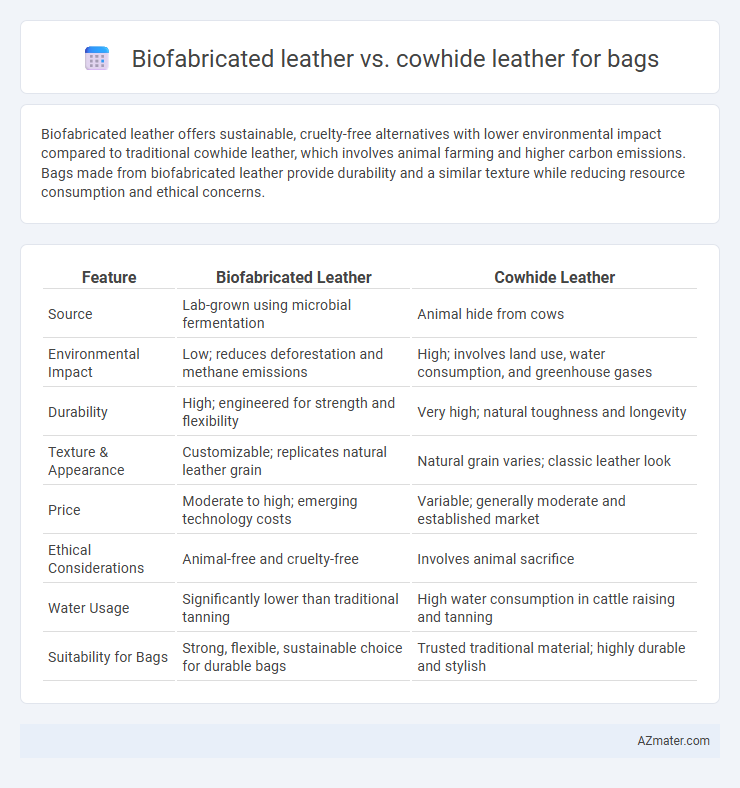
Biofabricated leather offers sustainable, cruelty-free alternatives with lower environmental impact compared to traditional cowhide leather, which involves animal farming and higher carbon emissions. Bags made from biofabricated leather provide durability and a similar texture while reducing resource consumption and ethical concerns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Cowhide Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown using microbial fermentation | Animal hide from cows |
| Environmental Impact | Low; reduces deforestation and methane emissions | High; involves land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gases |
| Durability | High; engineered for strength and flexibility | Very high; natural toughness and longevity |
| Texture & Appearance | Customizable; replicates natural leather grain | Natural grain varies; classic leather look |
| Price | Moderate to high; emerging technology costs | Variable; generally moderate and established market |
| Ethical Considerations | Animal-free and cruelty-free | Involves animal sacrifice |
| Water Usage | Significantly lower than traditional tanning | High water consumption in cattle raising and tanning |
| Suitability for Bags | Strong, flexible, sustainable choice for durable bags | Trusted traditional material; highly durable and stylish |
Introduction to Biofabricated Leather and Cowhide Leather
Biofabricated leather is an innovative material created through cellular agriculture, using cultured animal cells or plant-based proteins to replicate the texture and durability of traditional leather without animal harm. Cowhide leather, derived from the tanned hide of cows, is renowned for its strength, natural grain patterns, and long-lasting quality widely used in premium bags. The emerging biofabricated leather offers sustainable alternatives with reduced environmental impact, while cowhide leather remains a benchmark for luxury, texture, and heritage craftsmanship.
Raw Materials and Production Processes
Biofabricated leather utilizes lab-grown collagen produced through microbial fermentation, minimizing reliance on animal hides, while cowhide leather depends on traditional cattle farming with environmental impacts like deforestation and methane emissions. The production of biofabricated leather involves controlled bioreactors and scalable tissue engineering techniques, ensuring consistent material quality and reduced waste. In contrast, cowhide leather requires chemical-intensive tanning processes, often involving chromium salts, which contribute to toxic effluent disposal challenges and longer production cycles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Biofabricated leather significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating the need for animal farming, which decreases greenhouse gas emissions, land use, and water consumption compared to traditional cowhide leather. The production process of biofabricated leather utilizes renewable resources and generates fewer pollutants, promoting greater sustainability in the fashion industry. Cowhide leather, while durable, relies on livestock farming that contributes to deforestation and high carbon footprints, making biofabricated alternatives more eco-friendly for bag manufacturing.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Biofabricated leather offers enhanced resistance to cracking and water damage compared to traditional cowhide leather, making it ideal for high-performance bags exposed to varying weather conditions. Cowhide leather provides robust tensile strength and develops a natural patina over time, improving its durability with proper care. The sustainable manufacturing process of biofabricated leather contributes to consistent quality and eliminates the variability found in animal hides, ensuring reliable performance in daily use.
Aesthetics and Customization Options
Biofabricated leather offers a sleek, uniform appearance with the ability to mimic various textures and colors, enhancing aesthetic versatility for bags. Cowhide leather features natural grain and unique imperfections that provide distinctive character and a classic look cherished by traditional leather enthusiasts. Customization options are broader with biofabricated leather due to its controlled production process, allowing precise color matching and pattern designs that are difficult to achieve with the organic inconsistencies of cowhide.
Cost Analysis: Biofabricated vs. Cowhide Leather
Biofabricated leather typically commands a higher initial price per square meter, ranging from $150 to $300, compared to cowhide leather, which usually costs between $50 and $100. Manufacturing biofabricated leather involves advanced biotechnological processes, driving up production expenses, whereas cowhide benefits from established supply chains and economies of scale. Despite higher upfront costs, biofabricated leather offers potential long-term savings due to lower environmental compliance fees and waste management costs.
Ethical Considerations in Material Choices
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional cowhide leather, eliminating the need for animal farming and reducing its associated ethical concerns such as animal welfare and environmental degradation. Cowhide leather production involves livestock farming practices that raise issues of animal rights and contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation. Choosing biofabricated leather supports ethical material sourcing by minimizing animal exploitation and promoting innovations that align with sustainable and humane manufacturing principles.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Biofabricated leather offers an eco-friendly alternative to cowhide leather, with consumers increasingly valuing sustainability and animal welfare in their purchasing decisions. Market trends highlight a growing demand for biofabricated leather bags, driven by advancements in biotechnology and a shift toward cruelty-free materials. Despite traditional preferences for cowhide leather's durability and texture, innovative biofabricated options are gaining traction among younger, environmentally conscious consumers.
Care, Maintenance, and Longevity
Biofabricated leather requires minimal maintenance, as it resists cracking and fading better than traditional cowhide leather, making it ideal for durable bags. Unlike cowhide leather, which demands regular conditioning and careful exposure to moisture to prevent drying and cracking, biofabricated leather maintains its appearance with simple cleaning using a damp cloth. The longevity of biofabricated leather bags also surpasses cowhide due to its engineered resistance to wear, reducing the need for frequent repairs or treatments.
Future Outlook for Leather Bags
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional cowhide leather, reducing environmental impact by minimizing water usage and greenhouse gas emissions. Advances in biotechnology are rapidly improving the durability and texture of biofabricated leather, making it increasingly viable for high-quality leather bags. The future outlook for leather bags favors biofabricated options as consumer demand shifts towards eco-friendly materials and scalable production methods.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Cowhide leather for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com