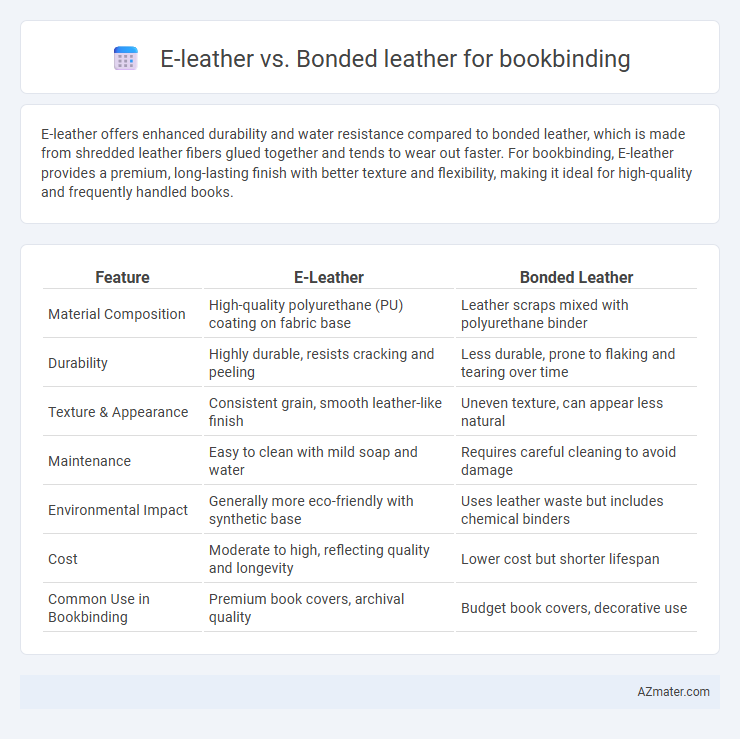
E-leather offers enhanced durability and water resistance compared to bonded leather, which is made from shredded leather fibers glued together and tends to wear out faster. For bookbinding, E-leather provides a premium, long-lasting finish with better texture and flexibility, making it ideal for high-quality and frequently handled books.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | E-Leather | Bonded Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-quality polyurethane (PU) coating on fabric base | Leather scraps mixed with polyurethane binder |
| Durability | Highly durable, resists cracking and peeling | Less durable, prone to flaking and tearing over time |
| Texture & Appearance | Consistent grain, smooth leather-like finish | Uneven texture, can appear less natural |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean with mild soap and water | Requires careful cleaning to avoid damage |
| Environmental Impact | Generally more eco-friendly with synthetic base | Uses leather waste but includes chemical binders |
| Cost | Moderate to high, reflecting quality and longevity | Lower cost but shorter lifespan |
| Common Use in Bookbinding | Premium book covers, archival quality | Budget book covers, decorative use |
Introduction to E-Leather and Bonded Leather
E-leather, a synthetic material combining polyurethane with natural fibers, offers durability and a consistent texture ideal for bookbinding applications. Bonded leather is created by blending shredded leather scraps with polyurethane or latex, resulting in a cost-effective but less resilient cover option. Both materials provide distinct tactile experiences and aesthetic qualities, influencing the selection process for durable, attractive book covers.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
E-leather consists of a textile base coated with a polyurethane layer, created through a chemical bonding process that enhances durability and flexibility, making it ideal for bookbinding applications requiring wear resistance. Bonded leather is produced by shredding leather scraps and fibers, which are then mixed with a polyurethane binder and pressed onto a fiber backing, resulting in a material that mimics genuine leather but with lower durability. The manufacturing process of E-leather emphasizes uniform texture and color through advanced lamination techniques, whereas bonded leather's process focuses on recycling leather waste into a cost-effective, composite sheet for decorative purposes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
E-leather for bookbinding is made from recycled polyurethane and natural fibers, offering a more sustainable alternative by reducing plastic waste and minimizing resource use. Bonded leather combines leather scraps with synthetic materials, resulting in lower durability and increased environmental burden due to chemical adhesives and limited recyclability. Choosing E-leather supports eco-friendly practices with reduced landfill contribution and better biodegradability compared to bonded leather's significant ecological footprint.
Durability and Longevity in Bookbinding
E-leather, made from synthetic materials, offers superior durability and resistance to wear compared to bonded leather, which consists of leather scraps bonded with adhesives. In bookbinding, e-leather maintains its integrity longer under frequent handling, resisting cracking and peeling better than bonded leather, which tends to degrade and delaminate over time. The longevity of e-leather makes it a preferred choice for high-quality, long-lasting book covers designed for frequent use and archival purposes.
Aesthetic Appeal and Texture Comparison
E-leather offers a smooth, consistent texture that mimics genuine leather's grain, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of bookbinding with a luxurious and polished finish. Bonded leather, composed of shredded leather fibers bonded with polyurethane, provides a varied texture that can appear less uniform and may show wear more quickly, affecting its long-term visual appeal. The choice between E-leather and bonded leather hinges on the desired balance between durability, tactile experience, and the refined look essential for high-quality bookbinding projects.
Cost Analysis: E-Leather vs Bonded Leather
E-leather offers a higher durability and premium finish at a cost typically 20-30% above bonded leather, making it a preferable choice for long-lasting book covers. Bonded leather, composed of shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane, is significantly cheaper but tends to degrade faster, affecting overall bookbinding value. For budget-conscious projects, bonded leather provides an economical option, though e-leather's investment can yield better longevity and aesthetic appeal.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
E-leather in bookbinding offers superior durability and easier maintenance compared to bonded leather, resisting cracks and stains due to its synthetic composition. Bonded leather, made from shredded leather fibers glued together, requires more delicate care to prevent peeling and moisture damage, often needing specialized conditioners. Regular cleaning with a damp cloth suits e-leather, while bonded leather demands gentle cleaning and prompt protection from humidity to extend its lifespan.
Popular Applications in Bookbinding
E-leather, known for its durability and eco-friendly properties, is increasingly used in premium bookbinding for luxury journals, archival books, and limited-edition collections. Bonded leather, composed of shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane, is favored in cost-effective mass-market bookbinding such as textbooks, planners, and paperback covers due to its affordability and leather-like appearance. The choice between E-leather and bonded leather significantly impacts the longevity and aesthetic quality of the bound books, with E-leather preferred for long-lasting, high-end editions and bonded leather for budget-friendly, widely distributed publications.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences in bookbinding reveal a growing inclination towards E-leather due to its enhanced durability, eco-friendliness, and affordability compared to bonded leather. Market trends highlight a significant rise in demand for E-leather products driven by increased awareness of sustainable materials and improved manufacturing technologies that offer a consistent texture and appearance. Bonded leather remains popular for budget-conscious consumers but faces declining market share as E-leather's superior performance and lower environmental impact gain traction.
Which is Better for Bookbinding?
E-leather, a synthetic leather made from polyurethane, offers superior durability, water resistance, and consistent texture, making it ideal for bookbinding that demands longevity. Bonded leather, composed of scraps bonded with adhesives, tends to wear out faster and is less resistant to moisture, leading to potential peeling and cracking over time. For high-quality bookbinding projects requiring resilience and aesthetic consistency, e-leather proves to be the better choice.
Infographic: E-leather vs Bonded leather for Bookbinding
 azmater.com
azmater.com