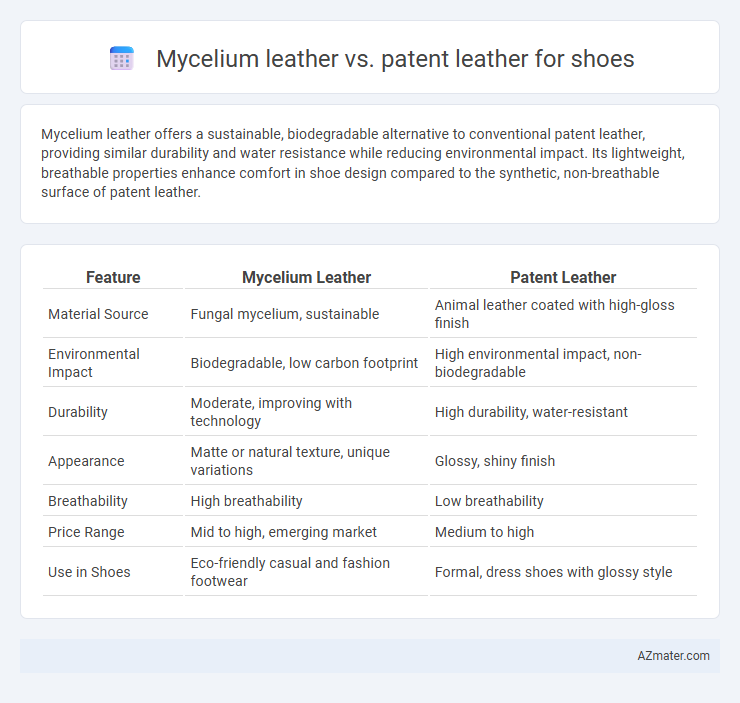
Mycelium leather offers a sustainable, biodegradable alternative to conventional patent leather, providing similar durability and water resistance while reducing environmental impact. Its lightweight, breathable properties enhance comfort in shoe design compared to the synthetic, non-breathable surface of patent leather.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mycelium Leather | Patent Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Fungal mycelium, sustainable | Animal leather coated with high-gloss finish |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | High environmental impact, non-biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate, improving with technology | High durability, water-resistant |
| Appearance | Matte or natural texture, unique variations | Glossy, shiny finish |
| Breathability | High breathability | Low breathability |
| Price Range | Mid to high, emerging market | Medium to high |
| Use in Shoes | Eco-friendly casual and fashion footwear | Formal, dress shoes with glossy style |
Introduction to Mycelium and Patent Leather
Mycelium leather, derived from the root structure of mushrooms, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional materials by mimicking the texture and durability of animal leather. Patent leather is a type of coated leather distinguished by its glossy, high-shine finish achieved through a lacquer or plastisol coating over a cotton or leather base. Both materials differ significantly in environmental impact and aesthetic properties, with mycelium leather emphasizing eco-friendly innovation while patent leather is prized for its polished appearance and water-resistant surface.
Composition and Production Processes
Mycelium leather is crafted from the root structure of fungi, utilizing a sustainable, bio-based growth process that involves cultivating mycelium on organic substrates, resulting in a biodegradable and eco-friendly material. Patent leather, in contrast, is traditionally made from coated animal hide, involving a multi-step tanning process followed by application of layers of lacquer or plastic to achieve its high-gloss finish, which is less environmentally sustainable. Mycelium leather production emphasizes low environmental impact and renewable resources, whereas patent leather relies on chemical-intensive treatments and synthetic coatings to enhance durability and shine.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Mycelium leather, derived from mushroom roots, offers a biodegradable and low-impact alternative to traditional patent leather, which relies on petrochemical-based coatings and toxic tanning processes harmful to ecosystems. The production of mycelium leather consumes significantly less water and energy, reducing carbon emissions compared to the highly polluting chromium tanning in patent leather manufacturing. Choosing mycelium leather for shoes supports circular economy principles by minimizing waste and promoting renewable materials in sustainable fashion.
Durability and Longevity
Mycelium leather offers remarkable durability due to its fibrous cellular structure, making it resistant to wear and tear while maintaining flexibility over time. Patent leather, characterized by its glossy, plastic-coated surface, tends to be less durable as the coating can crack and peel with prolonged use and exposure to environmental factors. Compared to patent leather, mycelium leather ensures greater longevity by resisting cracking, peeling, and environmental degradation, resulting in shoes that maintain their integrity and appearance for an extended period.
Comfort and Breathability
Mycelium leather offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to patent leather, making it ideal for increased comfort during extended wear. Its natural, porous structure allows better airflow, reducing foot sweat and odor buildup, whereas patent leather's non-breathable surface can cause overheating and discomfort. Mycelium leather's flexibility also provides a softer, more adaptive fit, enhancing overall foot comfort in shoes.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Mycelium leather offers a unique, textured aesthetic that mimics natural leather with eco-friendly appeal, making it ideal for contemporary and sustainable shoe designs. Patent leather provides a glossy, high-shine finish that enhances formal and classic shoe styles with a sleek and polished look. While patent leather excels in delivering bold and reflective surfaces, mycelium leather allows greater customization in color and texture, supporting innovative and diverse footwear designs.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Mycelium leather offers a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional patent leather, with production costs generally lower due to its renewable fungal biomass source compared to the energy-intensive processes of patent leather manufacturing. Market availability of mycelium leather is rapidly expanding, driven by growing demand for eco-friendly footwear, yet it remains less prevalent and more niche than widely available patent leather, which benefits from established supply chains and mass production. Pricing for mycelium leather shoes varies based on innovation and scale but is expected to decrease as technology advances, while patent leather shoes maintain stable pricing due to mature market dynamics.
Ethical Considerations
Mycelium leather offers a sustainable alternative to patent leather by utilizing fungal networks that require less water, land, and chemicals, significantly reducing environmental impact. Patent leather, derived from animal hides with synthetic coatings, raises ethical concerns related to animal welfare and pollution from toxic finishes. Choosing mycelium leather supports cruelty-free fashion practices and promotes circular economy principles, making it a preferable option for ethically conscious consumers.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Mycelium leather requires minimal maintenance, needing only occasional wiping with a damp cloth and natural conditioners to preserve its texture and durability. Patent leather demands regular cleaning with a soft cloth and specialized patent leather cleaners to maintain its glossy finish and prevent cracking. Unlike patent leather, mycelium leather is more breathable and resistant to moisture damage, reducing the risk of stiffness and cracking over time.
Future Outlook in Footwear Industry
Mycelium leather offers a sustainable alternative to traditional patent leather, reducing environmental impact through its biodegradable and renewable properties. Innovations in mycelium processing enable customization in texture and durability, positioning it as a viable material for eco-conscious footwear brands. Market trends indicate growing consumer demand for cruelty-free and eco-friendly shoes, forecasting increased adoption of mycelium leather in the footwear industry.
Infographic: Mycelium leather vs Patent leather for Shoe
 azmater.com
azmater.com