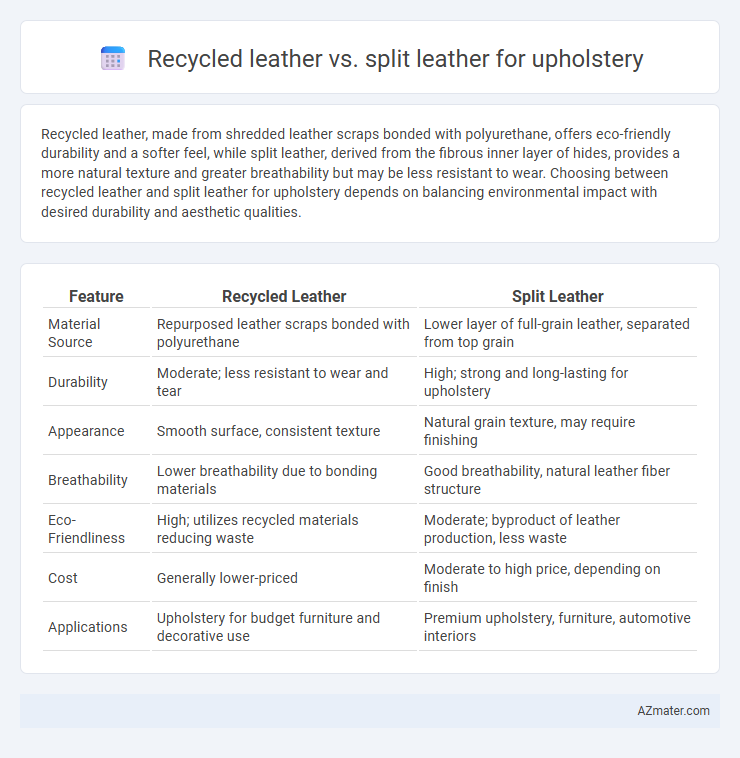
Recycled leather, made from shredded leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, offers eco-friendly durability and a softer feel, while split leather, derived from the fibrous inner layer of hides, provides a more natural texture and greater breathability but may be less resistant to wear. Choosing between recycled leather and split leather for upholstery depends on balancing environmental impact with desired durability and aesthetic qualities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Repurposed leather scraps bonded with polyurethane | Lower layer of full-grain leather, separated from top grain |
| Durability | Moderate; less resistant to wear and tear | High; strong and long-lasting for upholstery |
| Appearance | Smooth surface, consistent texture | Natural grain texture, may require finishing |
| Breathability | Lower breathability due to bonding materials | Good breathability, natural leather fiber structure |
| Eco-Friendliness | High; utilizes recycled materials reducing waste | Moderate; byproduct of leather production, less waste |
| Cost | Generally lower-priced | Moderate to high price, depending on finish |
| Applications | Upholstery for budget furniture and decorative use | Premium upholstery, furniture, automotive interiors |
Introduction to Leather Types in Upholstery
Recycled leather, made from shredded leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, offers an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional upholstery materials. Split leather, derived from the fibrous part of the hide beneath the top grain, provides durability and a natural look while being more affordable than full-grain leather. Both options present unique textures and performance characteristics suited for varying upholstery needs in residential or commercial applications.
What is Recycled Leather?
Recycled leather, also known as bonded leather, is manufactured by shredding genuine leather scraps and fibers, which are then mixed with a polyurethane binder to create a durable material suitable for upholstery. This process repurposes leather waste, offering an eco-friendly alternative with a leather-like appearance at a lower cost compared to full-grain or split leather. While recycled leather provides a sustainable option, it tends to be less breathable and durable than split leather, which is derived from the fibrous part of the hide beneath the top grain.
What is Split Leather?
Split leather is derived from the fibrous lower portion of a hide after the top grain has been separated for higher quality leather production. It retains durability suitable for upholstery but generally lacks the refined surface and strength of full-grain or top-grain leather. Compared to recycled leather, split leather offers a more consistent texture and better wear resistance, making it a practical choice for furniture applications.
Production Process: Recycled Leather vs Split Leather
Recycled leather is produced by shredding scrap leather pieces and bonding them together with polyurethane or latex to create a uniform material, emphasizing sustainability and reducing waste. Split leather comes from the fibrous underside of a hide, separated from the top grain layer, and often undergoes processes like embossing or coating to enhance durability and appearance. The production of recycled leather involves combining multiple leather remnants, while split leather is directly derived from separating the internal layers of a single hide.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Comparison
Recycled leather significantly reduces environmental impact by repurposing leather scraps, minimizing landfill waste, and lowering the demand for raw animal hides, thus conserving natural resources and reducing carbon emissions. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of animal hides, requires additional chemical treatments that contribute to pollution and resource depletion during production. Choosing recycled leather for upholstery supports circular economy practices and promotes sustainable material use in the furniture industry.
Durability and Longevity
Recycled leather, composed of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, tends to have lower durability and a shorter lifespan compared to split leather, which is derived from the fibrous underside of top-grain leather offering better strength and wear resistance. Split leather's dense fiber structure provides enhanced resistance to cracking, tearing, and wear, making it more suitable for high-traffic upholstery applications. While recycled leather is more eco-friendly, split leather outperforms it significantly in terms of longevity and durability for furniture upholstery.
Appearance and Texture Differences
Recycled leather features a uniform appearance with a smooth, consistent texture due to its composite nature made from shredded leather fibers bonded with polyurethane, offering a synthetic leather look. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of a hide, exhibits a more natural, grainy texture with visible pores and irregularities, providing an authentic leather feel but often requiring finishing treatments for durability. The visual and tactile differences impact upholstery choices, where recycled leather offers cost-effective uniformity, while split leather delivers a traditional, rugged aesthetic.
Cost Efficiency for Upholstery Projects
Recycled leather offers significant cost efficiency for upholstery projects by utilizing scraps and fibers bonded together, resulting in a lower price point compared to traditional materials. Split leather, derived from the fibrous part of animal hides, tends to be more expensive due to its durability and resemblance to full-grain leather. Choosing recycled leather reduces expenses without compromising on aesthetic appeal, making it an economical choice for budget-conscious upholstery applications.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Recycled leather requires more frequent cleaning and conditioning to prevent cracking and maintain its appearance due to its composite nature made from leather scraps and synthetic binders. Split leather, derived from the lower layer of a hide, is more porous and demands regular conditioning with leather-specific products to avoid drying out and staining. Both materials benefit from avoiding direct sunlight and excessive moisture to prolong their upholstery lifespan.
Choosing the Right Leather: Key Factors to Consider
Recycled leather offers an eco-friendly option by blending leather scraps with polyurethane, providing durability and a consistent look, while split leather, derived from the lower layers of hides, delivers natural texture and breathability but may be less durable. Key factors to consider when choosing include the intended use of the upholstery, exposure to wear and tear, maintenance requirements, and budget constraints. Prioritizing sustainability, longevity, and aesthetic appeal will help determine whether recycled or split leather best suits your upholstery needs.
Infographic: Recycled leather vs Split leather for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com