Bonded leather belts offer affordability and a consistent finish by combining genuine leather fibers with adhesives, while suede leather belts provide a softer texture and a luxurious matte appearance derived from the underside of the animal hide. Choosing between bonded leather and suede leather hinges on durability preferences and desired aesthetic, with bonded leather being more resistant to wear and suede delivering a distinctive tactile experience.
Table of Comparison
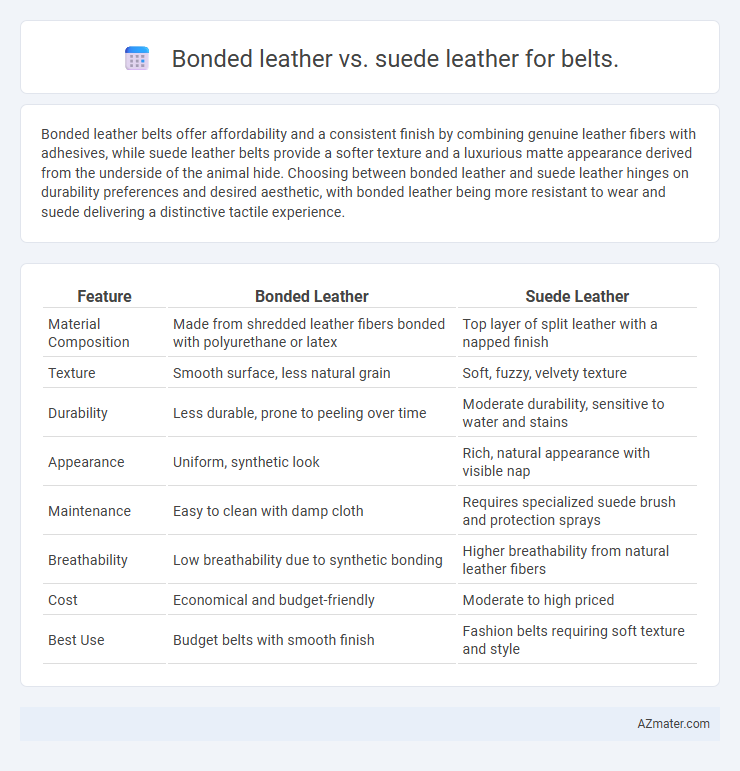
| Feature | Bonded Leather | Suede Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Made from shredded leather fibers bonded with polyurethane or latex | Top layer of split leather with a napped finish |
| Texture | Smooth surface, less natural grain | Soft, fuzzy, velvety texture |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to peeling over time | Moderate durability, sensitive to water and stains |
| Appearance | Uniform, synthetic look | Rich, natural appearance with visible nap |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean with damp cloth | Requires specialized suede brush and protection sprays |
| Breathability | Low breathability due to synthetic bonding | Higher breathability from natural leather fibers |
| Cost | Economical and budget-friendly | Moderate to high priced |
| Best Use | Budget belts with smooth finish | Fashion belts requiring soft texture and style |
Introduction to Bonded Leather and Suede Leather
Bonded leather is created by combining shredded genuine leather fibers with a polyurethane binder, offering an affordable and eco-friendly alternative to full-grain leather for belts. Suede leather, derived from the underside of animal hides, features a soft, napped surface that provides a distinct texture and a more casual appearance. Both materials have unique characteristics suited for belt construction, with bonded leather emphasizing durability and cost-efficiency, while suede highlights softness and aesthetic appeal.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Bonded leather belts are crafted by combining shredded leather fibers with polyurethane or latex binders, resulting in an artificial composite that mimics genuine leather while reducing cost. Suede leather belts originate from the inner split layer of animal hides, primarily calf or goat, featuring a napped finish achieved through buffing and sanding for softness and texture. The manufacturing process of suede involves precise tanning and careful abrasion to maintain durability, whereas bonded leather relies on compressing leather scraps into sheets, affecting longevity and feel.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Bonded leather belts typically exhibit a smooth, consistent surface with a polished finish, offering a sleek and uniform appearance, while suede leather belts feature a soft, napped texture that provides a matte, velvety look distinguished by its natural grain. The texture of bonded leather feels firmer and less flexible, whereas suede leather is characterized by its supple, slightly fuzzy touch that enhances grip and comfort. In terms of appearance, bonded leather tends to look more synthetic and uniform, whereas suede leather displays unique variations and a richer, more organic aesthetic.
Durability and Longevity
Bonded leather belts feature a composite material made from leather scraps fused with polyurethane, resulting in lower durability and susceptibility to peeling over time compared to suede leather. Suede leather, derived from the underside of animal hides, offers a softer texture with enhanced breathability but requires more maintenance to preserve its longevity. For belt longevity, genuine suede leather provides better wear resistance and durability than bonded leather, which tends to deteriorate faster under frequent use.
Comfort and Flexibility
Bonded leather belts offer moderate comfort and flexibility due to their composite structure, but they may stiffen over time and are less breathable compared to suede leather. Suede leather belts provide superior softness and flexibility, conforming easily to the wrist's shape and enhancing overall comfort during extended wear. The natural nap of suede also allows for better airflow, making suede belts more comfortable in warm conditions.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Bonded leather belts require minimal maintenance with occasional wiping using a damp cloth to remove dirt, but they are prone to cracking and peeling over time due to their synthetic bonding process. Suede leather belts need more careful maintenance, including regular brushing with a suede brush to lift the nap and prevent dirt buildup, as well as avoiding water exposure to maintain texture and prevent stains. Both materials benefit from storing belts in a cool, dry place, yet suede demands more frequent conditioning with specialized suede protectants to preserve its softness.
Price and Affordability
Bonded leather belts offer a highly affordable option, typically costing significantly less than suede leather belts due to their composite material made from leather scraps and synthetic binders. Suede leather belts, crafted from the soft underside of animal hides, generally come with a higher price point reflecting the quality and durability of genuine leather. For buyers prioritizing budget, bonded leather provides cost-effective style, while suede delivers superior texture and longevity at a premium cost.
Environmental Impact
Bonded leather is produced by recycling leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, reducing waste but involving synthetic adhesives that may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Suede leather, derived from the underside of animal hides, requires extensive processing and chemical treatments that contribute to higher water usage and pollution in tanneries. In terms of environmental impact, bonded leather offers waste minimization but has concerns over synthetic components, while suede's natural origin is offset by intensive resource consumption and chemical use during production.
Style and Versatility
Bonded leather belts offer a polished, uniform appearance suitable for formal and casual wear, while suede leather belts provide a textured, matte finish that enhances casual and smart-casual outfits with a stylish, relaxed feel. Bonded leather's smooth surface pairs well with suits and dress pants, whereas suede's soft, velvety texture complements denim and chinos, adding depth to everyday ensembles. Versatility in bonded leather belts lies in their classic look and durability, whereas suede belts excel in adding tactile contrast and contemporary flair to diverse wardrobe choices.
Which Leather is Better for Belts?
Bonded leather, made from leftover leather fibers bonded with polyurethane, offers a budget-friendly, durable option but lacks the natural breathability and aging qualities of genuine leather. Suede leather, derived from the underside of animal hides, provides a soft texture and stylish appearance but requires more care to maintain its look and is less resistant to moisture and wear. For belts, bonded leather suits those seeking affordability and durability, while suede leather is better for consumers prioritizing comfort and a refined, fashion-forward aesthetic.
Infographic: Bonded leather vs Suede leather for Belt
 azmater.com
azmater.com