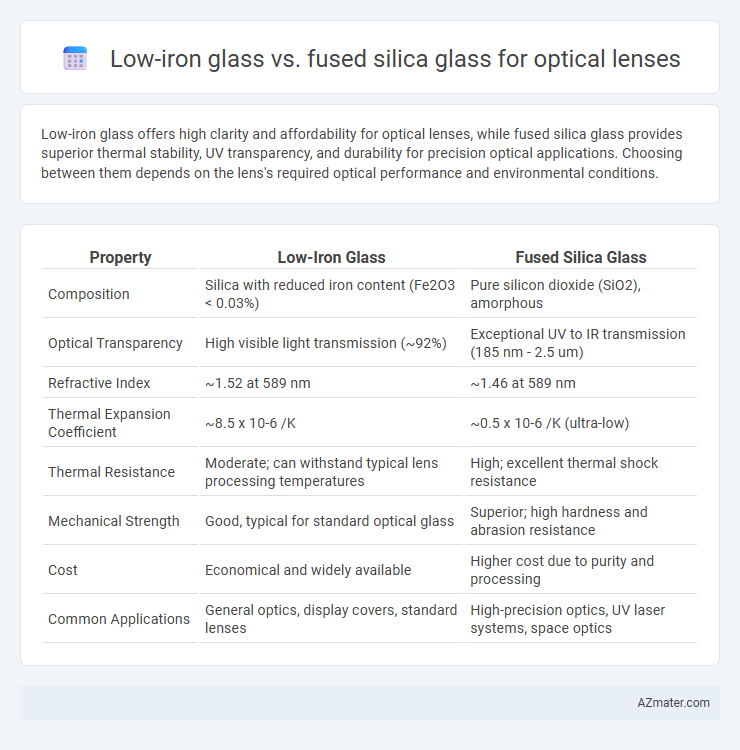
Low-iron glass offers high clarity and affordability for optical lenses, while fused silica glass provides superior thermal stability, UV transparency, and durability for precision optical applications. Choosing between them depends on the lens's required optical performance and environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Low-Iron Glass | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica with reduced iron content (Fe2O3 < 0.03%) | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), amorphous |
| Optical Transparency | High visible light transmission (~92%) | Exceptional UV to IR transmission (185 nm - 2.5 um) |
| Refractive Index | ~1.52 at 589 nm | ~1.46 at 589 nm |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | ~8.5 x 10-6 /K | ~0.5 x 10-6 /K (ultra-low) |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate; can withstand typical lens processing temperatures | High; excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Good, typical for standard optical glass | Superior; high hardness and abrasion resistance |
| Cost | Economical and widely available | Higher cost due to purity and processing |
| Common Applications | General optics, display covers, standard lenses | High-precision optics, UV laser systems, space optics |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Low-iron glass offers enhanced clarity and reduced greenish tint compared to standard glass, making it suitable for optical lenses where high transmission and color accuracy are critical. Fused silica glass, composed primarily of silicon dioxide, provides superior thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent UV transparency, ideal for precision optics and high-power laser applications. Both materials optimize optical performance, but the choice depends on specific requirements such as wavelength range, mechanical durability, and environmental conditions.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of silica-based glass specifically refined to reduce iron content, resulting in higher clarity and enhanced light transmission compared to standard glass. It exhibits a low absorption rate in the visible and near-infrared spectrum, making it ideal for optical lenses requiring minimal color distortion and maximum transparency. Unlike fused silica glass, which offers superior thermal stability and UV resistance, low-iron glass provides a cost-effective solution with improved optical performance for applications like camera lenses, display covers, and solar panels.
Understanding Fused Silica Glass
Fused silica glass offers superior optical clarity and ultra-low thermal expansion compared to low-iron glass, making it ideal for precision lenses in high-performance optical applications. Unlike low-iron glass, which primarily reduces iron content to enhance transparency, fused silica is composed of pure silicon dioxide, providing exceptional UV transmission and resistance to thermal shock. This makes fused silica lenses critical in demanding environments such as semiconductor lithography, laser optics, and space instrumentation.
Optical Properties Comparison
Low-iron glass offers excellent light transmission with minimal green tint, resulting in high clarity and good color accuracy, while fused silica glass surpasses it by providing superior ultraviolet (UV) transmission and extremely low thermal expansion, enhancing optical stability in varying temperatures. Fused silica's refractive index is typically around 1.46, slightly lower than low-iron glass, which ranges from 1.50 to 1.52, affecting focal length and image sharpness in lens design. The exceptional homogeneity and minimal birefringence of fused silica make it ideal for high-precision optical lenses, especially in UV and infrared applications where low-iron glass may show reduced performance.
Transmission and Clarity Performance
Low-iron glass exhibits excellent transmission in the visible spectrum with reduced green tint, enhancing clarity and color fidelity for optical lenses. Fused silica glass outperforms low-iron glass by offering superior ultraviolet transmission and minimal optical distortion due to its ultra-high purity and low thermal expansion. The choice between these materials depends on application-specific requirements, with fused silica preferred for high-precision UV optics and low-iron glass favored for cost-effective visible light imaging.
Thermal Stability and Expansion Rates
Low-iron glass offers moderate thermal stability with expansion rates typically around 8.5 x 10^-6 /degC, making it suitable for applications with less stringent thermal demands. Fused silica glass exhibits exceptional thermal stability due to its ultra-low thermal expansion coefficient of approximately 0.5 x 10^-6 /degC, ensuring minimal distortion under temperature fluctuations. This superior thermal performance of fused silica makes it ideal for high-precision optical lenses used in environments requiring consistent optical properties across varying temperatures.
UV and IR Light Transmission Differences
Low-iron glass exhibits higher UV light transmission compared to standard glass, allowing better clarity for applications requiring deep UV wavelengths, while fused silica glass surpasses both in UV transmittance with minimal absorption below 200 nm. In the infrared (IR) spectrum, fused silica glass maintains excellent transmission up to approximately 3.5 microns, whereas low-iron glass significantly attenuates IR light beyond 2.5 microns due to increased absorption. These transmission characteristics make fused silica glass the preferred choice for precise UV and IR optical lenses in high-performance scientific and industrial devices.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Low-iron glass offers moderate durability and chemical resistance, suitable for standard optical lens applications, but it is more prone to scratching and chemical attack compared to fused silica glass. Fused silica glass excels with exceptional hardness, thermal stability, and superior resistance to harsh chemicals and environmental degradation, making it ideal for high-precision and high-durability optical lenses. Its low thermal expansion coefficient ensures minimal deformation under extreme conditions, enhancing long-term performance in demanding optical systems.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Low-iron glass offers a cost-effective option for optical lenses due to its widespread availability and simpler manufacturing process, making it suitable for budget-conscious applications. Fused silica glass, while significantly more expensive, provides superior optical clarity and thermal stability, justifying the higher cost in precision-demanding environments such as high-performance optics and scientific instruments. The limited production volume and specialized processing of fused silica result in greater lead times and reduced availability compared to more common low-iron glass materials.
Choosing the Right Glass for Optical Lenses
Low-iron glass offers enhanced transparency and reduced greenish tint compared to standard glass, making it suitable for applications requiring clear vision and minimal color distortion in optical lenses. Fused silica glass excels with superior thermal stability, high UV transmission, and exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion, ideal for precision lenses in high-performance optical systems. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing optical clarity, environmental durability, and application-specific wavelength requirements to achieve optimal lens performance.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Fused silica glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com