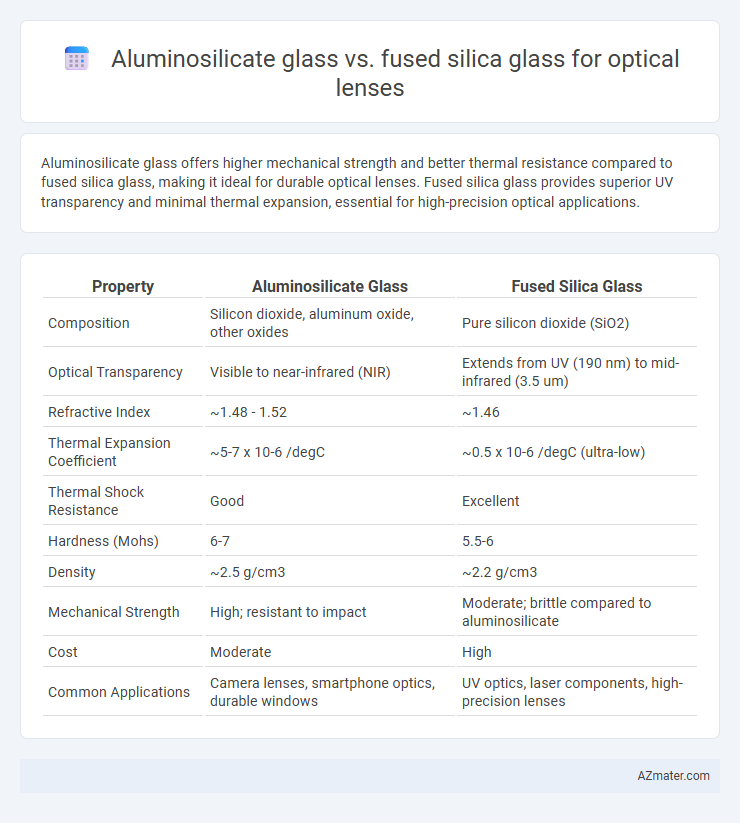
Aluminosilicate glass offers higher mechanical strength and better thermal resistance compared to fused silica glass, making it ideal for durable optical lenses. Fused silica glass provides superior UV transparency and minimal thermal expansion, essential for high-precision optical applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aluminosilicate Glass | Fused Silica Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide, other oxides | Pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) |
| Optical Transparency | Visible to near-infrared (NIR) | Extends from UV (190 nm) to mid-infrared (3.5 um) |
| Refractive Index | ~1.48 - 1.52 | ~1.46 |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | ~5-7 x 10-6 /degC | ~0.5 x 10-6 /degC (ultra-low) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 6-7 | 5.5-6 |
| Density | ~2.5 g/cm3 | ~2.2 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High; resistant to impact | Moderate; brittle compared to aluminosilicate |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Common Applications | Camera lenses, smartphone optics, durable windows | UV optics, laser components, high-precision lenses |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Aluminosilicate glass and fused silica glass are prominent materials used in optical lens manufacturing, each offering distinct properties tailored to specific applications. Aluminosilicate glass provides enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for high-stress environments, while fused silica glass is renowned for its exceptional optical clarity, low thermal expansion, and excellent UV transmission. The choice between these materials depends on factors such as wavelength requirements, environmental conditions, and durability demands in optical systems.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of engineered glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) and silicon dioxide (SiO2), offering superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to traditional glasses. This glass type is widely used in optical lenses due to its high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for demanding environments. In comparison to fused silica glass, aluminosilicate glass provides enhanced durability while maintaining excellent optical clarity, beneficial for precision lens applications.
What is Fused Silica Glass?
Fused silica glass is a high-purity, non-crystalline form of silicon dioxide known for its exceptional optical transparency and low thermal expansion. It offers superior resistance to thermal shock and ultraviolet radiation, making it ideal for precision optical lenses in high-performance environments. Compared to aluminosilicate glass, fused silica provides enhanced durability and minimal refractive index variability, crucial for advanced optical applications.
Optical Clarity: Aluminosilicate vs Fused Silica
Aluminosilicate glass offers high optical clarity with excellent light transmission in the visible spectrum, but fused silica surpasses it by providing superior transparency across a broader wavelength range including ultraviolet and infrared. Fused silica exhibits minimal internal scattering and absorption, making it ideal for high-precision optical lenses requiring exceptional image quality and durability under extreme conditions. The choice between aluminosilicate and fused silica depends on specific optical performance needs, with fused silica favored for applications demanding maximum clarity and minimal distortion.
Transmission Properties and UV/IR Performance
Aluminosilicate glass offers high transmission in the visible spectrum with moderate UV blocking capabilities, making it suitable for general optical lens applications, while fused silica glass outperforms in UV transmission with excellent transparency down to 185 nm and superior IR transmission up to 3.5 microns. Fused silica's low absorption and high damage threshold under UV and IR radiation provide enhanced performance for high-precision optical systems requiring stability in harsh environments. Aluminosilicate glass is more cost-effective but less efficient in extreme UV/IR conditions compared to the exceptional UV and IR transmission qualities of fused silica glass.
Thermal Stability and Expansion Comparison
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits higher thermal stability and lower thermal expansion coefficients, typically around 3.2 x 10^-6 /degC, making it more resistant to thermal shock compared to fused silica glass, which has an ultra-low thermal expansion coefficient of approximately 0.5 x 10^-6 /degC. Fused silica glass is preferred in high-precision optical lenses due to its superior dimensional stability over a wide temperature range, ensuring minimal distortion and maintenance of optical performance. Thermal expansion differences directly impact lens focusing accuracy and durability in applications requiring exposure to fluctuating temperatures.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Aluminosilicate glass exhibits higher mechanical strength than fused silica glass, making it more resistant to impacts and scratches, which is crucial for optical lenses subjected to harsh environments. Its enhanced durability stems from the incorporation of aluminum oxide, improving thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion compared to pure fused silica. Although fused silica offers superior optical clarity and UV transmission, aluminosilicate glass is preferred in applications where lens longevity and mechanical robustness are prioritized.
Chemical Resistance: Which Glass Performs Better?
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior chemical resistance compared to fused silica glass, particularly against alkalis and acids, making it ideal for harsh chemical environments. Fused silica glass exhibits exceptional resistance to high-purity acids but is more vulnerable to alkaline solutions, resulting in possible surface degradation over time. The enhanced durability of aluminosilicate glass in corrosive conditions often makes it the preferred choice for optical lenses used in chemically aggressive settings.
Cost Considerations for Optical Lens Manufacturers
Aluminosilicate glass offers a cost-effective solution for optical lens manufacturers due to its lower raw material and production expenses compared to fused silica glass. Fused silica glass, while more expensive, provides superior thermal stability and optical clarity, justifying its higher price in high-precision applications. Manufacturers must balance budget constraints with performance requirements when choosing between aluminosilicate and fused silica materials for optical lens production.
Applications: Choosing the Right Glass for Optical Lenses
Aluminosilicate glass offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it ideal for rugged optical lenses used in industrial and automotive applications. Fused silica glass provides exceptional UV transparency and low thermal expansion, preferred for high-precision lenses in scientific instruments and laser systems. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing durability requirements with optical performance, where aluminosilicate excels in impact resistance and fused silica dominates in optical clarity and thermal resilience.
Infographic: Aluminosilicate glass vs Fused silica glass for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com