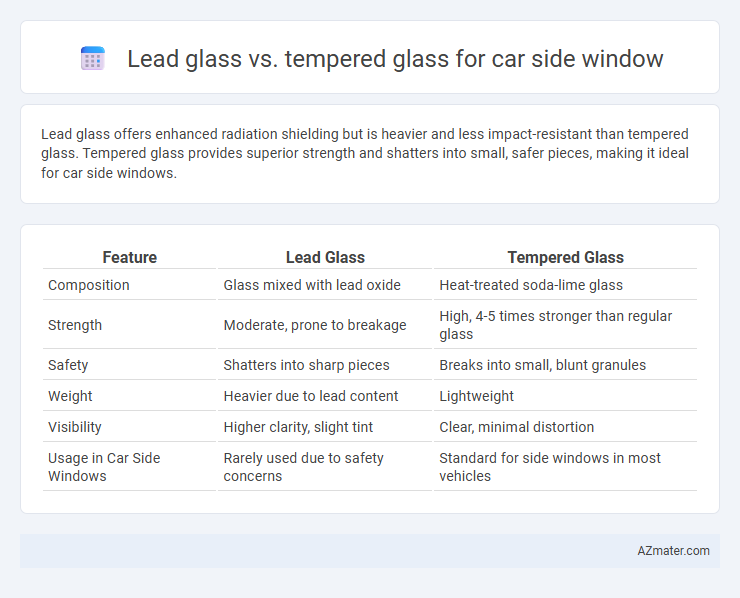
Lead glass offers enhanced radiation shielding but is heavier and less impact-resistant than tempered glass. Tempered glass provides superior strength and shatters into small, safer pieces, making it ideal for car side windows.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Glass mixed with lead oxide | Heat-treated soda-lime glass |
| Strength | Moderate, prone to breakage | High, 4-5 times stronger than regular glass |
| Safety | Shatters into sharp pieces | Breaks into small, blunt granules |
| Weight | Heavier due to lead content | Lightweight |
| Visibility | Higher clarity, slight tint | Clear, minimal distortion |
| Usage in Car Side Windows | Rarely used due to safety concerns | Standard for side windows in most vehicles |
Introduction to Car Side Window Materials
Car side windows commonly utilize tempered glass due to its high strength, safety features, and shatter-resistant properties that minimize injury risks during accidents. Lead glass, known for its radiation shielding and optical clarity, is rarely used in automotive applications because of its weight and brittleness. The automotive industry favors tempered glass for side windows to balance durability, safety standards, and cost-effectiveness.
What is Lead Glass?
Lead glass, also known as lead crystal, contains a significant percentage of lead oxide, enhancing its density, brilliance, and sound insulation properties, but it is rarely used for car side windows due to its weight and brittleness. Tempered glass, commonly used for car side windows, is heat-treated for increased strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing injury risk during impact. Unlike lead glass, tempered glass prioritizes safety and durability in automotive applications.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass is a type of safety glass processed through controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury, making it ideal for car side windows. Lead glass, containing lead oxide, offers high density and radiation shielding but lacks the safety shatter properties required for automotive side windows.
Safety Features: Lead Glass vs Tempered Glass
Tempered glass for car side windows offers enhanced safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, reducing injury risk compared to lead glass, which contains lead oxide but lacks impact-resistant properties. While lead glass provides radiation shielding, it does not improve impact resistance or shatter patterns critical for automotive safety. Tempered glass complies with vehicle safety standards by balancing strength and controlled breakage for passenger protection.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Tempered glass used in car side windows offers superior durability and impact resistance compared to lead glass, as it undergoes a controlled thermal treatment that increases its strength by up to four times. Lead glass, despite its high density and radiation shielding properties, lacks the structural integrity required for automotive safety standards and is more prone to cracking under stress. The shattering pattern further distinguishes tempered glass by breaking into small, blunt granules, reducing injury risk during collisions and enhancing overall vehicle safety.
Optical Clarity and Visibility
Lead glass, due to its higher density and unique composition, offers superior optical clarity compared to tempered glass, minimizing distortion and providing clearer visibility through car side windows. Tempered glass, while incredibly strong and shatter-resistant, can exhibit slight optical imperfections caused by the heat treatment process, potentially affecting visibility under certain lighting conditions. The enhanced clarity of lead glass makes it ideal for applications where precise vision and reduced glare are critical in automotive side windows.
UV and Radiation Protection
Lead glass offers superior protection against UV rays and harmful radiation due to its high lead content, which effectively blocks a wide spectrum of ultraviolet light and radioactive particles. Tempered glass, while significantly stronger and more impact-resistant, provides limited UV protection typically enhanced only through additional coatings or films. For car side windows, lead glass ensures enhanced safety against radiation exposure, whereas tempered glass prioritizes mechanical strength and shatter resistance.
Cost Considerations
Tempered glass for car side windows generally offers a more cost-effective solution due to its lower manufacturing expenses and widespread availability compared to lead glass. Lead glass, containing added lead oxide for radiation shielding and enhanced density, incurs higher production costs and is rarely used in automotive side windows. Cost considerations favor tempered glass as it balances durability, safety, and affordability in automotive applications.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Tempered glass used in car side windows offers superior recyclability due to its uniform composition and absence of lead, minimizing environmental hazards during disposal. Lead glass contains lead oxide, which poses toxic risks and complicates recycling processes, requiring specialized facilities to prevent soil and water contamination. Choosing tempered glass reduces environmental impact by enabling more efficient recycling streams and lowering the risk of hazardous material leakage.
Choosing the Best Glass for Your Car
Choosing the best glass for your car side window involves weighing the safety and durability of tempered glass against the clarity and radiation protection of lead glass. Tempered glass is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces on impact, reducing injury risk during collisions, while lead glass offers enhanced radiation shielding and superior optical clarity but is heavier and more brittle. Prioritizing tempered glass for automotive side windows ensures compliance with safety standards and optimal performance under stress, making it the preferred choice for drivers focused on safety and durability.
Infographic: Lead glass vs Tempered glass for Car side window
 azmater.com
azmater.com