestation and methane emissions, lab-grown leather is produced through biofabrication processes that utilize fewer natural resources and generate less pollution. This emerging material offers a scalable, eco-friendly alternative that aligns with sustainable furniture manufacturing and supports circular economy principles.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Lab-grown leather for upholstery currently incurs higher production costs compared to traditional animal leather due to advanced biotechnological processes and limited large-scale manufacturing. Animal leather remains more economically accessible with well-established supply chains and mass production, keeping its market availability widespread and consistent. Market trends indicate increasing interest and investment in lab-grown leather, but it remains a niche product with limited commercial accessibility compared to the mainstream use of animal leather in upholstery.
Aesthetic and Textural Differences
Lab-grown leather for upholstery offers a uniform texture and consistent finish, often mimicking high-quality animal leather with customizable grain patterns and color options. Animal leather provides natural variations in texture and patina that develop over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal and uniqueness. The tactile feel of lab-grown leather is smoother and more controlled, while animal leather conveys authenticity with its irregularities and natural softness.
Health and Allergen Considerations
Lab-grown leather reduces exposure to harmful chemicals and allergens often found in animal leather, such as chromium and formaldehyde used in traditional tanning processes. It offers a hypoallergenic alternative, minimizing risks of skin irritation and respiratory issues for sensitive individuals. This innovation supports healthier indoor environments by limiting allergen accumulation typically associated with animal-derived upholstery materials.
Ethical Implications and Animal Welfare
Lab-grown leather offers significant ethical advantages over traditional animal leather by eliminating the need for animal slaughter, thus promoting animal welfare and reducing cruelty in upholstery production. This innovative material aligns with growing consumer demand for sustainable and humane products, minimizing the environmental footprint associated with livestock farming. Choosing lab-grown leather supports ethical manufacturing practices while maintaining the durability and aesthetic qualities valued in upholstery applications.
Consumer Trends and Industry Adoption
Lab-grown leather is rapidly gaining traction in upholstery due to rising consumer demand for sustainable and cruelty-free materials, with market studies indicating a projected CAGR of over 20% in bio-fabricated leather adoption by 2028. Major furniture manufacturers, including IKEA and Natuzzi, are integrating lab-grown leather samples into their product lines, leveraging its lower environmental footprint and consistent quality compared to traditional animal leather. Industry reports highlight a shift toward circular economy principles, driving broader acceptance of lab-grown leather as a premium, eco-conscious alternative in luxury and mass-market upholstery segments.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Upholstery
Lab-grown leather offers sustainable alternatives to traditional animal leather by utilizing biotechnology and reducing environmental impact in upholstery applications. Innovations such as bio-fabrication techniques and plant-based composites enhance durability and aesthetic appeal, meeting modern consumer demands. The future of upholstery heavily leans towards lab-grown leather integration due to its ethical advantages, scalability, and potential for customization in texture and color.
Infographic: Lab-grown leather vs Animal leather for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com