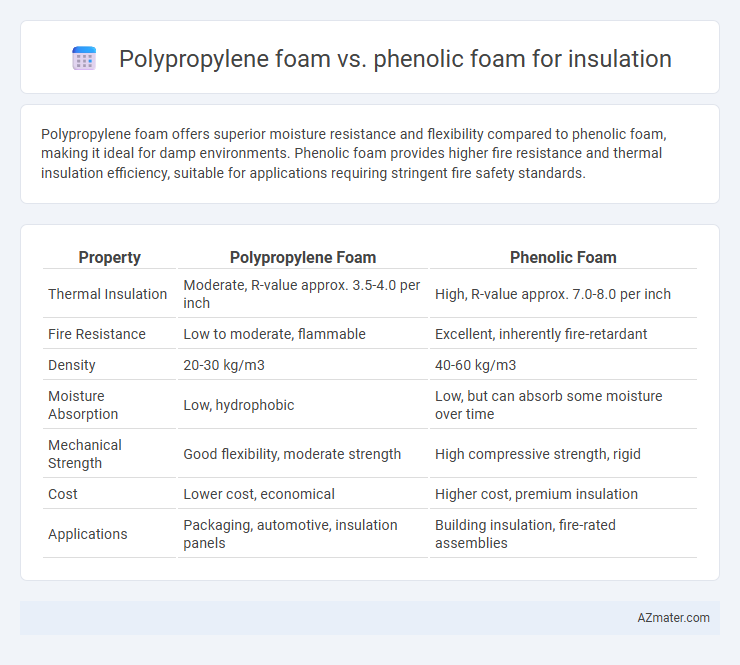
Polypropylene foam offers superior moisture resistance and flexibility compared to phenolic foam, making it ideal for damp environments. Phenolic foam provides higher fire resistance and thermal insulation efficiency, suitable for applications requiring stringent fire safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate, R-value approx. 3.5-4.0 per inch | High, R-value approx. 7.0-8.0 per inch |
| Fire Resistance | Low to moderate, flammable | Excellent, inherently fire-retardant |
| Density | 20-30 kg/m3 | 40-60 kg/m3 |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, hydrophobic | Low, but can absorb some moisture over time |
| Mechanical Strength | Good flexibility, moderate strength | High compressive strength, rigid |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical | Higher cost, premium insulation |
| Applications | Packaging, automotive, insulation panels | Building insulation, fire-rated assemblies |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Polypropylene foam offers lightweight, moisture-resistant properties with excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and durability. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal performance, often used in commercial and industrial insulation. Both materials serve critical roles in insulation, with polypropylene foam favored for moisture-prone environments and phenolic foam preferred for stringent fire safety standards.
Overview of Polypropylene Foam
Polypropylene foam offers excellent thermal insulation properties, high chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it a durable choice for various insulation applications. Its closed-cell structure provides superior impact resistance and lightweight characteristics compared to phenolic foam. Polypropylene foam is commonly used in automotive, construction, and packaging industries where flexibility and thermal efficiency are essential.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulation material known for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for building and industrial applications. It features a closed-cell structure that provides enhanced moisture resistance and dimensional stability compared to other foams like polypropylene. Phenolic foam's ability to maintain structural integrity under high temperatures and reduce heat transfer contributes to safer, more energy-efficient environments.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Polypropylene foam exhibits lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.028 to 0.035 W/m*K, making it highly effective for thermal insulation in residential and commercial applications. Phenolic foam, known for its closed-cell structure, offers superior fire resistance and thermal stability with thermal conductivity values approximately 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K, delivering excellent performance in harsh environments. When comparing thermal insulation performance, phenolic foam generally outperforms polypropylene foam by providing lower heat transfer rates and enhanced long-term thermal resistance.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polypropylene foam, characterized by higher limiting oxygen index (LOI) values and lower smoke emission during combustion, making it preferable for safety-critical insulation applications. Polypropylene foam, while effective for thermal insulation, tends to have lower fire retardancy and generates more toxic smoke when exposed to flames, posing a greater risk in fire incidents. Phenolic foam's inherent self-extinguishing properties and low flame spread rates meet stringent fire safety standards, enhancing overall building protection.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to phenolic foam, making it highly effective in damp environments where water absorption can compromise insulation performance. Phenolic foam, while offering excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance, is more susceptible to chemical degradation and moisture penetration, which can reduce its insulating properties over time. The hydrophobic nature of polypropylene foam ensures enhanced durability against chemical exposure and moisture-related damage, positioning it as a preferred choice for applications requiring long-term resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Polypropylene foam exhibits higher durability and resistance to chemical degradation, making it suitable for long-term insulation in moist or acidic environments. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal stability, but its brittleness can reduce longevity under mechanical stress or frequent handling. The choice between polypropylene and phenolic foam depends on the specific application demands of durability and lifespan in insulation systems.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene foam offers superior environmental benefits due to its recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to phenolic foam, which relies on formaldehyde-based resins and produces toxic byproducts during manufacturing and disposal. Polypropylene foam's lightweight structure contributes to reduced transportation emissions, enhancing overall sustainability, whereas phenolic foam's rigid composition results in limited recyclability and higher landfill persistence. Emphasizing renewable feedstocks and closed-loop recycling systems, polypropylene foam aligns better with green building certifications and long-term eco-friendly insulation practices.
Cost Effectiveness and Installation
Polypropylene foam offers cost-effective insulation with lightweight properties that reduce installation time and labor expenses compared to phenolic foam. While phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and thermal performance, its higher material and installation costs can impact overall project budgets. Polypropylene's ease of handling and compatibility with various construction methods make it a preferred choice for budget-conscious insulation projects.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Insulation Needs
Polypropylene foam offers excellent moisture resistance, lightweight properties, and thermal insulation, making it ideal for environments prone to humidity and requiring impact absorption. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal performance, suitable for applications demanding stringent fire safety standards. Selecting the right foam depends on prioritizing moisture resistance and flexibility versus fire safety and thermal efficiency for optimized insulation performance.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Phenolic foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com