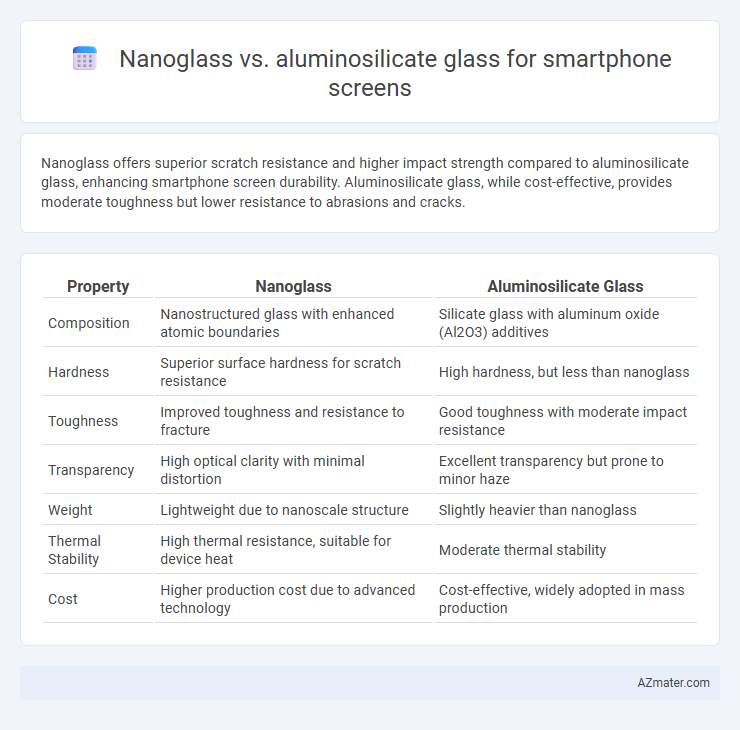
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and higher impact strength compared to aluminosilicate glass, enhancing smartphone screen durability. Aluminosilicate glass, while cost-effective, provides moderate toughness but lower resistance to abrasions and cracks.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanoglass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nanostructured glass with enhanced atomic boundaries | Silicate glass with aluminum oxide (Al2O3) additives |
| Hardness | Superior surface hardness for scratch resistance | High hardness, but less than nanoglass |
| Toughness | Improved toughness and resistance to fracture | Good toughness with moderate impact resistance |
| Transparency | High optical clarity with minimal distortion | Excellent transparency but prone to minor haze |
| Weight | Lightweight due to nanoscale structure | Slightly heavier than nanoglass |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal resistance, suitable for device heat | Moderate thermal stability |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to advanced technology | Cost-effective, widely adopted in mass production |
Introduction: Nanoglass vs Aluminosilicate Glass
Nanoglass and aluminosilicate glass are advanced materials used for smartphone screens, with nanoglass featuring a unique nanoscale structure that enhances strength and scratch resistance. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphones, offers a balanced combination of hardness, chemical durability, and impact resistance. The comparison between nanoglass and aluminosilicate glass centers on their mechanical properties, durability under stress, and potential for improved screen longevity.
What is Nanoglass?
Nanoglass is an advanced material engineered at the nanoscale, offering superior hardness, scratch resistance, and impact absorption compared to traditional glasses like aluminosilicate. Unlike aluminosilicate glass, which is strengthened through chemical ion exchange, nanoglass incorporates nanostructures that enhance durability and reduce brittleness, improving smartphone screen longevity. This innovation provides better clarity and resistance to environmental damage, making nanoglass a promising alternative for next-generation smartphone displays.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a high-strength, chemically strengthened glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, commonly used in smartphone screens for its excellent scratch resistance and durability. Its unique molecular structure provides enhanced toughness and resistance to impacts compared to traditional soda-lime glass, making it ideal for protecting sensitive smartphone displays. Nanoglass, on the other hand, utilizes nanotechnology to offer even greater flexibility and strength, but aluminosilicate remains a popular choice due to its reliable performance and cost-effectiveness.
Key Differences in Chemical Composition
Nanoglass features a nanoscale silica-based matrix with enhanced structural uniformity, while aluminosilicate glass incorporates aluminum oxide (Al2O3) into the silicate network to improve toughness and chemical durability. The presence of alumina increases the glass's resistance to scratches and impacts, whereas nanoglass, due to its unique nanostructure, offers superior mechanical strength and transparency. These chemical composition differences directly influence the thermal stability, hardness, and overall durability of smartphone screens using these materials.
Scratch Resistance Comparison
Nanoglass exhibits superior scratch resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass due to its enhanced hardness and molecular structure designed to minimize surface abrasions. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens, offers robust durability but is more susceptible to visible scratches over prolonged use. The advanced composition of nanoglass enables it to maintain clarity and integrity under harsher conditions, making it a preferred choice for premium devices requiring long-lasting scratch protection.
Impact and Drop Protection
Nanoglass exhibits superior impact resistance and enhanced drop protection compared to aluminosilicate glass, owing to its nanostructured composition that dissipates impact energy more effectively. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable and scratch-resistant, tends to be more brittle under high-impact stress, increasing the risk of screen fractures during drops. The advanced toughness and flexibility of nanoglass technology significantly reduce screen damage, making it a preferable choice for smartphone manufacturers prioritizing drop protection.
Clarity and Touch Sensitivity
Nanoglass offers superior clarity with higher light transmittance and reduced glare compared to aluminosilicate glass, enhancing display sharpness and color accuracy on smartphone screens. Its nanostructured surface also improves touch sensitivity by enabling more precise and responsive capacitive input detection. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable and scratch-resistant, typically lacks the advanced optical properties and tactile responsiveness found in nanoglass technology.
Durability and Longevity
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to traditional aluminosilicate glass, making it highly suited for smartphone screens exposed to daily wear and tear. Its nano-engineered structure enhances longevity by preventing cracks and chips, significantly extending the screen's usable life. Aluminosilicate glass, while durable and chemically strengthened, generally falls short in toughness and long-term resilience against extreme impacts.
Cost and Availability
Nanoglass offers enhanced scratch resistance and durability but comes with higher production costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and limited commercial availability. Aluminosilicate glass, commonly used in smartphone screens like Gorilla Glass, provides a balance of affordability and widespread availability from established suppliers. Manufacturers favor aluminosilicate for its cost-efficiency and scalable production, whereas nanoglass remains a premium option with restricted market penetration.
Which Glass is Best for Your Smartphone?
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced durability due to its nanostructured composition, making it highly effective against everyday wear and accidental drops. Aluminosilicate glass, such as Gorilla Glass, provides robust chemical strength and excellent impact resistance, maintaining high clarity and touch sensitivity. For smartphone users prioritizing extreme toughness and long-term screen integrity, nanoglass presents a cutting-edge option, while aluminosilicate glass remains a proven, reliable choice for balanced protection and performance.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Smartphone screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com