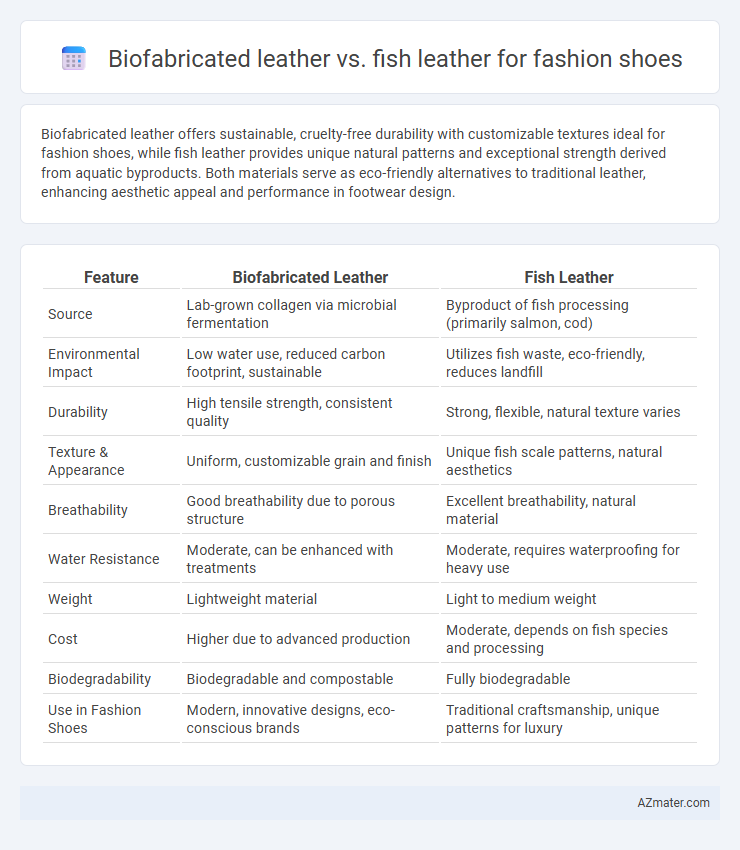
Biofabricated leather offers sustainable, cruelty-free durability with customizable textures ideal for fashion shoes, while fish leather provides unique natural patterns and exceptional strength derived from aquatic byproducts. Both materials serve as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional leather, enhancing aesthetic appeal and performance in footwear design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Fish Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown collagen via microbial fermentation | Byproduct of fish processing (primarily salmon, cod) |
| Environmental Impact | Low water use, reduced carbon footprint, sustainable | Utilizes fish waste, eco-friendly, reduces landfill |
| Durability | High tensile strength, consistent quality | Strong, flexible, natural texture varies |
| Texture & Appearance | Uniform, customizable grain and finish | Unique fish scale patterns, natural aesthetics |
| Breathability | Good breathability due to porous structure | Excellent breathability, natural material |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can be enhanced with treatments | Moderate, requires waterproofing for heavy use |
| Weight | Lightweight material | Light to medium weight |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced production | Moderate, depends on fish species and processing |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and compostable | Fully biodegradable |
| Use in Fashion Shoes | Modern, innovative designs, eco-conscious brands | Traditional craftsmanship, unique patterns for luxury |
Introduction to Sustainable Leathers in Fashion
Biofabricated leather, created through microbial fermentation, offers a cutting-edge sustainable alternative to traditional animal-based materials, reducing environmental impact by minimizing water usage and eliminating harmful chemicals. Fish leather, sourced from by-products of the fishing industry, provides a durable and eco-friendly option with unique textures and patterns that enhance fashion shoe designs. Both materials contribute to the growing demand for sustainable leathers by promoting circular fashion and reducing reliance on conventional leather production.
What is Biofabricated Leather?
Biofabricated leather is an innovative material created through cellular agriculture, growing collagen proteins in a lab to mimic traditional animal leather without harming animals. This sustainable alternative offers customizable textures and durability suitable for fashion shoes, reducing environmental impacts like water usage and carbon emissions common in fish leather production. The ability to scale production ethically makes biofabricated leather a promising option compared to exotic fish leather, which relies on natural resources and can vary in quality.
What is Fish Leather?
Fish leather is a durable, sustainable material made by tanning and processing fish skins, primarily from species like salmon, cod, or tilapia, that would otherwise be discarded as waste. It offers unique textures ranging from smooth to embossed scales, making it an attractive choice for fashion shoe design seeking eco-friendly alternatives. Compared to biofabricated leather, fish leather retains natural patterns and requires less energy-intensive processing, appealing to brands emphasizing authenticity and environmental responsibility.
Production Processes Compared
Biofabricated leather is produced through microbial fermentation, where engineered cells synthesize collagen or other proteins that are then assembled into durable, flexible materials resembling traditional leather. Fish leather involves tanning skins of fish species such as salmon or cod, using natural or chemical treatments to preserve and enhance their texture and strength for footwear applications. The biofabrication process emphasizes sustainability by reducing animal waste and resource consumption, while fish leather leverages byproducts of the fishing industry, offering a more circular and eco-friendly alternative to conventional leather production.
Environmental Impact: Biofabricated vs Fish Leather
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative with a significantly lower carbon footprint and reduced water consumption compared to traditional fish leather, which depends on fishing industries that often contribute to overfishing and aquatic ecosystem disruption. While fish leather is biodegradable and utilizes byproducts from the seafood industry, biofabricated leather is produced through cell culturing processes that minimize waste and eliminate the need for harmful tanning chemicals. The environmental impact of biofabricated leather presents a promising shift towards eco-friendly fashion by addressing resource efficiency and pollution concerns more effectively than fish leather.
Durability and Performance in Shoes
Biofabricated leather demonstrates superior durability and water resistance compared to fish leather, making it highly suitable for fashion shoes exposed to varied environments. Fish leather offers unique texture and natural breathability but tends to wear faster and requires more maintenance to preserve its performance. Performance-wise, biofabricated leather maintains consistent strength and flexibility over time, enhancing comfort and longevity in footwear applications.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Biofabricated leather offers exceptional design flexibility with its uniform texture and ability to be customized in color, thickness, and patterns, making it ideal for innovative fashion shoe designs. Fish leather stands out with its natural scale patterns and unique texture, providing an organic aesthetic appeal that enhances the exclusivity of luxury footwear. While biofabricated leather supports sleek, modern aesthetics, fish leather delivers distinctive, artisanal qualities that cater to niche fashion markets.
Ethical Considerations and Animal Welfare
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative in fashion shoe production by eliminating the need for animal farming and reducing environmental impact, thereby promoting higher ethical standards and animal welfare. Fish leather, while utilizing byproducts from the fishing industry and reducing waste, still involves the use of animal skins and often relies on practices associated with animal harvesting. Prioritizing biofabricated leather supports cruelty-free innovation by avoiding animal harm altogether, aligning with growing consumer demand for ethically sourced, sustainable materials.
Market Adoption and Consumer Perception
Biofabricated leather is gaining rapid market adoption due to its sustainable production methods and cruelty-free appeal, attracting environmentally conscious consumers in the fashion shoe industry. Fish leather, valued for its unique texture and natural origin, holds a niche market primarily in luxury and artisanal segments but faces challenges in scalability and consistent supply. Consumer perception favors biofabricated leather for innovation and ethical advantages, while fish leather is appreciated for its authenticity and exotic aesthetic, influencing brand positioning and pricing strategies.
Future Trends in Sustainable Shoe Materials
Biofabricated leather, derived from microbial fermentation, offers a highly customizable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional animal hides, significantly reducing water usage and carbon emissions in shoe manufacturing. Fish leather, particularly sourced from sustainable fisheries, provides a unique texture and durability while utilizing byproducts that would otherwise contribute to waste. Future trends in sustainable shoe materials emphasize integrating biofabricated leather with fish leather to create innovative, biodegradable footwear that meets the growing demand for ethical and environmentally responsible fashion.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Fish leather for Fashion shoe
 azmater.com
azmater.com