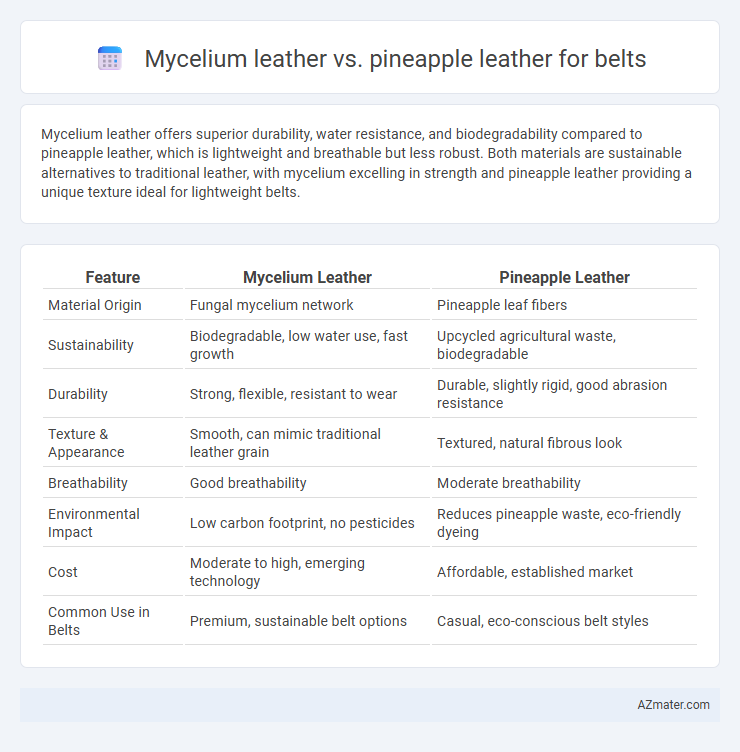
Mycelium leather offers superior durability, water resistance, and biodegradability compared to pineapple leather, which is lightweight and breathable but less robust. Both materials are sustainable alternatives to traditional leather, with mycelium excelling in strength and pineapple leather providing a unique texture ideal for lightweight belts.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mycelium Leather | Pineapple Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Fungal mycelium network | Pineapple leaf fibers |
| Sustainability | Biodegradable, low water use, fast growth | Upcycled agricultural waste, biodegradable |
| Durability | Strong, flexible, resistant to wear | Durable, slightly rigid, good abrasion resistance |
| Texture & Appearance | Smooth, can mimic traditional leather grain | Textured, natural fibrous look |
| Breathability | Good breathability | Moderate breathability |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, no pesticides | Reduces pineapple waste, eco-friendly dyeing |
| Cost | Moderate to high, emerging technology | Affordable, established market |
| Common Use in Belts | Premium, sustainable belt options | Casual, eco-conscious belt styles |
Introduction to Sustainable Leather Alternatives
Mycelium leather, derived from fungal root structures, offers a biodegradable and low-impact alternative to traditional leather, while pineapple leather, produced from pineapple leaf fibers, utilizes agricultural waste to reduce environmental footprints. Both materials demonstrate innovative approaches to sustainable fashion by minimizing resource consumption and chemical use in the production process. Their application in belts highlights a growing market demand for eco-friendly, cruelty-free accessories that align with circular economy principles.
What is Mycelium Leather?
Mycelium leather is a sustainable material derived from the root structure of mushrooms, known for its durability and eco-friendliness. It offers a biodegradable alternative to traditional leather, with natural breathability and flexibility ideal for belts. Compared to pineapple leather, mycelium leather typically provides a more consistent texture and greater resistance to wear and tear.
What is Pineapple Leather (Piñatex)?
Pineapple Leather, or Pinatex, is an innovative sustainable material made from pineapple leaf fibers, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional leather suitable for belts. This plant-based textile is lightweight, durable, and biodegradable, providing a vegan option that reduces waste by utilizing agricultural byproducts. Compared to Mycelium leather, Pinatex features a unique natural texture and requires less water and chemical processing, making it a popular choice in ethical fashion accessories.
Environmental Impact: Mycelium vs Pineapple Leather
Mycelium leather, derived from fungal mycelium, offers a sustainable alternative with rapid growth rates and minimal water usage compared to traditional leather. Pineapple leather, made from pineapple leaf fibers, utilizes agricultural waste, reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices. Both materials exhibit lower carbon footprints than animal leather, but mycelium's faster biodegradability and less intensive cultivation make it particularly advantageous for environmentally conscious belt production.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Mycelium leather offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it highly suitable for belt production with long-lasting performance under daily stress. Pineapple leather, while eco-friendly and lightweight, tends to be less durable and more susceptible to surface damage over time. The fungal structure of mycelium creates a tough, flexible material that outperforms pineapple leather in tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Mycelium leather offers a unique, fibrous texture with natural earthy tones that enhance the rustic aesthetic of belts, while pineapple leather provides a smoother surface with subtle grain patterns ideal for refined, polished designs. The design flexibility of mycelium leather allows for diverse finishes and dye absorption, supporting bold and organic styles, whereas pineapple leather's consistent texture excels in precise embossing and intricate detailing. Both materials contribute innovative sustainability, but their distinct visual and tactile qualities cater to different fashion aesthetics and creative requirements in belt design.
Production Processes Explained
Mycelium leather production involves cultivating mushroom roots in controlled environments, where the mycelium fibers grow into dense mats that are harvested, dried, and treated to create a leather-like material with natural durability and flexibility. Pineapple leather, known as Pinatex, is made by extracting cellulose fibers from pineapple leaf waste, which undergoes a wet processing method to form a non-woven mesh that is then coated with bio-based polymers for enhanced strength and water resistance. Both processes emphasize sustainability by utilizing agricultural waste and minimizing chemical treatments, but mycelium leather offers faster growth cycles, while pineapple leather relies on existing farming byproducts to reduce environmental impact.
Cost and Market Availability
Mycelium leather typically costs between $50 to $100 per square meter, making it moderately priced but less widely available due to limited large-scale production. Pineapple leather, also known as Pinatex, ranges from $30 to $70 per square meter and enjoys broader market availability thanks to more established supply chains and commercial partnerships. Both materials offer sustainable alternatives to traditional leather, but pineapple leather's cost-effectiveness and market presence make it more accessible for belt manufacturing.
Animal Welfare and Ethical Considerations
Mycelium leather, derived from fungal root structures, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional leather by eliminating the need for animal exploitation, aligning with strong animal welfare values. Pineapple leather, made from pineapple leaf fibers, also supports ethical fashion by repurposing agricultural waste and reducing environmental impact without harming animals. Both materials promote cruelty-free production processes, appealing to consumers prioritizing ethical and vegan-friendly belts.
Which Is Better for Belts: Mycelium or Pineapple Leather?
Mycelium leather offers exceptional durability and flexibility, making it ideal for belts that require long-lasting wear and comfort, while pineapple leather provides a lighter, more breathable alternative with a unique texture. Mycelium's rapid growth and natural rigidity contribute to its resilience against stretching and cracking, which is crucial for belt longevity. Pineapple leather excels in eco-friendliness and vibrant aesthetics, but mycelium leather's superior strength and moisture resistance generally make it the better choice for functional, everyday belts.
Infographic: Mycelium leather vs Pineapple leather for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com