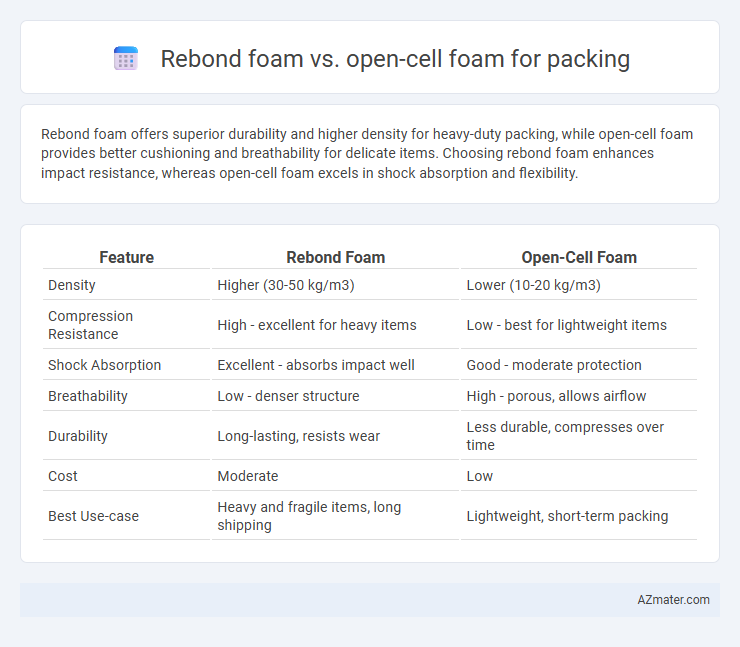
Rebond foam offers superior durability and higher density for heavy-duty packing, while open-cell foam provides better cushioning and breathability for delicate items. Choosing rebond foam enhances impact resistance, whereas open-cell foam excels in shock absorption and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Higher (30-50 kg/m3) | Lower (10-20 kg/m3) |
| Compression Resistance | High - excellent for heavy items | Low - best for lightweight items |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent - absorbs impact well | Good - moderate protection |
| Breathability | Low - denser structure | High - porous, allows airflow |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resists wear | Less durable, compresses over time |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Best Use-case | Heavy and fragile items, long shipping | Lightweight, short-term packing |
Introduction: Rebond Foam vs Open-Cell Foam for Packing
Rebond foam consists of shredded foam scraps bonded together, offering high density and excellent durability ideal for heavy-duty packing applications. Open-cell foam features a porous structure that provides superior cushioning and shock absorption but is less dense and resilient compared to rebond foam. Choosing between rebond foam and open-cell foam depends on packing requirements such as load protection, compression resistance, and impact absorption.
What is Rebond Foam?
Rebond foam is a dense, durable material made by compressing and bonding shredded foam scraps with adhesive, commonly used for heavy-duty packing and cushioning applications. Unlike open-cell foam, which is lightweight and porous, rebond foam offers superior impact resistance and support, making it ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping. Its high density and resilience ensure that packaged goods remain secure and absorb shocks effectively in transit.
What is Open-Cell Foam?
Open-cell foam is a lightweight, flexible material characterized by interconnected pores that allow air to pass through, making it highly breathable and cushioning. Its structure provides excellent shock absorption and pressure distribution, ideal for delicate items during packing. Compared to rebond foam, open-cell foam offers superior impact protection and conforms better to irregular shapes, enhancing packing security.
Key Differences Between Rebond and Open-Cell Foam
Rebond foam features high density and durability, created by recycling scrap foam bonded together, making it ideal for heavy-duty packing and shock absorption. Open-cell foam has a lower density with a porous structure, providing excellent cushioning but less compression resistance, suitable for lightweight or delicate item protection. Key differences include rebond's superior firmness and resilience versus open-cell's flexibility and breathability in packing applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Rebond foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to open-cell foam due to its dense composition made from recycled foam materials bonded together under high heat and pressure. This structural density makes rebond foam highly resistant to compression, wear, and tear, extending its useful life in packing applications. In contrast, open-cell foam, characterized by its lighter, porous structure, tends to degrade faster under mechanical stress and repeated impacts, resulting in reduced lifespan for protective packaging.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Rebond foam provides superior cushioning and shock absorption due to its dense and firm structure made from shredded foam pieces bonded together, making it ideal for heavy-duty packing needs. Open-cell foam offers excellent flexibility and breathability with a softer feel, but it has lower shock absorption compared to rebond foam. For applications requiring maximum impact protection and durability, rebond foam is the preferred choice, while open-cell foam suits lightweight and delicate items.
Weight and Density Considerations
Rebond foam typically has a higher density, ranging from 40 to 100 kg/m3, making it heavier but more durable and supportive for packing heavy or fragile items. Open-cell foam has a lower density, usually between 10 and 30 kg/m3, resulting in a lighter weight ideal for cushioning but less effective for loading heavy objects. Weight and density differences directly impact their protective capabilities, with rebond foam offering firmer support and open-cell foam providing softer, lighter cushioning.
Cost Effectiveness for Packing Applications
Rebond foam offers superior cost effectiveness for packing applications due to its recycled composition, resulting in lower production expenses compared to open-cell foam. Open-cell foam, while providing excellent cushioning and breathability, generally incurs higher costs because of its more complex manufacturing process and raw material requirements. Businesses seeking budget-friendly yet durable packing solutions often prefer rebond foam for its balance of performance and affordability.
Best Use Cases for Each Foam Type
Rebond foam is ideal for heavy-duty packing applications requiring high durability and impact resistance, such as cushioning industrial equipment or electronics during shipping. Open-cell foam excels in packaging delicate items needing breathability and gentle cushioning, making it perfect for fragile goods like glassware or electronics with sensitive components. Selecting the correct foam depends on the balance between protection level and weight, where rebond foam provides robust support and open-cell foam offers lightweight, flexible padding.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packing Needs
Rebond foam offers superior durability and firmness, making it ideal for heavy-duty packing and long-term protection of bulky items. Open-cell foam provides excellent cushioning and shock absorption, suited for delicate and lightweight objects requiring gentle handling. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific protection level, weight, and fragility of the items being packed.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Open-cell foam for Packing
 azmater.com
azmater.com