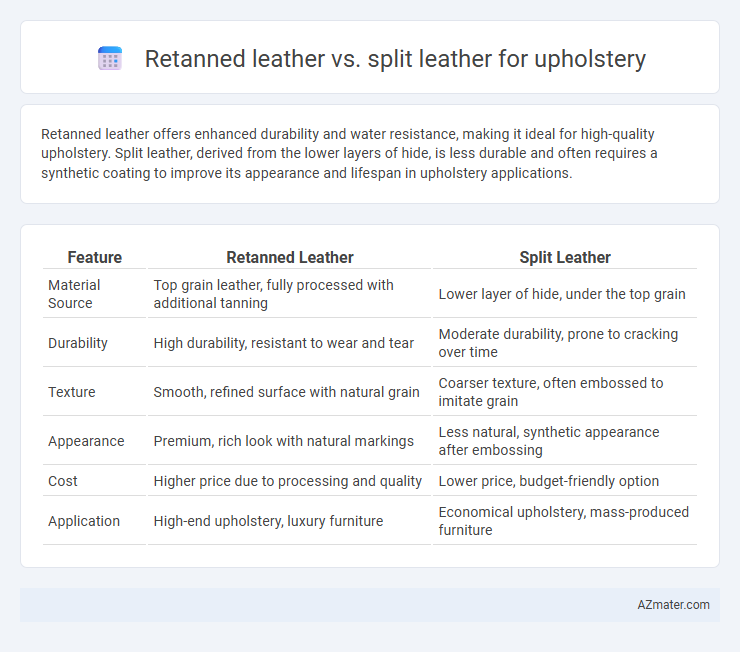
Retanned leather offers enhanced durability and water resistance, making it ideal for high-quality upholstery. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of hide, is less durable and often requires a synthetic coating to improve its appearance and lifespan in upholstery applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Retanned Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Top grain leather, fully processed with additional tanning | Lower layer of hide, under the top grain |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to wear and tear | Moderate durability, prone to cracking over time |
| Texture | Smooth, refined surface with natural grain | Coarser texture, often embossed to imitate grain |
| Appearance | Premium, rich look with natural markings | Less natural, synthetic appearance after embossing |
| Cost | Higher price due to processing and quality | Lower price, budget-friendly option |
| Application | High-end upholstery, luxury furniture | Economical upholstery, mass-produced furniture |
Introduction to Leather Types in Upholstery
Retanned leather and split leather represent two distinct categories in upholstery materials, each offering unique characteristics and durability levels. Retanned leather undergoes a secondary tanning process that enhances its strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-use furniture pieces. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, is typically thinner and less durable but provides a cost-effective option with a suede-like texture often used in decorative or low-traffic upholstery.
What is Retanned Leather?
Retanned leather refers to hide that has undergone a secondary tanning process to enhance its durability, texture, and color retention, making it ideal for high-quality upholstery applications. This leather maintains a balanced moisture content and exhibits superior resistance to wear and aging compared to split leather, which is derived from the lower layers of the hide and often lacks the full grain's strength. Retanned leather's improved structural integrity and aesthetic appeal provide a premium upholstery material that withstands daily use while maintaining a refined appearance.
What is Split Leather?
Split leather is derived from the lower layers of a hide after the top grain has been separated, often processed and retanned to improve durability and appearance for upholstery applications. Retanned leather undergoes an additional tanning process to enhance softness, strength, and resistance to wear, making it more suitable for high-quality furniture. Split leather typically offers a more affordable alternative but may lack the natural grain texture and longevity of retanned top grain leather.
Composition and Structure Differences
Retanned leather undergoes multiple tanning processes, combining chrome and vegetable tanning to enhance durability, flexibility, and richness, resulting in a dense, smooth surface ideal for high-end upholstery. Split leather originates from the lower layers of a hide, lacks the grain layer, and is typically thinner and less durable, often coated or embossed to mimic top-grain leather's appearance. The structural difference lies in retanned leather's intact fibrous grain structure that provides strength and texture, whereas split leather's fibrous layer is more open and weaker, affecting its longevity and tactile quality in upholstery applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Retanned leather exhibits superior durability and longevity in upholstery due to its enhanced fiber bonding, which resists wear and tear more effectively than split leather. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, tends to be less resilient and prone to cracking or peeling over time when subjected to frequent use. The retanning process strengthens leather structure, making retanned leather a preferred choice for high-traffic furniture requiring long-lasting performance.
Aesthetic Appeal: Texture and Appearance
Retanned leather offers a rich, uniform texture with a smooth, polished finish that enhances upholstery's aesthetic appeal, making furniture look sophisticated and high-end. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, has a rougher texture that is often embossed to mimic full grain but lacks the natural grain's depth and character. The choice between retanned and split leather significantly affects the visual authenticity and tactile sensation of upholstered pieces.
Comfort and Flexibility Factors
Retanned leather offers superior comfort and flexibility for upholstery due to its enhanced softness and durability achieved through additional tanning processes. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, tends to be less flexible and can feel stiffer, which may reduce comfort over prolonged use. The retanning process improves fiber alignment, making retanned leather more adaptable to body contours and better suited for high-quality, comfortable furniture applications.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Retanned leather offers enhanced durability and resistance to wear, requiring regular conditioning to maintain its suppleness and prevent cracking in upholstery applications. Split leather, being more porous and less dense, demands more frequent cleaning and protection from moisture to avoid staining and deterioration. Proper maintenance of retanned leather involves less intensive care routines, while split leather upholstery often necessitates specialized treatments to preserve its appearance and lifespan.
Cost Considerations for Upholstery Projects
Retanned leather typically incurs higher costs due to its multi-step tanning process that enhances durability and appearance, making it a premium choice for upholstery projects. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of hides, is more affordable but may require additional treatments or finishes to improve its wear resistance and aesthetics. Budget-conscious upholstery projects often favor split leather for cost savings, while retanned leather is preferred for long-term investment in quality and longevity.
Best Use Cases: Retanned vs. Split Leather
Retanned leather offers superior durability, rich texture, and enhanced resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic upholstery applications in commercial spaces or vintage-style furniture. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, is more affordable but less durable, best suited for decorative purposes or light-use upholstery such as accent chairs or cushions. Choosing retanned leather ensures longevity and a premium look, while split leather provides a cost-effective option for budget-conscious or low-usage furniture projects.
Infographic: Retanned leather vs Split leather for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com