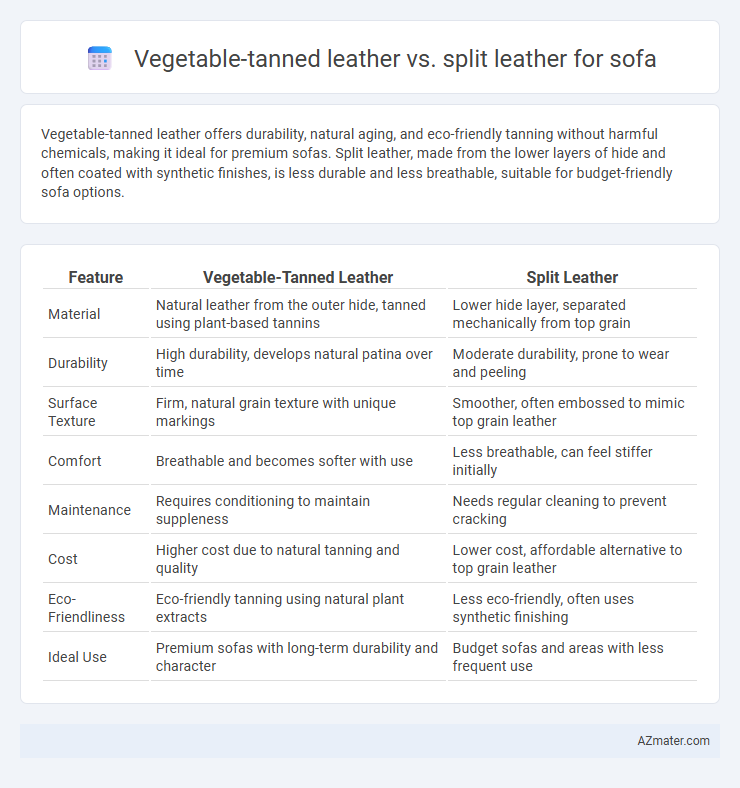
Vegetable-tanned leather offers durability, natural aging, and eco-friendly tanning without harmful chemicals, making it ideal for premium sofas. Split leather, made from the lower layers of hide and often coated with synthetic finishes, is less durable and less breathable, suitable for budget-friendly sofa options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural leather from the outer hide, tanned using plant-based tannins | Lower hide layer, separated mechanically from top grain |
| Durability | High durability, develops natural patina over time | Moderate durability, prone to wear and peeling |
| Surface Texture | Firm, natural grain texture with unique markings | Smoother, often embossed to mimic top grain leather |
| Comfort | Breathable and becomes softer with use | Less breathable, can feel stiffer initially |
| Maintenance | Requires conditioning to maintain suppleness | Needs regular cleaning to prevent cracking |
| Cost | Higher cost due to natural tanning and quality | Lower cost, affordable alternative to top grain leather |
| Eco-Friendliness | Eco-friendly tanning using natural plant extracts | Less eco-friendly, often uses synthetic finishing |
| Ideal Use | Premium sofas with long-term durability and character | Budget sofas and areas with less frequent use |
Introduction to Leather Types for Sofas
Vegetable-tanned leather, crafted using natural tannins from tree bark and plants, offers durability, rich patina development, and eco-friendly qualities ideal for premium sofas. Split leather, derived from the fibrous layers beneath the top grain, is often more affordable but less durable and typically requires a surface coating to enhance appearance and resistance. Choosing between these types influences sofa longevity, texture, and maintenance requirements.
What Is Vegetable-Tanned Leather?
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins found in tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, resulting in a durable, eco-friendly material that develops a rich patina over time. This type of leather is known for its firm texture, breathability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for high-quality sofas that age gracefully. Unlike split leather, which is made from the lower layers of the hide and often coated for appearance, vegetable-tanned leather retains the full-grain surface, offering superior strength and a more authentic, natural look.
What Is Split Leather?
Split leather is derived from the lower layers of a hide after the top grain has been separated, resulting in a material that is less durable and lacks the natural grain patterns of vegetable-tanned leather. This type of leather is often coated with a polyurethane or latex finish to enhance its appearance and durability but cannot match the breathability and aging qualities of vegetable-tanned leather. In contrast, vegetable-tanned leather retains the full hide thickness, offers superior strength, and develops a rich patina over time, making it a premium choice for sofas.
Durability Comparison: Vegetable-Tanned vs Split Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather is known for its superior durability and ability to develop a rich patina over time, making it ideal for long-lasting sofa upholstery. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of a hide, is less durable and more prone to wear and tear, often requiring a protective coating to enhance its lifespan. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather ensures a sturdier, more resilient sofa surface compared to the more budget-friendly but less enduring split leather.
Comfort and Aesthetic Appeal
Vegetable-tanned leather offers a rich, natural patina that enhances the aesthetic appeal of sofas while providing a durable yet supple texture that improves comfort over time. Split leather, derived from the lower layer of the hide, tends to be less breathable and may feel stiffer, affecting long-term comfort but often comes at a lower cost. Opting for vegetable-tanned leather ensures a more luxurious feel and a visually appealing aging process, making it ideal for high-end sofa upholstery.
Environmental Impact and Eco-Friendliness
Vegetable-tanned leather, crafted using natural tannins from tree bark and plants, offers a more eco-friendly option with fewer harmful chemicals and lower environmental pollution compared to chrome-tanned split leather. Split leather, derived from the fibrous lower layers of the hide and commonly treated with synthetic chemicals, typically has a higher environmental footprint due to intensive processing and reduced biodegradability. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather for sofas supports sustainable practices by promoting biodegradability and reducing toxic waste in the leather industry.
Maintenance and Aging Over Time
Vegetable-tanned leather requires minimal maintenance, developing a rich patina that enhances with age, while split leather often demands more frequent cleaning and conditioning to prevent cracking and fading. Over time, vegetable-tanned leather maintains durability and aesthetic appeal as it naturally softens and darkens, whereas split leather tends to deteriorate faster, showing wear and becoming brittle. Proper care extends the lifespan of vegetable-tanned leather more effectively than split leather, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting sofa upholstery.
Cost Differences and Value
Vegetable-tanned leather for sofas commands a higher price due to its natural tanning process, durability, and rich patina development, offering long-term value and enhanced aesthetic appeal. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide and often coated with synthetic finishes, is more affordable but less durable and prone to wear over time, reducing its overall value. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather balances initial investment with longevity, while split leather suits budget-conscious buyers seeking short-term use.
Suitability for Different Sofa Styles
Vegetable-tanned leather offers a rich, natural patina and firmness ideal for classic and traditional sofa styles, enhancing elegance and durability over time. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of hide, provides a more affordable, uniform finish suitable for casual and contemporary sofas, though it lacks the robustness of full-grain vegetable-tanned leather. Choosing between these leathers depends on the desired aesthetic, budget, and long-term wear for specific sofa designs.
Choosing the Best Leather for Your Sofa
Vegetable-tanned leather offers durability and a natural patina that enhances its appearance over time, making it an ideal choice for premium sofas seeking longevity and character. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, is less durable and often finished with synthetic coatings, providing a budget-friendly but less authentic option. When choosing the best leather for your sofa, prioritize vegetable-tanned leather for its natural aging properties and superior strength, especially in high-traffic living spaces.
Infographic: Vegetable-tanned leather vs Split leather for Sofa
 azmater.com
azmater.com