Raw leather offers superior durability and natural breathability, making it ideal for high-quality furniture. Bonded leather, composed of leather scraps and polyurethane, provides a budget-friendly alternative but lacks the longevity and texture of genuine leather.
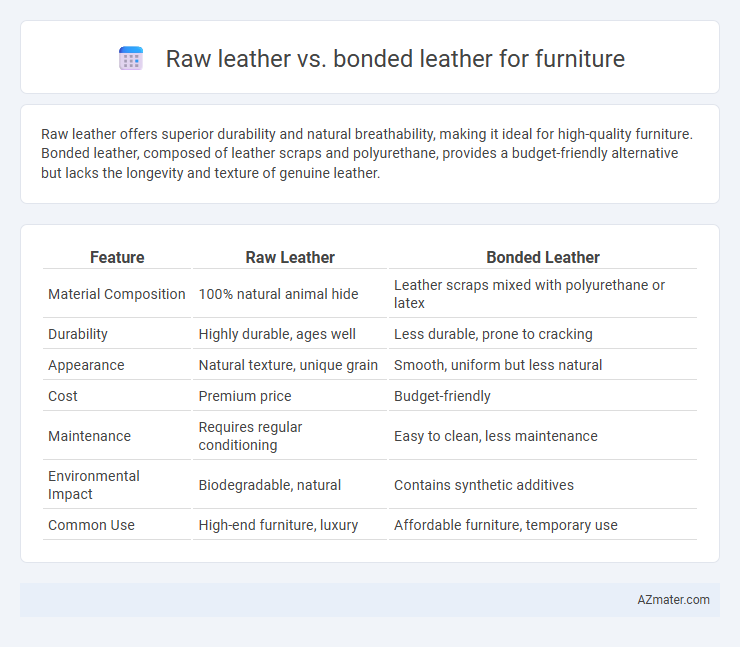
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raw Leather | Bonded Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | 100% natural animal hide | Leather scraps mixed with polyurethane or latex |
| Durability | Highly durable, ages well | Less durable, prone to cracking |
| Appearance | Natural texture, unique grain | Smooth, uniform but less natural |
| Cost | Premium price | Budget-friendly |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning | Easy to clean, less maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, natural | Contains synthetic additives |
| Common Use | High-end furniture, luxury | Affordable furniture, temporary use |
Introduction to Raw Leather and Bonded Leather
Raw leather, also known as full-grain leather, is derived directly from animal hides and retains the natural texture, strength, and durability, making it a premium choice for high-quality furniture. Bonded leather is manufactured by blending shredded leather fibers with polyurethane or latex binders, resulting in a more affordable but less durable material with a synthetic feel. The distinction between these two materials significantly affects the longevity, appearance, and maintenance requirements of furniture upholstery.
What is Raw Leather?
Raw leather, also known as full-grain leather, is the highest quality leather used in furniture, made from the top layer of animal hide without any sanding or buffing. It retains the natural grain, strength, and breathability, offering superior durability and a unique patina that develops over time. Unlike bonded leather, raw leather resists cracking and peeling, making it a premium choice for long-lasting furniture upholstery.
What is Bonded Leather?
Bonded leather is a material made by combining shredded leather fibers with a polyurethane or latex backing, creating a composite that mimics the appearance of genuine raw leather. It offers a more affordable alternative for furniture upholstery while providing a smooth texture and consistent finish. However, bonded leather typically lacks the durability, natural breathability, and aging characteristics found in raw leather, making it less suitable for long-term use.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Raw leather, also known as full-grain leather, undergoes minimal processing, preserving its natural grain and strength by being tanned and finished without significant alterations. Bonded leather is manufactured by bonding leftover leather scraps with polyurethane or latex onto a fiber backing, resulting in a lower durability and less natural texture compared to raw leather. The manufacturing process of raw leather emphasizes quality and longevity, while bonded leather focuses on cost efficiency and appearance by utilizing recycled materials.
Durability and Longevity Differences
Raw leather offers superior durability and longevity for furniture due to its natural fiber strength and resistance to wear, often lasting decades with proper care. Bonded leather, made from shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane, tends to deteriorate faster, showing signs of peeling and cracking within a few years under regular use. Choosing raw leather ensures a robust, long-lasting investment in furniture quality compared to the short-term lifespan of bonded leather.
Comfort and Aesthetic Appeal
Raw leather offers superior comfort with its natural breathability and soft, supple texture that ages gracefully, enhancing the furniture's aesthetic appeal over time. Bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, provides a more uniform appearance but lacks the same durability and comfort, often feeling less natural and breathable. Furniture upholstered in raw leather retains a luxurious look and feel, making it a preferred choice for both comfort and long-term visual appeal.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Raw leather requires regular cleaning with a damp cloth and conditioning every 6-12 months to prevent drying and cracking, while avoiding harsh chemicals that can damage the surface. Bonded leather demands gentler maintenance, including wiping with a soft cloth and mild soap, as it is more prone to peeling and cannot be conditioned like raw leather. Raw leather's natural durability offers longer lifespan with proper care, whereas bonded leather's synthetic composition often results in shorter usability and more frequent replacement.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Raw leather, sourced directly from animal hides with minimal processing, offers durability and longevity but raises concerns about animal welfare and the environmental impact of livestock farming, including high water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Bonded leather, made from shredded leather scraps mixed with synthetic materials, reduces waste by recycling leather remnants but often involves plastics and adhesives that challenge biodegradability and may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Choosing between these options involves weighing the ethical preference for animal-derived products against the sustainability practices of waste reduction and chemical usage in manufacturing.
Cost and Value Analysis
Raw leather offers superior durability and develops a unique patina over time, making it a higher-cost investment with greater long-term value for furniture. Bonded leather, composed of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, provides an affordable alternative but tends to wear and peel quicker, reducing its lifespan and overall worth. Evaluating cost relative to durability, raw leather delivers enhanced value through resilience, whereas bonded leather suits budget-conscious consumers seeking short-term aesthetic appeal.
Which Leather is Best for Your Furniture?
Raw leather, also known as full-grain leather, offers unmatched durability, natural breathability, and a rich patina that improves with age, making it ideal for high-quality furniture that lasts longer. Bonded leather, composed of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, is less durable and prone to peeling over time, but it provides a more affordable and uniform appearance for budget-conscious buyers. Choosing raw leather ensures longevity and premium texture, while bonded leather suits short-term use or decorative purposes without heavy wear.
Infographic: Raw leather vs Bonded leather for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com