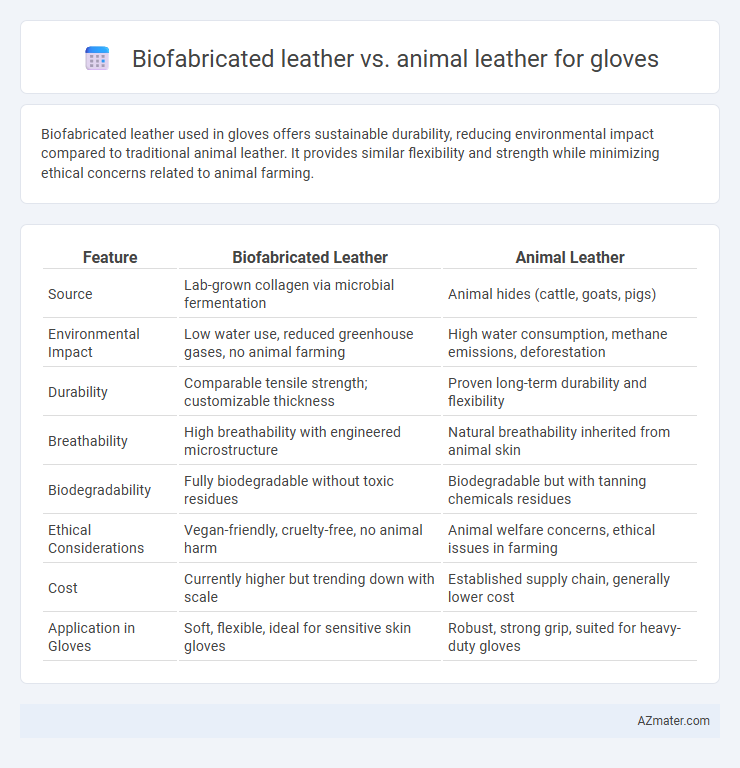
Biofabricated leather used in gloves offers sustainable durability, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional animal leather. It provides similar flexibility and strength while minimizing ethical concerns related to animal farming.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Animal Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown collagen via microbial fermentation | Animal hides (cattle, goats, pigs) |
| Environmental Impact | Low water use, reduced greenhouse gases, no animal farming | High water consumption, methane emissions, deforestation |
| Durability | Comparable tensile strength; customizable thickness | Proven long-term durability and flexibility |
| Breathability | High breathability with engineered microstructure | Natural breathability inherited from animal skin |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable without toxic residues | Biodegradable but with tanning chemicals residues |
| Ethical Considerations | Vegan-friendly, cruelty-free, no animal harm | Animal welfare concerns, ethical issues in farming |
| Cost | Currently higher but trending down with scale | Established supply chain, generally lower cost |
| Application in Gloves | Soft, flexible, ideal for sensitive skin gloves | Robust, strong grip, suited for heavy-duty gloves |
Introduction: The Evolution of Glove Materials
Biofabricated leather represents a cutting-edge innovation in glove materials, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional animal leather derived from cowhide or other hides. This evolution in glove manufacturing incorporates lab-grown collagen or plant-based materials that replicate the durability, flexibility, and tactile qualities of conventional leather. By reducing reliance on animal agriculture, biofabricated leather minimizes environmental impacts such as deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water usage commonly associated with animal leather production.
What Is Biofabricated Leather?
Biofabricated leather is a sustainable material created through biotechnological processes that cultivate collagen proteins or other natural fibers in a lab environment, eliminating the need for animal hides. This innovative leather alternative offers comparable durability and flexibility to traditional animal leather while significantly reducing environmental impact such as greenhouse gas emissions and water usage. Biofabricated leather is increasingly used for gloves, combining eco-friendly production with high performance and ethical standards.
Animal Leather: Traditional Choice for Gloves
Animal leather remains the traditional choice for gloves due to its durability, natural breathability, and superior fit that molds to the hand over time. Its inherent strength and resistance to wear make it ideal for protective and high-performance glove applications. Despite emerging alternatives like biofabricated leather, animal leather maintains a preferred status for its proven comfort and longevity in glove manufacturing.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Biofabricated leather for gloves is derived from cultured cells or plant-based materials, offering a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional animal leather, which is made from the tanned hide of animals like cows. The molecular structure of biofabricated leather allows for more uniform material properties and customizable textures, while animal leather contains natural fibers like collagen that provide characteristic durability and breathability. Differences in environmental impact stem from biofabricated leather's lower carbon footprint and reduced water consumption compared to the intensive resource use in animal leather production.
Comfort and Fit: User Experience Compared
Biofabricated leather for gloves offers enhanced breathability and flexibility, contributing to superior comfort during extended wear compared to traditional animal leather. Its uniform texture allows for a more precise fit, reducing break-in time and minimizing stiffness often associated with animal leather gloves. Users frequently report that biofabricated leather gloves adapt better to hand movements, improving overall dexterity and comfort.
Durability and Longevity: Which Lasts Longer?
Biofabricated leather, engineered through sustainable biotechnology, offers enhanced resistance to wear, water, and environmental stress, often surpassing traditional animal leather in durability. Animal leather, known for its natural toughness and ability to develop a unique patina over time, provides long-lasting performance but requires regular maintenance to prevent cracking and degradation. In terms of longevity, biofabricated leather maintains consistent quality and shape longer under harsh conditions, making it a compelling alternative for gloves demanding extended durability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Biofabricated leather for gloves offers a sustainable alternative by significantly reducing water usage, greenhouse gas emissions, and land requirements compared to traditional animal leather. Unlike animal leather, which involves livestock farming responsible for deforestation and methane emissions, biofabricated leather is produced through cellular agriculture, minimizing environmental degradation. This innovation lowers the carbon footprint and chemical waste associated with tanning processes, making biofabricated leather a more eco-friendly choice for glove manufacturing.
Ethical Considerations: Animal Welfare vs. Innovation
Biofabricated leather for gloves significantly reduces animal suffering by eliminating the need for livestock farming, addressing critical animal welfare concerns inherent in traditional animal leather production. Innovation in biofabrication offers sustainable alternatives by utilizing lab-grown collagen or plant-based materials, minimizing environmental degradation linked to animal agriculture. Ethical considerations favor biofabricated leather as it promotes cruelty-free practices while supporting advancements in material science and sustainable fashion.
Cost and Market Availability
Biofabricated leather offers a potentially sustainable alternative to animal leather for gloves but remains more expensive due to high production costs and limited scalability. Animal leather dominates the glove market with widespread availability and established supply chains, making it more cost-effective for mass production. Market adoption of biofabricated leather is currently niche, hindered by price premiums and constrained manufacturing capacity.
Future Trends in Glove Manufacturing
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative to animal leather in glove manufacturing, reducing environmental impact through lab-grown collagen and plant-based materials. Innovations in biofabrication enable customizable textures and enhanced durability, meeting growing consumer demand for ethical and high-performance gloves. Future trends highlight increased adoption of biofabricated leather as advanced production techniques lower costs and improve scalability in the glove industry.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Animal leather for Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com