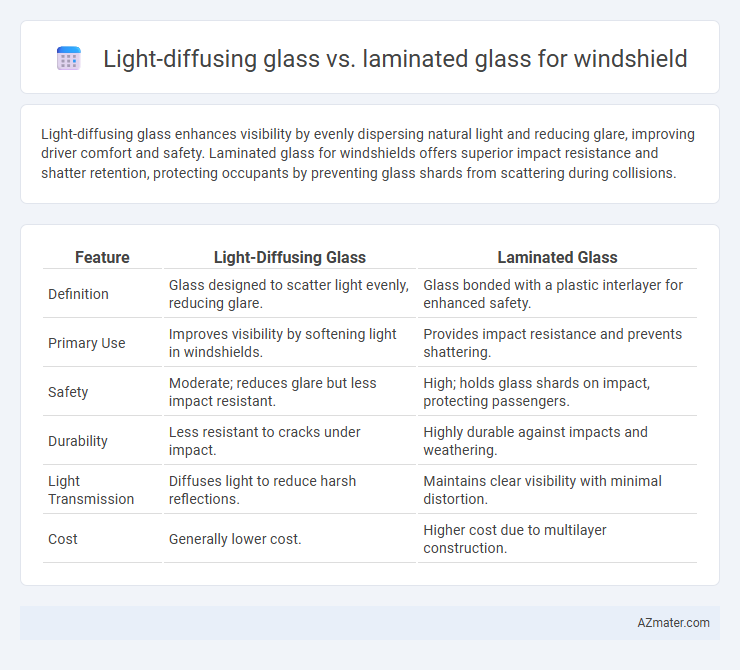
Light-diffusing glass enhances visibility by evenly dispersing natural light and reducing glare, improving driver comfort and safety. Laminated glass for windshields offers superior impact resistance and shatter retention, protecting occupants by preventing glass shards from scattering during collisions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Light-Diffusing Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Glass designed to scatter light evenly, reducing glare. | Glass bonded with a plastic interlayer for enhanced safety. |
| Primary Use | Improves visibility by softening light in windshields. | Provides impact resistance and prevents shattering. |
| Safety | Moderate; reduces glare but less impact resistant. | High; holds glass shards on impact, protecting passengers. |
| Durability | Less resistant to cracks under impact. | Highly durable against impacts and weathering. |
| Light Transmission | Diffuses light to reduce harsh reflections. | Maintains clear visibility with minimal distortion. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost. | Higher cost due to multilayer construction. |
Introduction to Windshield Glass Technologies
Windshield glass technologies have advanced to enhance safety and visibility, with light-diffusing glass and laminated glass representing two key innovations. Light-diffusing glass scatters incoming light to reduce glare and improve driver vision during various lighting conditions, utilizing micro-structured surfaces or embedded particles. Laminated glass consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing superior impact resistance, shatter retention, and increased occupant protection during collisions.
What is Light-Diffusing Glass?
Light-diffusing glass scatters incoming light to reduce glare and improve visibility, enhancing driver safety by minimizing blinding reflections on windshields. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of layers bonded with a plastic interlayer for shatter resistance and UV protection, light-diffusing glass specifically optimizes light transmission and diffusion properties. This type of glass is designed to create a uniform light distribution, improving comfort during daytime and nighttime driving conditions.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a durable interlayer, typically polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety and impact resistance for windshields. This structure prevents shattering upon impact, holding the glass fragments in place to protect passengers and maintain visibility. Compared to light-diffusing glass, laminated glass offers superior strength, durability, and safety performance, making it the preferred choice for automotive windshields.
Key Differences Between Light-Diffusing and Laminated Glass
Light-diffusing glass for windshields disperses incoming light to reduce glare and improve visibility in various lighting conditions, while laminated glass is designed with a plastic interlayer that holds shattered pieces together for enhanced safety and impact resistance. Light-diffusing glass primarily addresses optical clarity and comfort by minimizing harsh light penetration, whereas laminated glass focuses on structural integrity and occupant protection during collisions. The key differences lie in light management versus mechanical strength, making light-diffusing glass optimal for glare reduction and laminated glass essential for crash safety.
Optical Clarity and Visibility Comparisons
Light-diffusing glass enhances windshield optical clarity by scattering light to reduce glare and improve visibility in varying lighting conditions, while laminated glass offers high transparency and impact resistance with clear visibility but limited glare reduction. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, maintaining clarity under normal and adverse weather but may exhibit minor distortion compared to light-diffusing glass. Both types ensure safety, yet light-diffusing glass provides superior performance in minimizing light scattering effects for clearer vision during bright or low-light driving scenarios.
Safety and Impact Resistance Analysis
Light-diffusing glass enhances visibility and reduces glare, improving driver safety through better light management, but it typically offers lower impact resistance compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers with an interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, significantly increasing safety by preventing glass from shattering and reducing the risk of injury during collisions. The impact resistance of laminated glass makes it the preferred choice for windshields, as it maintains structural integrity and protects occupants in accidents.
UV Protection and Heat Insulation Properties
Light-diffusing glass for windshields enhances UV protection by scattering harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing interior fading and skin exposure, while laminated glass incorporates a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that blocks up to 99% of UV radiation, offering superior protection. In terms of heat insulation, light-diffusing glass disperses sunlight to minimize glare but provides moderate thermal control, whereas laminated glass significantly improves heat insulation by limiting solar heat transfer through its multiple layers and interlayer composition. The combination of enhanced UV filtering and effective thermal resistance makes laminated glass the preferred choice for windshield applications requiring advanced protection and energy efficiency.
Acoustic Performance: Noise Reduction Capabilities
Light-diffusing glass enhances acoustic performance by scattering sound waves, which reduces noise transmission and improves in-cabin quietness compared to standard windshield materials. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), provides superior noise reduction by absorbing and dampening sound vibrations, effectively minimizing external road and wind noise. In terms of acoustic performance, laminated glass is generally preferred for windshields due to its better noise isolation qualities and improved passenger comfort.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Light-diffusing glass for windshields typically incurs a higher initial cost compared to laminated glass due to its advanced light-scattering technology. Maintenance expenses for light-diffusing glass can be greater because specialized repair techniques and materials are often required to preserve its optical properties. Laminated glass is more cost-effective and easier to maintain, benefiting from widespread availability and simpler repair processes after chips or cracks.
Which Glass Type is Best for Your Windshield?
Light-diffusing glass enhances visibility by scattering light to reduce glare and improve driver comfort, making it ideal for windshield applications in bright or variable lighting conditions. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass with an interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, providing superior safety and durability against collisions and road debris. For optimal windshield performance, laminated glass is generally preferred for its enhanced protection and structural integrity, while light-diffusing glass suits environments prioritizing glare reduction and visibility.
Infographic: Light-diffusing glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com