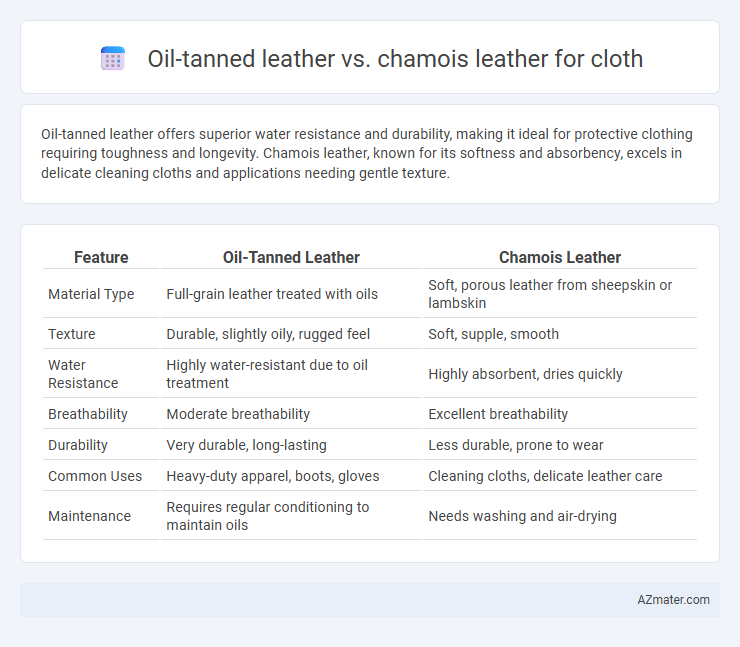
Oil-tanned leather offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for protective clothing requiring toughness and longevity. Chamois leather, known for its softness and absorbency, excels in delicate cleaning cloths and applications needing gentle texture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oil-Tanned Leather | Chamois Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Full-grain leather treated with oils | Soft, porous leather from sheepskin or lambskin |
| Texture | Durable, slightly oily, rugged feel | Soft, supple, smooth |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant due to oil treatment | Highly absorbent, dries quickly |
| Breathability | Moderate breathability | Excellent breathability |
| Durability | Very durable, long-lasting | Less durable, prone to wear |
| Common Uses | Heavy-duty apparel, boots, gloves | Cleaning cloths, delicate leather care |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning to maintain oils | Needs washing and air-drying |
Introduction to Oil-Tanned and Chamois Leather
Oil-tanned leather undergoes a specialized tanning process using oil to create a durable, water-resistant material ideal for robust apparel and outdoor use. Chamois leather is known for its exceptionally soft, absorbent properties, traditionally derived from the skin of chamois or sheepskin, often used for cleaning cloths or delicate garments. Both types offer distinct textures and functionalities, with oil-tanned leather excelling in toughness and longevity, while chamois leather provides superior softness and moisture absorption.
Defining Oil-Tanned Leather: Characteristics and Process
Oil-tanned leather is a durable, water-resistant material treated with oils and waxes during the tanning process to enhance its softness and flexibility, making it ideal for heavy-duty cloth applications. This leather undergoes a specialized treatment where natural oils penetrate the hide, providing a supple texture coupled with high resistance to wear, stains, and moisture. Its unique finishing technique ensures longevity and a distinctive patina that develops over time, setting it apart from other types of leather like chamois, which is softer and more absorbent but less rugged.
Defining Chamois Leather: Characteristics and Process
Chamois leather is a soft, pliable material known for its exceptional absorbency and smooth texture, produced through a unique oil-tanning process that uses natural oils to preserve suppleness. This leather is primarily made from the flesh side of sheepskin or lambskin, treated to remove impurities while retaining flexibility and breathability. Unlike standard oil-tanned leather, chamois leather excels in gentle cleaning applications and moisture absorption, making it ideal for delicate cloth care and polishing tasks.
Durability Comparison: Oil-Tanned vs Chamois Leather
Oil-tanned leather offers superior durability compared to chamois leather due to its dense, water-resistant surface and robust tanning process that enhances resistance to wear and environmental damage. Chamois leather, while softer and more absorbent, is less resistant to abrasion and moisture, making it prone to faster wear in heavy-use or wet conditions. For long-lasting cloth applications requiring toughness and weather resistance, oil-tanned leather is generally the preferred choice.
Softness and Texture Differences
Oil-tanned leather features a rich, supple texture achieved by infusing oils during the tanning process, resulting in a durable yet soft surface ideal for rugged cloth applications. Chamois leather offers an exceptionally smooth and velvety feel, created through a unique tanning method that enhances its lightweight softness and pliability, making it perfect for delicate cloth items requiring gentle contact. While oil-tanned leather emphasizes robustness with a slightly waxy finish, chamois leather prioritizes breathability and softness with a more matte, suede-like texture.
Water Resistance and Maintenance
Oil-tanned leather offers superior water resistance due to the oils infused during tanning, making it highly durable and less prone to water damage compared to chamois leather. Chamois leather, while soft and absorbent, requires frequent drying and conditioning to prevent mold and deterioration when exposed to moisture. Maintenance of oil-tanned leather involves occasional re-oiling to preserve its waterproof qualities, whereas chamois leather demands gentle cleaning and careful air drying to maintain its texture and longevity.
Practical Applications in Clothing
Oil-tanned leather offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for rugged outerwear, work jackets, and heavy-duty garments that require protection against harsh weather. Chamois leather, known for its softness, breathability, and excellent moisture absorption, is commonly used in lightweight clothing, gloves, and linings where comfort and flexibility are essential. Practical applications favor oil-tanned leather for robust, weatherproof clothing and chamois leather for breathable, comfortable wear in mild conditions.
Comfort and Breathability in Garments
Oil-tanned leather provides superior durability and a water-resistant finish but tends to be less breathable and heavier, potentially reducing overall comfort in garments. Chamois leather, derived from goat or sheep skin, is exceptionally soft, lightweight, and highly breathable, making it ideal for apparel where comfort and moisture-wicking are priorities. For clothing applications prioritizing breathability and comfort, chamois leather is often favored due to its natural ability to regulate temperature and prevent overheating.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Oil-tanned leather typically commands higher prices due to its durable finishing and labor-intensive production process, making it less accessible in mass markets compared to chamois leather. Chamois leather, derived from lamb or goat skin with natural oils preserved, is generally more affordable and widely available, especially for clothing and cleaning applications. Availability of oil-tanned leather is often limited to premium or specialty suppliers, whereas chamois leather is commonly stocked by general leather goods and textile retailers.
Which Leather is Best for Cloth?
Oil-tanned leather offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for rugged, weather-resistant clothing that requires long-lasting wear. Chamois leather is exceptionally soft and breathable, providing excellent comfort and moisture absorption, suited for lightweight, delicate apparel. For outdoor garments requiring toughness and protection, oil-tanned leather is best, whereas chamois leather excels in comfort-focused clothing.
Infographic: Oil-tanned leather vs Chamois leather for Cloth
 azmater.com
azmater.com