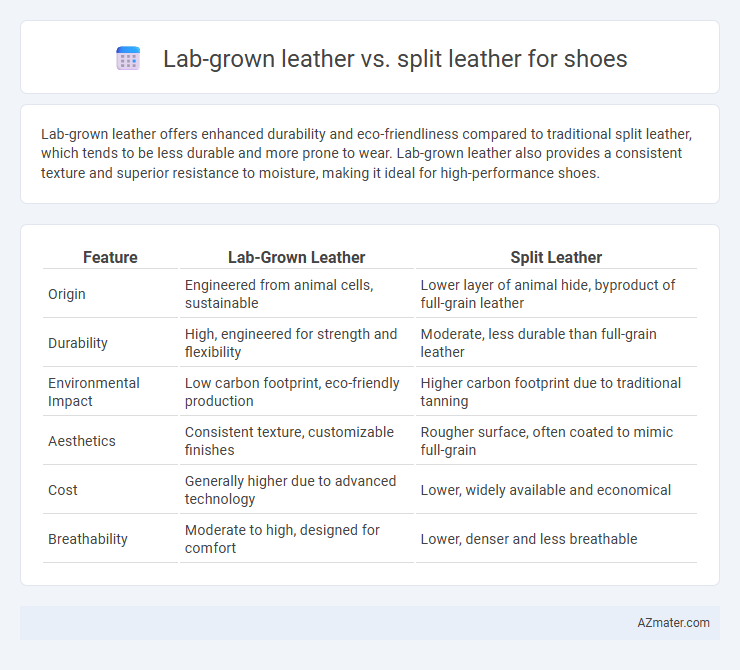
Lab-grown leather offers enhanced durability and eco-friendliness compared to traditional split leather, which tends to be less durable and more prone to wear. Lab-grown leather also provides a consistent texture and superior resistance to moisture, making it ideal for high-performance shoes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lab-Grown Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Engineered from animal cells, sustainable | Lower layer of animal hide, byproduct of full-grain leather |
| Durability | High, engineered for strength and flexibility | Moderate, less durable than full-grain leather |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, eco-friendly production | Higher carbon footprint due to traditional tanning |
| Aesthetics | Consistent texture, customizable finishes | Rougher surface, often coated to mimic full-grain |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced technology | Lower, widely available and economical |
| Breathability | Moderate to high, designed for comfort | Lower, denser and less breathable |
Introduction to Lab-Grown Leather and Split Leather
Lab-grown leather, cultivated from animal cells in controlled environments, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional leather by reducing environmental impact and eliminating animal slaughter. Split leather, derived from the fibrous layers beneath the top grain of animal hides, maintains durability but often requires additional treatments to enhance appearance and performance in shoe production. The innovative use of lab-grown leather in footwear prioritizes ethical sourcing and consistent quality, while split leather remains favored for its affordability and textured finish.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Lab-grown leather for shoes utilizes cellular agriculture techniques, cultivating collagen fibers in bioreactors to create a sustainable and animal-free material with controlled thickness and texture. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of animal hides, undergoes mechanical splitting and chemical treatments to enhance durability but often lacks uniformity and sustainability. Manufacturing lab-grown leather reduces environmental impact by eliminating the need for animal farming and extensive tanning processes compared to traditional split leather production.
Material Composition and Structure
Lab-grown leather consists of cultured animal cells grown in a lab environment, resulting in a uniform, fibrous protein matrix without the fibrous grain layers found in traditional leather. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of animal hide, retains a fibrous structure but lacks the dense grain surface, making it more porous and less durable than full-grain leather. The material composition of lab-grown leather offers consistent texture and reduced environmental impact, while split leather relies on natural collagen fibers but varies in strength and finish due to its altered grain structure.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Lab-grown leather exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to traditional split leather, as its engineered structure reduces the likelihood of cracking and peeling over time. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of animal hide, tends to be less resilient and more prone to surface damage due to its fibrous texture. Footwear crafted from lab-grown leather offers enhanced long-term performance, maintaining its appearance and structural integrity under frequent use and harsh conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lab-grown leather offers a significantly lower environmental footprint than split leather by reducing water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during production. Split leather, derived from lower layers of animal hides, involves extensive chemical treatments that contribute to pollution and waste. Choosing lab-grown leather supports sustainable fashion by minimizing deforestation, animal farming, and toxic tanning processes often associated with traditional leather manufacturing.
Comfort and Breathability in Footwear
Lab-grown leather offers superior comfort and breathability in footwear due to its engineered porous structure that promotes airflow and moisture-wicking, reducing foot sweat and odor. Split leather, being a lower-quality layer derived from the hide's fibrous underside, often lacks uniformity and breathability, leading to less ventilation and increased heat retention inside shoes. Footwear made from lab-grown leather enhances overall wearability by combining durability with advanced breathability features, unlike traditional split leather.
Aesthetic Appeal and Customization Options
Lab-grown leather offers a consistently smooth texture and vibrant, uniform color, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of shoes with a modern, high-quality finish compared to the more variable grain and natural imperfections found in split leather. Customization options are extensive with lab-grown leather, allowing for precise control over thickness, pigmentation, and pattern designs, while split leather provides limited customization due to its origin from lower layers of animal hide. The innovative manufacturing process of lab-grown leather enables tailored shoe designs that meet specific style preferences and performance requirements, surpassing traditional split leather's adaptability.
Cost Differences and Market Availability
Lab-grown leather for shoes typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced biotechnological processes, whereas split leather is more affordable, derived from the lower layers of cowhide. Market availability favors split leather, widely used in budget-friendly and mid-range footwear, while lab-grown leather remains limited to premium and experimental collections due to scale and price constraints. Cost differences influence adoption rates significantly, with split leather dominating mass-market shoes and lab-grown leather targeting eco-conscious consumers willing to pay a premium.
Ethical Considerations in Material Sourcing
Lab-grown leather offers a sustainable alternative to traditional split leather by eliminating the need for animal slaughter, reducing environmental impact, and addressing animal welfare concerns in shoe manufacturing. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of animal hides, often involves resource-intensive tanning processes and contributes to ethical controversies surrounding animal rights and deforestation. Choosing lab-grown leather enhances ethical sourcing by promoting cruelty-free production and minimizing ecological damage within the footwear industry.
Future Trends in Shoe Materials
Lab-grown leather is rapidly emerging as a sustainable alternative to traditional split leather, harnessing biotechnology to reduce environmental impact and improve durability in shoe manufacturing. Innovations in lab-grown leather enable customizable textures and enhanced resistance to wear, addressing limitations seen in conventional split leather's inconsistent quality and shorter lifespan. The future of shoe materials leans toward integrating lab-grown leather with recycled components, promoting eco-friendly production while meeting consumer demand for high-performance, cruelty-free footwear.
Infographic: Lab-grown leather vs Split leather for Shoe
 azmater.com
azmater.com