Fish leather offers superior durability and water resistance compared to pig leather, making it ideal for wallets exposed to moisture. Its unique texture and eco-friendly tanning process provide a sustainable alternative to traditional pig leather wallets.
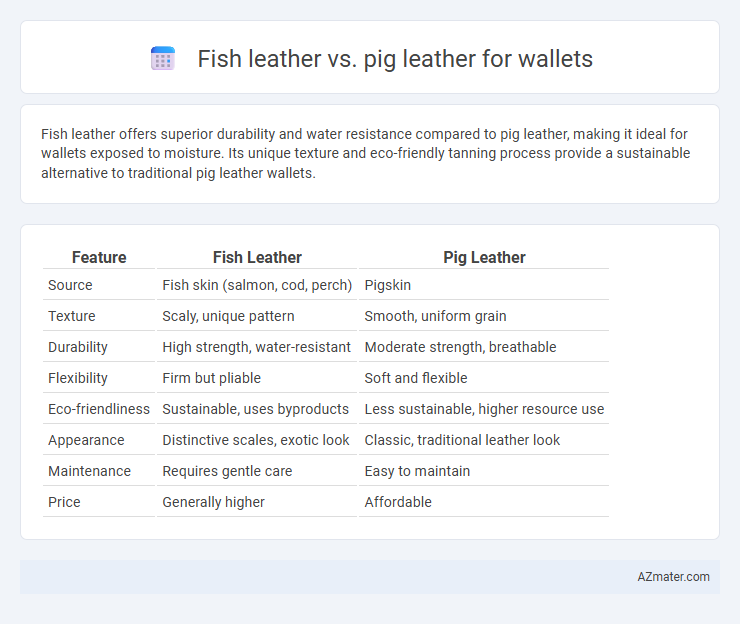
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fish Leather | Pig Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fish skin (salmon, cod, perch) | Pigskin |
| Texture | Scaly, unique pattern | Smooth, uniform grain |
| Durability | High strength, water-resistant | Moderate strength, breathable |
| Flexibility | Firm but pliable | Soft and flexible |
| Eco-friendliness | Sustainable, uses byproducts | Less sustainable, higher resource use |
| Appearance | Distinctive scales, exotic look | Classic, traditional leather look |
| Maintenance | Requires gentle care | Easy to maintain |
| Price | Generally higher | Affordable |
Introduction to Fish Leather and Pig Leather
Fish leather, derived from the durable skins of fish like salmon and cod, offers a unique texture and eco-friendly alternative to traditional pig leather commonly used in wallets. Pig leather is known for its toughness and natural breathability, featuring a distinctive grain pattern that ages well over time. Both materials provide sustainable options for wallet craftsmanship, with fish leather standing out for its water resistance and lightweight properties, while pig leather excels in flexibility and durability.
Origins and Sourcing of Fish and Pig Leather
Fish leather originates primarily from species like salmon, perch, and cod found in Nordic and Southeast Asian waters, often utilizing byproducts from the fishing industry to minimize waste. Pig leather comes from domesticated pigs raised mainly in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, sourced from farms where pigs are bred primarily for meat production. The sustainable sourcing of fish leather leverages leftover skins from fish processing, whereas pig leather depends on traditional livestock farming, impacting environmental footprints differently.
Unique Texture and Appearance Comparison
Fish leather offers a distinct, scale-patterned texture that is naturally embossed, creating a visually striking surface compared to the smooth, grainy appearance of pig leather. The iridescent qualities of fish leather reflect light differently, giving each wallet a unique shimmer and depth that pig leather lacks. Pig leather features a more uniform texture with visible pores and a matte finish, making fish leather wallets stand out for their exotic and tactile appeal.
Durability and Longevity: Fish vs Pig Leather
Fish leather, especially from species like salmon and cod, offers exceptional durability due to its dense fiber structure, making it highly resistant to wear and tear compared to pig leather. Pig leather, while tough and flexible, tends to absorb moisture more easily, which can shorten its lifespan when exposed to prolonged humidity or frequent use. For wallets requiring longevity, fish leather provides a more resilient option with natural water resistance and slower aging characteristics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fish leather offers a more sustainable alternative to pig leather for wallets due to its utilization of byproducts from the fishing industry, reducing waste and lowering environmental impact. Unlike pig leather, which requires intensive livestock farming contributing to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and high water consumption, fish leather production typically involves less resource-intensive processes. The biodegradability and durability of fish leather further enhance its environmental benefits, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious consumers.
Cost Differences Between Fish and Pig Leather
Fish leather generally costs more than pig leather due to the labor-intensive tanning process and the rarity of high-quality fish skins, such as salmon or cod. Pig leather is more widely available and produced in larger quantities, making it more affordable for wallet manufacturing. The price gap reflects not only material availability but also the unique texture and durability that premium fish leather offers.
Comfort and Practicality in Daily Use
Fish leather offers a lightweight, flexible texture that adapts easily to hand movements, enhancing comfort in daily wallet use. Pig leather provides a durable, thicker grain structure that resists wear and tear, making it highly practical for frequent handling and long-term use. Both materials balance comfort and practicality, but fish leather excels in softness while pig leather delivers superior strength and resilience.
Leather Maintenance and Care Tips
Fish leather, known for its unique scale pattern and water resistance, requires gentle cleaning with a damp cloth and occasional application of a specialized leather conditioner to maintain flexibility and prevent cracking. Pig leather, durable and porous, benefits from routine wiping and the use of leather moisturizers to avoid drying and preserve its softness over time. Both types demand storage in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent discoloration and structural damage.
Fashion and Design Versatility
Fish leather offers a unique texture and natural scale patterns that create distinctive, eye-catching wallets favored in high-fashion markets. Pig leather provides durability and a smooth finish, making it versatile for both classic and contemporary wallet designs. Designers prefer fish leather for eco-conscious, statement pieces, while pig leather supports a broader range of styles with its adaptable surface.
Which Leather Is Best for Wallets?
Fish leather, known for its unique texture and high durability, offers a lightweight and water-resistant option ideal for wallets requiring longevity and style. Pig leather, renowned for its softness and breathability, provides excellent flexibility and comfort, making it a popular choice for everyday wallet use. Choosing the best leather depends on preferences for texture, durability, and environmental impact, with fish leather being more sustainable due to its byproduct origin.
Infographic: Fish leather vs Pig leather for Wallet
 azmater.com
azmater.com