Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal insulation compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics and temperature-sensitive goods. Polyethylene foam provides excellent impact absorption and moisture resistance, suitable for cushioning fragile items during shipping.
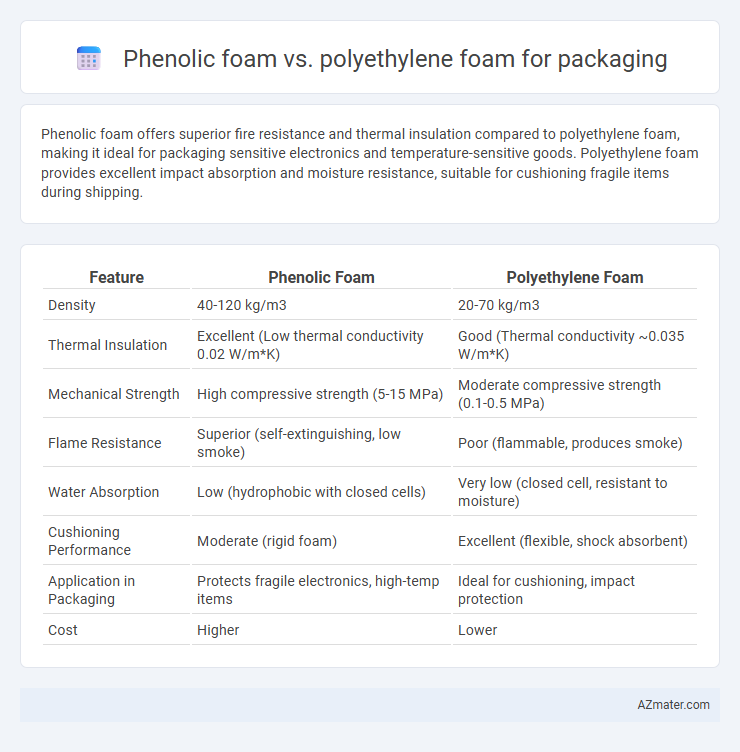
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phenolic Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 40-120 kg/m3 | 20-70 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (Low thermal conductivity 0.02 W/m*K) | Good (Thermal conductivity ~0.035 W/m*K) |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength (5-15 MPa) | Moderate compressive strength (0.1-0.5 MPa) |
| Flame Resistance | Superior (self-extinguishing, low smoke) | Poor (flammable, produces smoke) |
| Water Absorption | Low (hydrophobic with closed cells) | Very low (closed cell, resistant to moisture) |
| Cushioning Performance | Moderate (rigid foam) | Excellent (flexible, shock absorbent) |
| Application in Packaging | Protects fragile electronics, high-temp items | Ideal for cushioning, impact protection |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Phenolic and Polyethylene Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid, heat-resistant insulation material known for its excellent fire-retardant properties and low smoke emission, making it ideal for protective packaging that requires thermal and flame resistance. Polyethylene foam, in contrast, is a lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbent material commonly used to cushion delicate items during transport due to its superior impact resistance and moisture resistance. Both foams serve distinct packaging needs, with phenolic foam excelling in thermal and fire protection while polyethylene foam offers versatile cushioning and moisture barrier benefits.
Material Composition and Structure
Phenolic foam consists of a thermosetting resin derived from phenol and formaldehyde, characterized by a rigid, closed-cell structure with excellent fire resistance and thermal insulation properties. Polyethylene foam is made from ethylene polymers, featuring a flexible, open-cell or closed-cell structure that provides superior cushioning, impact absorption, and moisture resistance. The difference in chemical composition and cellular architecture directly influences their suitability for packaging applications requiring either thermal stability and flame retardance or shock protection and water resistance.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation properties compared to polyethylene foam, with a lower thermal conductivity typically around 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K, making it ideal for applications requiring high thermal resistance. Polyethylene foam generally exhibits higher thermal conductivity, approximately 0.035 to 0.045 W/m*K, resulting in less effective insulation performance. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam enhances its insulation efficiency by minimizing heat transfer, whereas polyethylene foam's flexibility and impact resistance are balanced against its relatively lower thermal insulating capability.
Cushioning Performance in Packaging
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation but has lower cushioning performance compared to polyethylene foam, which is highly flexible and provides excellent shock absorption for fragile items. Polyethylene foam's closed-cell structure enhances its resilience and ability to distribute impact forces evenly, making it ideal for protecting delicate electronics and glassware during transportation. Phenolic foam's rigid composition limits its energy absorption capacity, making polyethylene foam the preferred choice for packaging applications where cushioning performance is critical.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance with a high char yield and low smoke emission, making it ideal for packaging that requires enhanced fire safety. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and cushioning, is highly flammable and produces toxic fumes when burned, posing greater risks in fire scenarios. Choosing phenolic foam for packaging ensures compliance with stringent fire safety standards and reduces hazards associated with combustibility and smoke toxicity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation while being more fire-resistant and biodegradable compared to polyethylene foam, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum and has limited decomposition in landfills. Polyethylene foam's widespread use contributes significantly to plastic pollution due to its slow degradation and challenges in recycling, whereas phenolic foam's phenol-formaldehyde resin composition allows for better recyclability under controlled conditions. Choosing phenolic foam over polyethylene foam can reduce environmental impact through enhanced sustainability credentials and lower long-term ecological footprint.
Cost Efficiency Comparison
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation and flame resistance at a higher initial cost compared to polyethylene foam, which is more affordable but less effective in insulating properties. Polyethylene foam is widely favored for cost efficiency in packaging due to its lightweight nature, cushioning ability, and lower production expenses. The choice depends on balancing upfront material costs against long-term performance and protective requirements in packaging applications.
Customization and Versatility in Packaging Applications
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and rigid structure, making it ideal for customized protective packaging in high-temperature or sensitive product environments. Polyethylene foam excels in cushioning and flexibility, allowing versatile customization options such as die-cut shapes and varying densities to protect delicate or irregularly shaped items. Both materials provide distinct advantages depending on the packaging requirements, with phenolic foam suited for thermal insulation and polyethylene foam preferred for shock absorption and impact resistance.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Phenolic foam offers superior durability with excellent thermal stability and resistance to compression, maintaining its structural integrity over extended periods in packaging applications. Polyethylene foam provides good resilience and impact absorption but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV rays and mechanical stress. For long-term performance, phenolic foam is preferred in environments demanding sustained load-bearing capacity and fire resistance, while polyethylene foam suits lighter, short-to-medium-term cushioning needs.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
Phenolic foam excels in packaging applications requiring superior fire resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for electronics and aerospace industries. Polyethylene foam's high resilience, impact absorption, and moisture resistance suit it for automotive parts and consumer electronics packaging. Both materials serve distinct industry needs, with phenolic foam prioritized for safety-critical products and polyethylene foam favored for lightweight, durable cushioning.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com