Silica glass offers superior optical clarity and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-precision touchscreen displays. Alumina-silicate glass provides enhanced mechanical strength and scratch resistance, improving durability for everyday touchscreen use.
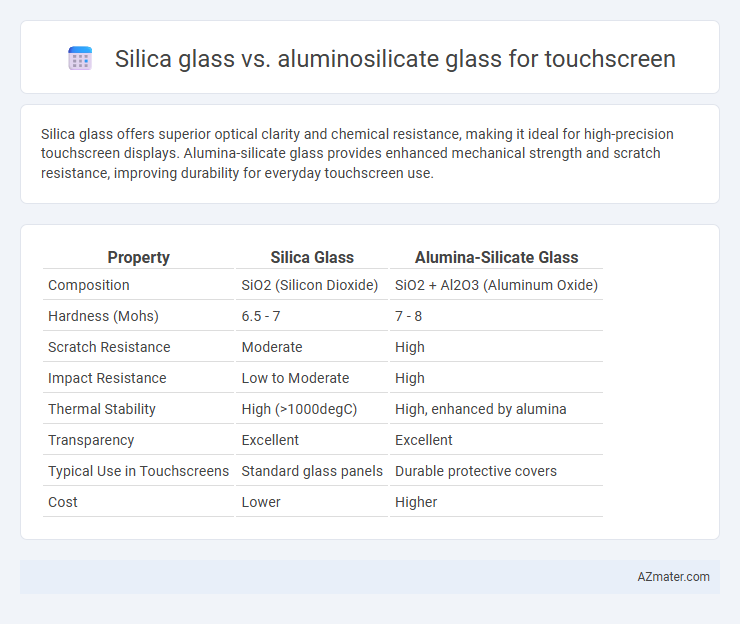
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | Alumina-Silicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | SiO2 (Silicon Dioxide) | SiO2 + Al2O3 (Aluminum Oxide) |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6.5 - 7 | 7 - 8 |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Impact Resistance | Low to Moderate | High |
| Thermal Stability | High (>1000degC) | High, enhanced by alumina |
| Transparency | Excellent | Excellent |
| Typical Use in Touchscreens | Standard glass panels | Durable protective covers |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Touchscreen Glass Materials
Silica glass and alumina-silicate glass are key materials in touchscreen technology, each offering unique properties for optical clarity and durability. Silica glass, composed primarily of silicon dioxide, provides excellent transparency and thermal stability but is relatively brittle. Alumina-silicate glass incorporates aluminum oxide, enhancing toughness and scratch resistance, making it more suitable for protective touchscreen applications.
Overview of Silica Glass Composition
Silica glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), offers exceptional transparency and chemical stability essential for touchscreen applications. Its high purity reduces optical distortion and enhances durability against scratches and thermal stress compared to alumina-silicate glass, which contains additional aluminum oxide (Al2O3) to improve mechanical strength. The precise control of SiO2 content in silica glass optimizes its hardness and resistance to environmental factors, making it a preferred choice for premium touchscreen displays.
Overview of Alumina-Silicate Glass Composition
Alumina-silicate glass used in touchscreens primarily consists of silica (SiO2) combined with aluminum oxide (Al2O3), where alumina content typically ranges from 5% to 15%. The incorporation of aluminum oxide enhances mechanical strength, thermal stability, and resistance to scratches compared to pure silica glass. This balanced composition makes alumina-silicate glass a preferred material for durable, high-performance touchscreen applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Alumina-silicate glass exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to silica glass, making it more resistant to scratches, impacts, and bending stresses in touchscreen applications. The presence of aluminum oxide in alumina-silicate glass enhances its hardness and toughness, providing superior durability and crack resistance under repeated mechanical stress. Silica glass, although chemically stable and transparent, lacks the reinforced structural integrity required for high-performance touchscreens subjected to frequent physical interaction.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Silica glass offers high scratch resistance due to its hardness of approximately 6.5 on the Mohs scale, but it is relatively brittle and prone to shattering under impact. Alumina-silicate glass, commonly used in Gorilla Glass technology, combines enhanced scratch resistance with superior impact resistance due to its chemically strengthened surface and alumina content, which improves toughness. The alumina-silicate composition provides a balanced performance for touchscreens, delivering durability in both abrasion and drop scenarios.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Silica glass offers superior optical clarity and higher transparency due to its low impurity levels and minimal light scattering properties, making it ideal for high-precision touchscreen displays. Alumina-silicate glass provides enhanced durability and scratch resistance but may exhibit slightly reduced transparency and light transmission compared to pure silica glass. Selecting between these materials depends on balancing optical performance with mechanical robustness for touchscreen applications.
Thermal Stability and Durability
Silica glass offers superior thermal stability due to its high melting point around 1713degC and low thermal expansion coefficient, making it resistant to deformation under rapid temperature changes in touchscreen applications. Alumina-silicate glass combines high mechanical strength with enhanced durability, benefiting from alumina's hardness, which improves scratch resistance and impact tolerance in consumer devices. The trade-off between silica glass's exceptional thermal properties and alumina-silicate glass's robust physical endurance informs material selection for various touchscreen environments demanding both thermal resilience and long-term durability.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost
Silica glass offers superior optical clarity and high thermal resistance, but its manufacturing process requires higher sintering temperatures and longer annealing periods, resulting in increased production costs. Alumina-silicate glass undergoes a more energy-efficient chemical strengthening process through ion exchange, enabling mass production at a lower cost with enhanced scratch resistance. The trade-off between durability and manufacturing expense makes alumina-silicate glass the preferred choice for cost-effective touchscreen applications.
Applications in Modern Touchscreen Devices
Silica glass offers exceptional optical clarity and high thermal resistance, making it ideal for precision touchscreen displays in smartphones and tablets. Alumina-silicate glass provides enhanced hardness and impact resistance, widely used in rugged smartphones and industrial touchscreen devices requiring durability. Modern touchscreen applications balance these materials to optimize transparency, strength, and cost-efficiency for consumer electronics and specialized environments.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Touchscreen
Silica glass offers exceptional optical clarity and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance touchscreens requiring superior transparency and durability. Alumina-silicate glass combines high mechanical strength and impact resistance, providing enhanced toughness and scratch resistance for everyday touchscreen devices. Choosing the right glass depends on balancing optical properties, toughness, and cost to meet the specific durability and usability needs of your touchscreen application.
Infographic: Silica glass vs Alumina-silicate glass for Touchscreen
 azmater.com
azmater.com