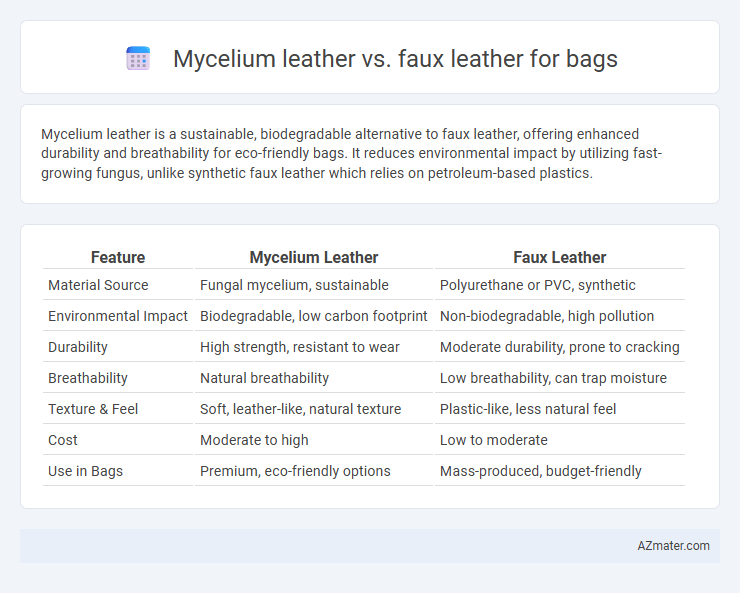
Mycelium leather is a sustainable, biodegradable alternative to faux leather, offering enhanced durability and breathability for eco-friendly bags. It reduces environmental impact by utilizing fast-growing fungus, unlike synthetic faux leather which relies on petroleum-based plastics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mycelium Leather | Faux Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Fungal mycelium, sustainable | Polyurethane or PVC, synthetic |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high pollution |
| Durability | High strength, resistant to wear | Moderate durability, prone to cracking |
| Breathability | Natural breathability | Low breathability, can trap moisture |
| Texture & Feel | Soft, leather-like, natural texture | Plastic-like, less natural feel |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Use in Bags | Premium, eco-friendly options | Mass-produced, budget-friendly |
Introduction to Mycelium Leather and Faux Leather
Mycelium leather, derived from the root structure of mushrooms, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional materials, displaying natural breathability and unique texture. Faux leather, typically made from polyurethane or PVC, mimics the appearance of genuine leather while being more affordable but less environmentally friendly due to its synthetic composition. Comparing these materials for bags highlights mycelium leather's innovation in eco-conscious fashion contrasted with faux leather's widespread use and durability.
Material Origins: Natural vs Synthetic
Mycelium leather is derived from the root structure of fungi, offering a fully natural and biodegradable alternative to traditional materials used in bag manufacturing. Faux leather, typically made from synthetic plastics like polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride, relies on petrochemical processes that contribute to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Choosing mycelium leather supports sustainable material innovation by harnessing renewable biological sources instead of fossil-fuel-based synthetics.
Production Processes Compared
Mycelium leather, derived from fungal mycelium, undergoes a bio-fabrication process where mushroom roots are grown and treated to form a durable, biodegradable material with a lower environmental impact than traditional options. Faux leather, typically made from plastic-based materials like polyurethane or PVC, involves chemical synthesis and polymerization that emit more greenhouse gases and contribute to microplastic pollution. The mycelium production process uses less water and energy, making it a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative for bag manufacturing compared to the resource-intensive and non-biodegradable faux leather production.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Mycelium leather, derived from mushroom roots, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional faux leather by utilizing biodegradable materials and requiring significantly less water and energy during production. Faux leather, typically made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyurethane (PU), relies on fossil fuels and releases harmful chemicals, contributing to pollution and non-biodegradable waste. Life cycle assessments highlight mycelium leather's lower carbon footprint and reduced environmental toxicity, making it an eco-friendlier choice for bags.
Durability and Longevity
Mycelium leather offers superior durability and longevity compared to conventional faux leather, as its natural fiber structure provides enhanced resistance to wear and tear. Unlike plastic-based faux leather, mycelium is biodegradable and maintains strength over time without cracking or peeling. Bags crafted from mycelium leather demonstrate excellent tensile strength, making them a sustainable and long-lasting alternative to synthetic options.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Mycelium leather offers a unique organic texture and natural variations that enhance the aesthetic appeal of bags, providing an authentic and eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials. Its flexible composition allows designers to experiment with intricate patterns, embossing, and dyeing techniques that mimic genuine leather's richness while maintaining sustainability. Faux leather, typically made from polyurethane or PVC, provides a consistent finish and wide color range but often lacks the depth and natural feel that mycelium leather achieves, limiting high-end design versatility.
Comfort and Usability in Bags
Mycelium leather offers superior breathability and flexibility compared to traditional faux leather, enhancing comfort during extended wear. The natural fibers in mycelium materials adapt to body temperature and reduce moisture buildup, making bags more user-friendly for diverse climates. Faux leather, typically made from PVC or PU, often lacks the same durability and comfort, leading to stiffness and less ergonomic usability in bag designs.
Price and Market Accessibility
Mycelium leather is emerging as an eco-friendly alternative with a higher price point, typically ranging from $150 to $300 per square meter, reflecting its sustainable production process and limited availability. Faux leather is significantly more affordable, averaging $20 to $50 per square meter, and benefits from widespread market accessibility and mass production. Consumers seeking sustainable options face limited sourcing and higher costs with mycelium leather, while faux leather remains easily obtainable and budget-friendly in the bag manufacturing industry.
Consumer Perceptions and Ethical Considerations
Mycelium leather, derived from mushroom roots, appeals to eco-conscious consumers due to its biodegradability and lower environmental footprint compared to traditional faux leather, which is often made from non-biodegradable plastics. Consumers increasingly perceive mycelium leather as a sustainable and innovative alternative that supports cruelty-free fashion, contrasting with faux leather's association with synthetic, petroleum-based materials and potential microplastic pollution. Ethical considerations favor mycelium leather for promoting natural resource use and reduced animal harm, while faux leather raises concerns about long-term environmental impact despite being animal-friendly.
Future Trends in Sustainable Bag Materials
Mycelium leather offers a biodegradable and low-impact alternative to faux leather, which is typically made from PVC or PU plastics that contribute to environmental pollution. Innovations in mycelium cultivation enable scalable production with customizable textures, making it a promising material for eco-conscious bag manufacturers aiming to reduce carbon footprints. The growing consumer demand for sustainable, cruelty-free products drives investment in mycelium leather technology, positioning it as a leading trend in the future of sustainable bag materials.
Infographic: Mycelium leather vs Faux leather for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com