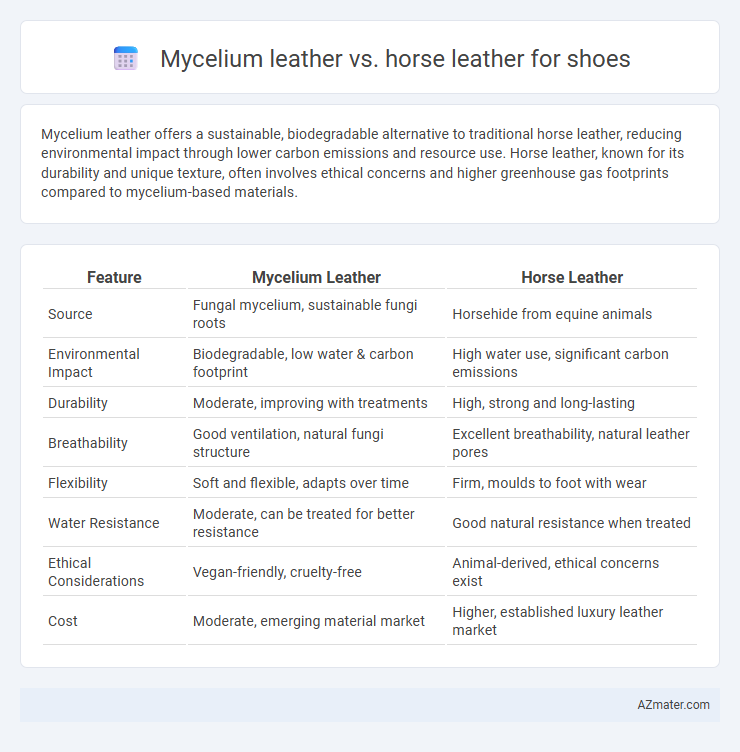
Mycelium leather offers a sustainable, biodegradable alternative to traditional horse leather, reducing environmental impact through lower carbon emissions and resource use. Horse leather, known for its durability and unique texture, often involves ethical concerns and higher greenhouse gas footprints compared to mycelium-based materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mycelium Leather | Horse Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fungal mycelium, sustainable fungi roots | Horsehide from equine animals |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low water & carbon footprint | High water use, significant carbon emissions |
| Durability | Moderate, improving with treatments | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Breathability | Good ventilation, natural fungi structure | Excellent breathability, natural leather pores |
| Flexibility | Soft and flexible, adapts over time | Firm, moulds to foot with wear |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can be treated for better resistance | Good natural resistance when treated |
| Ethical Considerations | Vegan-friendly, cruelty-free | Animal-derived, ethical concerns exist |
| Cost | Moderate, emerging material market | Higher, established luxury leather market |
Overview: Mycelium Leather vs Horse Leather
Mycelium leather, derived from mushroom roots, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional horse leather, which originates from animal hides and requires intensive animal farming. Mycelium leather provides comparable durability and flexibility while significantly reducing environmental impact, including lower carbon emissions and water usage. Horse leather remains favored for its natural texture and longevity, but mycelium leather is gaining traction in eco-conscious footwear markets due to its innovative production methods and cruelty-free attributes.
Material Origins and Production Processes
Mycelium leather, derived from the root structure of fungi, offers an innovative, sustainable alternative to traditional horse leather, which originates from the hides of horses. The production of mycelium leather involves cultivating fungal mycelium under controlled conditions to form a durable, biodegradable material, whereas horse leather is produced through tanning processes that treat horsehide to enhance durability and water resistance. Mycelium leather reduces reliance on animal agriculture and chemical tanning, promoting eco-friendly manufacturing with lower environmental impact compared to the resource-intensive and pollutant-heavy production of horse leather.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Mycelium leather, derived from fungal mycelium, offers a significantly lower environmental footprint than traditional horse leather by requiring less water, land, and energy during production. Horse leather involves high greenhouse gas emissions and chemical-intensive tanning processes, contributing to soil and water pollution. The biodegradability and renewable sourcing of mycelium leather make it a more sustainable alternative for eco-friendly shoe manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity
Mycelium leather offers impressive durability due to its fibrous cellular structure, which resists wear and tear while maintaining flexibility, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional horse leather. Horse leather is renowned for its toughness and longevity, often lasting several years with proper care due to its dense grain and natural oils that enhance resilience. Both materials provide sturdy options for shoes, but mycelium leather's rapid renewability and resistance to environmental degradation give it an edge in long-term sustainability without compromising durability.
Comfort and Breathability in Footwear
Mycelium leather offers superior breathability compared to traditional horse leather, allowing better air circulation and moisture management within footwear. The natural fibrous structure of mycelium contributes to enhanced comfort by reducing heat buildup and preventing foot odor. Horse leather provides durability but is less breathable, often resulting in a warmer, less ventilated shoe interior.
Visual Aesthetics and Customization
Mycelium leather offers a highly customizable surface that can be dyed in a wide range of colors and textured to mimic various patterns, providing innovative visual aesthetics for shoes. Horse leather boasts a natural grain and rich patina that develops over time, giving footwear a classic, luxurious appearance with unique character. While horse leather is prized for its durability and timeless look, mycelium leather allows designers greater flexibility in creating vibrant, eco-friendly, and fashion-forward shoe designs.
Ethical and Cruelty-Free Considerations
Mycelium leather offers a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional horse leather by using mushroom roots, eliminating the need for animal slaughter and reducing environmental impact. Horse leather production often involves ethical concerns related to animal welfare, including inhumane treatment and the use of by-products from the equine industry. Choosing mycelium leather for shoes supports vegan fashion trends and promotes eco-friendly practices with lower carbon footprints and resource consumption.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Mycelium leather requires minimal maintenance due to its natural resistance to water and stains, making it ideal for shoes with low upkeep demands. Horse leather, while durable and long-lasting, needs regular conditioning and cleaning to prevent drying and cracking, especially in humid or harsh conditions. Both materials benefit from avoiding prolonged exposure to moisture and direct sunlight to extend shoe lifespan.
Cost and Market Availability
Mycelium leather offers a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to traditional horse leather, as its production requires fewer resources and less environmental impact. While horse leather is widely available due to established supply chains and longstanding market presence, mycelium leather is still emerging, with limited but rapidly growing availability in niche and eco-conscious markets. Consumers seeking affordable, eco-friendly options may find mycelium leather increasingly accessible, although horse leather remains more prevalent in mainstream shoe manufacturing.
Future Trends in Sustainable Shoe Materials
Mycelium leather offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to traditional horse leather, aligning with growing consumer demand for sustainable and cruelty-free shoe materials. Innovations in mycelium cultivation accelerate production scalability while enhancing material durability and breathability, positioning it as a key player in eco-friendly footwear. As the fashion industry moves toward circular economy models, mycelium leather's lower carbon footprint and reduced resource consumption make it a promising future trend for sustainable shoe manufacturing.
Infographic: Mycelium leather vs Horse leather for Shoe
 azmater.com
azmater.com