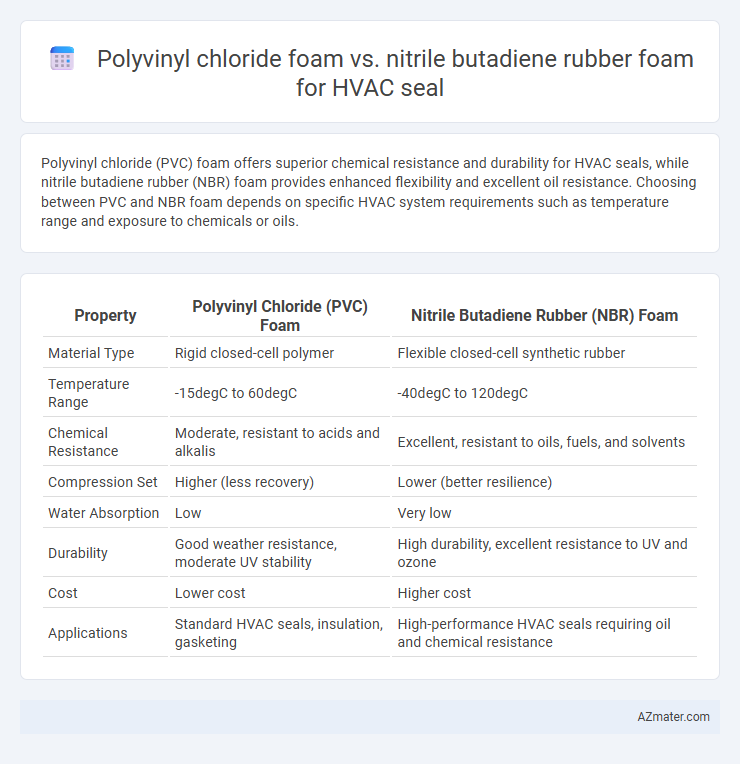
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior chemical resistance and durability for HVAC seals, while nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides enhanced flexibility and excellent oil resistance. Choosing between PVC and NBR foam depends on specific HVAC system requirements such as temperature range and exposure to chemicals or oils.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rigid closed-cell polymer | Flexible closed-cell synthetic rubber |
| Temperature Range | -15degC to 60degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, resistant to acids and alkalis | Excellent, resistant to oils, fuels, and solvents |
| Compression Set | Higher (less recovery) | Lower (better resilience) |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low |
| Durability | Good weather resistance, moderate UV stability | High durability, excellent resistance to UV and ozone |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Standard HVAC seals, insulation, gasketing | High-performance HVAC seals requiring oil and chemical resistance |
Introduction to Foam Materials in HVAC Sealing
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and fire, making it a durable choice for HVAC sealing applications where environmental exposure is a concern. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides superior flexibility, oil resistance, and cushioning, which enhances its sealing performance against air leaks and vibrations in HVAC systems. Selecting the appropriate foam material depends on factors like temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress specific to HVAC sealing requirements.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material commonly used in HVAC seals due to its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and versatility in temperature tolerance ranging from -15degC to 60degC. Its rigidity and resistance to moisture and abrasion make PVC foam ideal for maintaining airtight seals in ventilation and air conditioning systems. Compared to Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam, PVC foam offers superior structural integrity but slightly less flexibility under extreme cold conditions.
Overview of Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam exhibits superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam, making it ideal for HVAC seal applications exposed to harsh environments. NBR foam provides excellent flexibility, compression set resistance, and durability under varying temperatures, enhancing the lifespan of HVAC seals. Its closed-cell structure ensures effective thermal insulation and moisture resistance, critical for maintaining HVAC system efficiency.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent dimensional stability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for HVAC seals exposed to varying humidity and temperature conditions. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides superior flexibility, compression set resistance, and oil resistance, enhancing seal durability in mechanical and chemical environments. Comparing physical properties, PVC foam exhibits higher rigidity and tensile strength, while NBR foam excels in elongation and resilience, influencing their suitability based on HVAC system demands.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers moderate thermal insulation with a closed-cell structure that resists heat transfer, making it effective for maintaining temperature stability in HVAC systems. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides superior thermal insulation due to its excellent low thermal conductivity and high resistance to heat aging, ideal for applications requiring durability under fluctuating temperatures. When prioritizing thermal insulation performance, NBR foam generally outperforms PVC foam by maintaining efficiency across wider temperature ranges and providing enhanced resistance to thermal degradation.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly effective for HVAC seals exposed to humid environments. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam offers excellent chemical resistance, especially against oils, fuels, and solvents, which is crucial for HVAC systems dealing with aggressive chemical exposure. While PVC foam excels in preventing water absorption, NBR foam provides enhanced durability against chemical degradation, influencing the choice based on specific HVAC operating conditions.
Fire Retardancy and Safety Standards
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior fire retardancy compared to Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam, meeting stringent safety standards such as ASTM E84 Class A flame spread ratings. PVC foam's self-extinguishing properties and low smoke emission align with UL 94 V-0 classification, enhancing HVAC seal applications in fire-sensitive environments. In contrast, NBR foam typically falls short in high fire resistance requirements, making PVC foam the preferred choice for compliance with NFPA and International Mechanical Code (IMC) fire safety regulations.
Installation and Application Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent resistance to chemicals and UV exposure, making it ideal for outdoor HVAC seal installations requiring durability against environmental factors. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides superior flexibility and compression set resistance, which enhances sealing performance in dynamic or high-vibration HVAC applications. Installation of PVC foam typically involves adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening, suited for rigid surfaces, while NBR foam often requires pressure-sensitive adhesives for quick and easy application on irregular or moving parts.
Cost Effectiveness and Longevity
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers greater cost effectiveness for HVAC seals due to its lower manufacturing expenses and affordability in large-scale applications. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides superior longevity, resisting oils, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations better than PVC foam, which enhances HVAC system durability. Choosing between PVC and NBR foam hinges on prioritizing initial cost savings versus extended lifespan and performance reliability in HVAC sealing solutions.
Choosing the Right Foam for HVAC Seal Applications
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for HVAC seals exposed to oils, chemicals, and outdoor elements. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam provides superior flexibility and resistance to heat and compression set, which is beneficial for dynamic HVAC components requiring repeated movement. Selecting the right foam hinges on specific application needs, with PVC foam favored for harsh environments and NBR foam preferred for flexible, heat-resistant sealing solutions.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Nitrile butadiene rubber foam for HVAC Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com