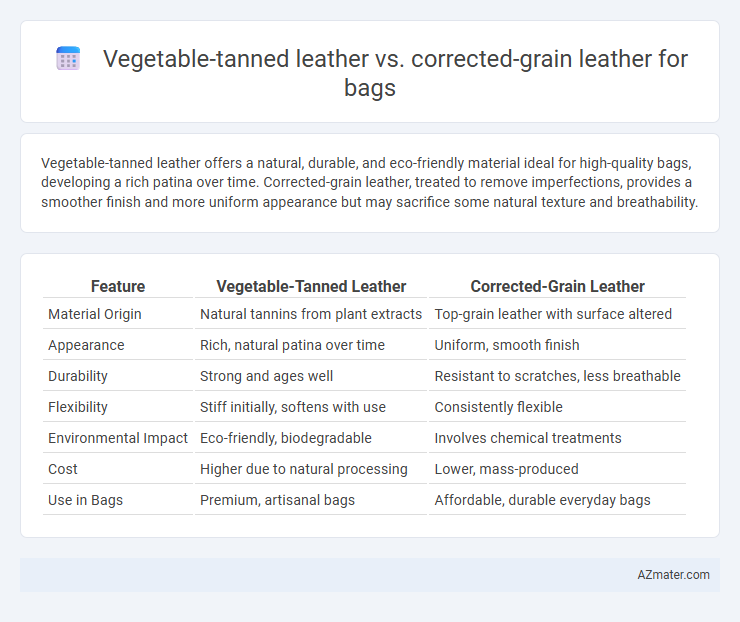
Vegetable-tanned leather offers a natural, durable, and eco-friendly material ideal for high-quality bags, developing a rich patina over time. Corrected-grain leather, treated to remove imperfections, provides a smoother finish and more uniform appearance but may sacrifice some natural texture and breathability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Corrected-Grain Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Natural tannins from plant extracts | Top-grain leather with surface altered |
| Appearance | Rich, natural patina over time | Uniform, smooth finish |
| Durability | Strong and ages well | Resistant to scratches, less breathable |
| Flexibility | Stiff initially, softens with use | Consistently flexible |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Involves chemical treatments |
| Cost | Higher due to natural processing | Lower, mass-produced |
| Use in Bags | Premium, artisanal bags | Affordable, durable everyday bags |
Introduction to Vegetable-Tanned and Corrected-Grain Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins from plant materials, resulting in a durable, eco-friendly material that develops a rich patina over time. Corrected-grain leather undergoes surface sanding and buffing to remove imperfections, followed by an artificial grain applied to create a uniform, smooth finish. For bags, vegetable-tanned leather offers a unique, natural look with increased breathability, while corrected-grain leather provides more consistent appearance and resistance to wear.
What is Vegetable-Tanned Leather?
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins found in tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, offering an eco-friendly and durable option for bags. This type of leather develops a rich patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal and character with use. Compared to corrected-grain leather, which undergoes heavy surface processing and artificial coloring, vegetable-tanned leather maintains its natural texture and breathability.
What is Corrected-Grain Leather?
Corrected-grain leather is a type of leather where the natural grain surface is sanded or buffed to remove imperfections, then coated with an artificial grain layer, often pigment or polyurethane, for a uniform appearance. This finish enhances durability and resistance to stains but sacrifices the natural texture and breathability found in vegetable-tanned leather. Bags made from corrected-grain leather typically offer a consistent look and budget-friendly option, while vegetable-tanned leather features a more authentic, developing patina over time.
Key Differences Between Vegetable-Tanned and Corrected-Grain Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins from plant extracts, resulting in a durable, eco-friendly material with a rich patina that develops over time, ideal for high-quality bags. Corrected-grain leather undergoes heavy sanding and buffing to remove imperfections, then is coated with a synthetic finish, offering a consistent appearance but less breathability and natural feel. Key differences include the tanning process, environmental impact, texture, durability, and aging characteristics, with vegetable-tanned leather favoring natural aesthetics and corrected-grain leather prioritizing surface uniformity.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Vegetable-tanned leather showcases a rich, natural patina with visible grain variations, offering a matte and organic texture that softens and deepens in color over time. Corrected-grain leather features a uniform, smooth surface achieved through buffing and embossing, delivering a consistent and polished look but lacks the natural texture and aging character of vegetable-tanned leather. Bags made from vegetable-tanned leather exhibit a handcrafted aesthetic with unique imperfections, while corrected-grain leather bags prioritize durability and a flawless finish ideal for mass production.
Durability and Longevity of Each Leather Type
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability and develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its longevity and resistance to wear for bags exposed to regular use. Corrected-grain leather undergoes heavy surface treatment, which can mask natural flaws but may reduce breathability and long-term durability compared to vegetable-tanned leather. For bags requiring robust endurance and aging character, vegetable-tanned leather is a preferred choice, while corrected-grain leather suits applications needing a uniform appearance with moderate durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Vegetable-tanned leather, derived from natural tannins found in tree bark and plants, offers a biodegradable and less chemically-intensive production process compared to corrected-grain leather, which involves significant chemical treatments and synthetic coatings to mask imperfections. The environmental footprint of vegetable-tanned leather is generally lower, with reduced water and energy consumption as well as minimal toxic waste, enhancing its sustainability profile for eco-conscious consumers. Corrected-grain leather often incorporates additional pollutants and non-biodegradable substances, making it less favorable for sustainable fashion and environmentally responsible bag manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Vegetable-Tanned vs Corrected-Grain Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather typically costs more than corrected-grain leather due to its natural tanning process that requires longer production time and premium raw materials. Corrected-grain leather is generally less expensive because it undergoes heavy processing, including sanding and artificial coating, which reduces production costs. For bag buyers prioritizing budget, corrected-grain leather offers affordability, while vegetable-tanned leather commands a premium for durability and natural aging.
Ideal Uses for Bags: Which Leather Performs Better?
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability and develops a rich patina over time, making it ideal for high-quality, long-lasting bags that age beautifully. Corrected-grain leather, coated with a protective finish, resists stains and scratches effectively, suitable for everyday, budget-friendly bags that require easy maintenance. For premium leather bags prioritizing natural aesthetics and longevity, vegetable-tanned leather performs better, while corrected-grain leather excels in practicality and durability for frequent use.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Leather for Bags
Vegetable-tanned leather offers natural durability, develops a rich patina over time, and is ideal for high-quality, long-lasting bags, while corrected-grain leather provides a more uniform appearance, is easier to clean, and is budget-friendly but lacks the same character and aging qualities. For premium bags that age beautifully and improve with wear, vegetable-tanned leather is the preferred choice, whereas corrected-grain leather suits affordable, low-maintenance options without patina development. Choosing the best leather depends on priorities: longevity and aesthetic evolution favor vegetable-tanned, while practicality and cost-effectiveness point to corrected-grain leather.
Infographic: Vegetable-tanned leather vs Corrected-grain leather for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com